Having a strong life purpose eases loneliness of COVID-19 isolation
Those who felt their life was guided by meaningful values or goals were more willing to engage in COVID-19 protective behaviors
2021-06-16
(Press-News.org) Why can some people weather the stress of social isolation better than others, and what implications does this have for their health? New research from the Communication Neuroscience Lab at the Annenberg School for Communication at the University of Pennsylvania found that people who felt a strong sense of purpose in life were less lonely during the COVID-19 pandemic. Did they achieve less loneliness by flouting public health guidance? No. Although lonelier people were less likely to want to follow public health guidance, people with a stronger sense of purpose also expressed more willingness to engage in social distancing, hand washing, and other COVID-19 protective behaviors.
Purpose in life, or a sense that your life is guided by personally meaningful values and goals — which could involve family ties, religion, activism, parenthood, career or artistic ambitions, or many other things — has been associated in prior research with a wide range of positive health outcomes, both physical and psychological.
"In the face of adversity, people with a stronger sense of purpose in life tend to be more resilient because they have a clear sense of goals that motivate actions that are aligned with personal values," says Yoona Kang, Ph.D., lead author and a Research Director of the Communication Neuroscience Lab. "People with strong purpose may also experience less conflict when making health decisions. We felt that the COVID-19 pandemic was an important context to test whether purpose in life relates to individuals' willingness to engage in behaviors to protect themselves and others."
Based on their prior research, Kang and her collaborators expected that people with higher sense of purpose would be more likely to engage in COVID-19 prevention behaviors than individuals with a lower sense of purpose. In order to test their theory, the researchers surveyed more than 500 adult participants to capture their levels of purpose in life, their current and pre-pandemic levels of loneliness, and the degrees to which they intended to engage in behaviors known to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
They found that higher levels of loneliness made people be less focused on protecting themselves from COVID-19, and more skeptical that behaviors to prevent COVID-19 would be effective. However, having a stronger sense of purpose was associated with lower levels of loneliness and a greater desire to take action to protect themselves from COVID-19. Those with a higher sense of purpose also expressed a stronger belief that COVID-19 prevention behaviors would work. Even when people who had a strong sense of purpose did report being lonely, they still felt strongly about taking precautions to prevent COVID-19.
"When faced with extreme loneliness and social isolation, like during the COVID-19 pandemic, wanting to connect with other people, despite the health risks, is a natural response," Kang says. "And yet, amidst this drastic shift in social life, we found that people with a higher sense of purpose were more likely to engage in prevention behaviors. This is striking because it shows that purpose in life can empower people to make life-saving health decisions that protect their own health and those around them."
Additionally, the researchers found that older people expressed less loneliness during the COVID-19 pandemic than younger people. Kang sees this as a sign of the resilience of older adults, and she hopes to further study how to enhance purpose in life and resilience in aging populations.
"Having a stronger sense of purpose was associated with really important, positive outcomes across the lifespan," says Emily Falk, senior author, Director of the Communication Neuroscience Lab, and Professor of Communication, Psychology, and Marketing. "Our upcoming work will test interventions to increase their sense of purpose, in hopes of bringing these benefits to more people."
INFORMATION:
The study, published this month in The Gerontologist, is entitled "Purpose in Life, Loneliness, and Protective Health Behaviors during the COVID-19 Pandemic." In addition to Kang and Falk, authors include Danielle Cosme, Ph.D.; Rui Pei, Ph.D.; Prateekshit Pandey; and José Carreras-Tartak.
About the Annenberg School for Communication
Founded in 1959 through the generosity and vision of diplomat and philanthropist Walter Annenberg, the Annenberg School for Communication at the University of Pennsylvania is devoted to furthering our understanding of the role of communication in public life through research, education, and service. With strengths in health communication, political communication, culture and communication, media institutions, digital media and social networks, and global communication, the Annenberg School is one of the top Communication schools in the nation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
A new study looking at the way human cells activate the immune system in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection could open the door to even more effective and powerful vaccines against the coronavirus and its rapidly emerging variants keeping the global pandemic smoldering.
Researchers from Boston University's National Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratories (NEIDL) and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard say it's the first real look at exactly what types of "red flags" the human body uses to enlist the help of T cells--killers sent out by the immune system to destroy infected cells. Until now, COVID vaccines have been focused on activating a different type of immune cell, B cells, which are responsible for creating antibodies. Developing vaccines to activate ...
2021-06-16
Steroid (sex) hormones play a central role in sexual development: They help determine how boys become boys and girls become girls. If these hormones are disrupted during fetal life, it can lead to a string of reproductive disorders at birth and later in life, including malformed genitals and decreased fertility.
