RUDN University biologist tested the resistance of bioplastics to aggressive environment
2021-06-16
(Press-News.org) RUDN University biologist studied the aggressive impact of environmental factors (water, salts, and ozone) on ultrathin nanofibers of biopolymers. The results will help choosing suitable bioplastic depending on the use; for example, for medical implants, biodegradable packaging or filters for water cleaning. The results are published in the journal Polymers.
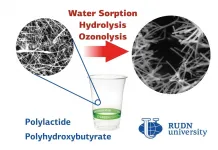
Bioplastics are an alternative to ordinary plastics. They are obtained from waste of plant and food industry. The safe composition allows using them as filters for gases and liquids, as "sponges" for cleaning reservoirs and medical implants. Depending on the field of use, bioplastics are exposed to different environmental factors -- light, water, temperature, and the physiological environment. It is still not known how the external environment affects the nanostructure of bioplastics products. The RUDN University biologist found out how the environment affects the nanofibers of two plastics of organic origin: polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate.
"We obtained the electrospun ultrathin fibers based on thermoelastic biopolyesters. Both of them produced from the naturally abundant renewable resources, namely, polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate. But our main aim was not to obtain the fibers themselves, but to determine whether their properties are preserved under the impact of aggressive environmental factors", Alexandre Vetcher, PhD, Deputy Director of the Scientific-educational centre "Nanotechnologies" of RUDN University
Biologists obtained six types of fibers from polyhydroxybutyrate powder and polylactide granules by electrospinning method. The polymer solution was placed in a high-voltage electrostatic field, which "pulled" the solution into thin jets. After cooling, they turned into fibers. Six types of finished fibers differed in the content of polymers in the composition-pure polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate and their blends in different ratios.
RUDN University biologists have studied the impact of water, physiological environment (internal environment of the body) and ozone on the resulting nanofibers. It turned out that the water vapor absorption depends on the polymer structure. The higher the proportion of polylactide, the more water the fibres absorb: up to 1% of the sample weight. Scientists used a phosphate buffer to simulate the internal environment of a living organism. Polylactide fibers lost more than 50% of their mass in solution over 21 days, and samples with a high polyhydroxybutyrate content lost less than 15%. Also, polymers with a high content of polylactide absorbed ozone molecules more quickly when treated with a stream of this gas and as a result of such intense oxidation they were destroyed. Ozone penetrated the fibers with a 50:50 ratio of the two polymers the fastest.
"We demonstrated that biodegradable nanofibers, which are characterized by a crystalline structure, are more resistant to decomposition by water and ozone. Now it is necessary to test these materials for resistance to UV light and microorganisms in order to determine the optimal applications for each type of fiber", Alexandre Vetcher, PhD, Deputy Director of the Scientific-educational centre "Nanotechnologies" of RUDN University.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
NEW YORK, NY (June 16, 2021)--Spectacular images of a molecule that shuttles omega-3 fatty acids into the brain may open a doorway for delivering neurological therapeutics to the brain.
"We've managed to obtain a three-dimensional structure of the transporter protein that provides a gateway for omega-3s to enter the brain. In this structure, we can see how omega-3s bind to the transporter. This information may allow for the design of drugs that mimic omega-3s to hijack this system and get into the brain," says first author Rosemary J. Cater, PhD, a Simons Society Fellow in the Mancia Lab at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
The study was published online on June 16 in the journal Nature.
A major challenge in treating ...
2021-06-16
Bay Area scientists have captured the real-time electrical activity of a beating heart, using a sheet of graphene to record an optical image -- almost like a video camera -- of the faint electric fields generated by the rhythmic firing of the heart's muscle cells.
The graphene camera represents a new type of sensor useful for studying cells and tissues that generate electrical voltages, including groups of neurons or cardiac muscle cells. To date, electrodes or chemical dyes have been used to measure electrical firing in these cells. But electrodes and dyes measure the voltage at one point only; a graphene sheet measures the voltage ...