Many environmental chemicals are known to disrupt the hormone system and are often referred to as endocrine disrupting chemicals. Azole fungicides constitute one group that can act as endocrine disruptors. Azoles are used to combat yeast infestations in seed and food crops, but are also used in medications for humans.
Most azoles used in medicines are tightly regulated and their use is well controlled. However, some are sold over-the-counter, for ...
2021-06-16
Philadelphia, June 16, 2021 - The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 may have the ability to reactivate dormant tuberculosis (TB). In a novel study scientists END ...
2021-06-16
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0011, Xiao-lei Yin, Dong-xue Liang, Lu Wang, Jing Qiu, Zhi-yun Yang, Jian-zeng Dong and Zhao-yuan Ma from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China; Capital Medical University, Beijing, China and The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China analyse coronary angiography video interpolation methods to reduce x-ray exposure frequency based on deep learning.
Cardiac coronary angiography is a major technique that assists physicians during interventional heart surgery. Under X-ray irradiation, the physician ...
2021-06-16
In a new publication from Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications; DOI https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2021.0013, Sharen Lee, Gary Tse, Xin Wang, Adrian Baranchuk and Tong Liu from Laboratory of Cardiovascular Physiology, Hong Kong, China, Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China and Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada consider ST-segment depression in leads I and aVL.
The 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is a routinely performed test but is susceptible to misinterpretation even by experienced physicians. The authors report a case of a 72-year-old lady with no prior cardiac history presenting with atypical chest pain. Her initial electrocardiogram shows an initial ST depression followed by positive deflections leads I and aVL. ...
2021-06-16
Commonplace pharmaceuticals, such as ibuprofen, can carry with them an inherent flaw in their atomic structure, which pairs the active, beneficial ingredient with a potentially ineffective -- or even toxic -- counterpart. New research could hold the key to more easily isolating the good while removing the unwanted.
Dr. Shoufeng Lan, assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker '66 Department of Mechanical Engineering at Texas A&M University, is leading a team investigating the use of electromagnetic control over the synthesis of chiral compounds at an atomic level -- a process that could lead to a plethora of practical ...
2021-06-16
How do top athletes talk about doping when they themselves are using performance-enhancing drugs? Or do they just avoid the issue? A new study by the University of Göttingen reveals that any decision to use drugs almost inevitably means the decision to engage in deceptive communication such as lying or omitting information. Those using drugs, for example, regularly describe anti-doping policies as being more intense than ever or overly restrictive, play down the extent of the doping problem, or portray themselves as victims. The results were published in the European Journal for Sport and Society.
Dr Marcel Reinold, Head of Sport and Health Sociology at the Institute of Sport and Exercise Sciences at Göttingen University, analysed autobiographies of professional ...
2021-06-16
A new paper in the journal Cognition examines the visual complexity of written language and how that complexity has evolved.
Using computational techniques to analyze more than 47,000 different characters from 133 living and extinct scripts, co-authors Helena Miton of the Santa Fe Institute and Oliver Morin of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, addressed several questions around why and how the characters of different writing systems vary in how complex they appear.
"When we started this project, we wanted to test whether you find a general simplification of characters over time," Miton says. "Do scripts simplify their ...
2021-06-16
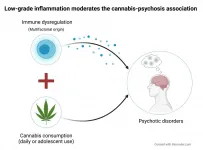
The presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the blood can boost the effects of daily cannabis use and heighten the risk of developing psychosis in adulthood. Similar results have been observed, also in the presence of cytokines, when cannabis is used during adolescence. Psychotic disorders have symptoms such as delirium, loss of a sense of reality, hallucinations, hearing voices, and cognitive and social impairments.
A study by researchers at the University of São Paulo's Ribeirão Preto Medical School (FMRP-USP) in Brazil, reported in an article in ...
2021-06-16
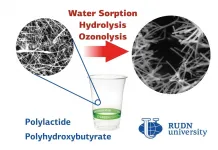
RUDN University biologist studied the aggressive impact of environmental factors (water, salts, and ozone) on ultrathin nanofibers of biopolymers. The results will help choosing suitable bioplastic depending on the use; for example, for medical implants, biodegradable packaging or filters for water cleaning. The results are published in the journal Polymers.
Bioplastics are an alternative to ordinary plastics. They are obtained from waste of plant and food industry. The safe composition allows using them as filters for gases and liquids, as "sponges" for cleaning reservoirs and medical implants. Depending on the field ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Having a strong life purpose eases loneliness of COVID-19 isolation
Those who felt their life was guided by meaningful values or goals were more willing to engage in COVID-19 protective behaviors