2021-06-16
Should zoos display legally protected species that have been smuggled out of their range countries? A new study suggests that a pause and rethink may be needed, as it reports that accredited zoos have acquired a rare and legally protected reptile, the earless monitor lizard endemic to Borneo, without any evidence that the animals were legally exported.
The earless monitor lizard occurs only on the island of Borneo and has been described as a "miniature Godzilla" and "the Holy Grail of Herpetology." Discovered by western scientists almost 150 years ago, for most of this period the species was known largely from pickled specimens in natural history collections, and wasn't recorded from ...
2021-06-16
American Indian and Alaska Native Enrollment in Clinical Studies in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program
Dejonna Vigil, Ninet Sinaji, and Barbara Karp
This is the first study to provide data about the inclusion of American Indians and Alaska Natives in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program (NIH-IRP), which provides eligible individuals with access to innovative research treatments that may not otherwise be available. The program's mission is to include all Americans. This study analyzed data from more than 1,800 NIH-IRP protocols active in 2014 and 2017. While the number of American ...
2021-06-16
When someone bumps their elbow against a wall, they not only feel pain but also might experience bruising. Robots and prosthetic limbs don't have these warning signs, which could lead to further injury. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed an artificial skin that senses force through ionic signals and also changes color from yellow to a bruise-like purple, providing a visual cue that damage has occurred.
Scientists have developed many different types of electronic skins, or e-skins, that can sense stimuli through electron transmission. However, these electrical conductors are not always biocompatible, which could limit their use in some types of prosthetics. In contrast, ionic skins, or I-skins, ...
2021-06-16
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden found industrial chemicals in the organs of fetuses conceived decades after many countries had banned the substances. In a study published in the journal Chemosphere, the researchers urge decision makers to consider the combined impact of the mix of chemicals that accumulate in people and nature.
"These are important findings that call for regulators to consider the collective impact of exposure to multiple chemicals rather than evaluating just one chemical at a time," says first author Richelle Duque Björvang, PhD student at the Department of Clinical ...
2021-06-16
As consumers and corporations alike become more environmentally conscious, the chemical industry is working to find solutions to the plastic waste crisis. One idea is to use biodegradable polymers known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) as replacements for traditional plastic packaging and other materials. A feature article in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explores the possibilities and pitfalls of PHA.
PHA is not a new human invention; this class of polymers can be found in nature and is used to store cellular energy, writes Senior Editor Alex Tullo. Commercially, it is manufactured through the industrial fermentation of sugars or lipids. As cities ...
2021-06-16
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have demonstrated a technology that rapidly detects pollutants in water by measuring their impacts on swimming microorganisms.
Their proof-of-concept, published in Scientific Reports, does not require any chemicals, reagents or laboratory equipment. Instead, it leverages the regular camera of a smartphone as well as microorganisms called Paramecia that are ubiquitous in water bodies--making it especially suitable for assessing water drinkability in underdeveloped regions.
Typically, levels of environmental pollutants are measured by assessing their impact on a given population. Though such impacts may be visible after several days for microorganisms, it takes several years for the true scale to be ...
2021-06-16
People with a rare autoimmune disease, who likely experience more serious isolation during a global pandemic, saw their anxiety and depression improve after receiving online mental health intervention through an international study involving investigators from Michigan Medicine.
The paper, END ...
2021-06-16
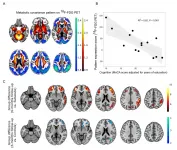
Reston, VA--The effects of COVID-19 on the brain can be accurately measured with positron emission tomography (PET), according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2021 Annual Meeting. In the study, newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients, who required inpatient treatment and underwent PET brain scans, were found to have deficits in neuronal function and accompanying cognitive impairment, and in some, this impairment continued six months after their diagnosis. The detailed depiction of areas of cognitive impairment, neurological symptoms and comparison of impairment over a six-month time frame has been selected as SNMMI's 2021 Image of the Year.
Each year, SNMMI chooses an image that best exemplifies the most promising ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University biologist tested the resistance of bioplastics to aggressive environment