(Press-News.org) People with a rare autoimmune disease, who likely experience more serious isolation during a global pandemic, saw their anxiety and depression improve after receiving online mental health intervention through an international study involving investigators from Michigan Medicine.
The paper, END
Online mental health therapy significantly aids the isolated, immunosuppressed in pandemic
Researchers say the support program could be extended to many patient populations
2021-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
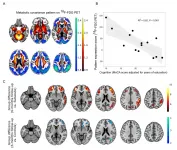
SNMMI Image of the Year: PET imaging measures cognitive impairment in COVID-19 patients
2021-06-16
Reston, VA--The effects of COVID-19 on the brain can be accurately measured with positron emission tomography (PET), according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2021 Annual Meeting. In the study, newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients, who required inpatient treatment and underwent PET brain scans, were found to have deficits in neuronal function and accompanying cognitive impairment, and in some, this impairment continued six months after their diagnosis. The detailed depiction of areas of cognitive impairment, neurological symptoms and comparison of impairment over a six-month time frame has been selected as SNMMI's 2021 Image of the Year.
Each year, SNMMI chooses an image that best exemplifies the most promising ...
Intestinal cancers: The 14-3-3sigma gene acts as a tumor suppressor
2021-06-16
LMU researchers have identified the 14-3-3sigma gene as an important suppressor of carcinogenesis in the gastrointestinal tract.
Intestinal cancers, also known as colorectal cancer, are among the most prevalent forms of malignancy worldwide. If detected early enough, tumors can be surgically excised. However, as cancer growth progresses, cells may escape from the primary tumor, which can then establish metastatic tumors in other organs. Once such satellite tumors have formed, survival rates fall significantly. Formation of the initial tumor can be triggered by mutations in any of a number of genes. Together with postdocs ...
Model helps analyze decision-making on adopting Type 2 diabetes medical guidelines
2021-06-16
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Health care workers often don't adopt new guidelines for best practices in medical care until well after those guidelines are established. A team of researchers led by Eunice E. Santos, the dean of the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has developed a new computational modeling and simulation framework to analyze decision-making and identify effective dissemination strategies for medical guidelines.
The research team examined guidelines for Type 2 diabetes that were established in 2012 and were still not adopted years later. The researchers found that health ...
What factors put Philippine birds at risk of extinction?
2021-06-16
The lush forests and more than 7,000 islands of the Philippines hold a rich diversity of life, with 258 bird species who live nowhere but the Philippine archipelago. A new study from University of Utah researchers suggests that, due to deforestation and habitat degradation, more bird species may be endangered that previously thought - including species that may not have been discovered yet. The study is published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
"Our study provides a roadmap for not only which species may warrant heightened conservation attention," says Kyle Kittelberger, a doctoral student in the University of Utah School of Biological Sciences, "but which traits ...
Algorithm reveals the mysterious foraging habits of narwhals
2021-06-16
An algorithm can predict when narwhals hunt - a task once nearly impossible to gain insight into. Mathematicians and computer scientists at the University of Copenhagen, together with marine biologists in Greenland, have made progress in gathering knowledge about this enigmatic Arctic whale at a time when climate change is pressuring them.
The small whale, known for its distinctively spiraled tusk, is under mounting pressure due to warming waters and the subsequent increase in Arctic shipping traffic. To better care for narwhals, we need to learn more about their foraging behaviour - and how these may change as a result of human disturbances and global warming. Biologists know almost nothing about this. Because narwhals live in isolated Arctic regions and ...
Smartphone bans in the workplace
2021-06-16
For many of us, our smartphone has become our ever-present companion and is usually far more than just a phone. Thanks to the constant availability of online content as well as our reachability through messenger services and social networks via our smartphone, this everyday object's potential to distract us is high - at work too. This is why many employers view the use of smartphones during work time with suspicion, and countermeasures taken range from asking staff to refrain voluntarily from using them to banning smartphones in the workplace through an internal agreement. But do such measures actually work and, if so, how?
This is the ...
Sweeping analysis concludes there's no cheating old age
2021-06-16
DURHAM, N.C. - Special diets, exercise programs, supplements and vitamins -- everywhere we look there is something supposed to help us live longer. Maybe those work: human average life expectancy has gone from a meager 40-ish years to a whopping 70-something since 1850. Does this mean we are slowing down death?
A new study comparing data from nine human populations and 30 populations of non-human primates says that we are probably not cheating the reaper. The researchers say the increase in human life expectancy is more likely the statistical outcome of improved survival for children and young adults, not slowing the aging clock.
"Populations get older mostly because more individuals get through those early stages of life," ...
Stoneflies: Youth influences adulthood
2021-06-16
In the majority of insects, metamorphosis fosters completely different looking larval and adult stages. For example, adult butterflies are completely different from their larval counterparts, termed caterpillars. This "decoupling" of life stages is thought to allow for adaptation to different environments. Researchers of the University of Bonn now falsified this text book knowledge of evolutionary theory for stoneflies. They found that the ecology of the larvae largely determines the morphology of the adults by investigating 219 earwig and stonefly species at high-resolution particle accelerators. The study has ...
Osteoporosis: New approach to understanding bone strength pays dividends
2021-06-16
Osteoporosis researchers at the UVA School of Medicine have taken a new approach to understanding how our genes determine the strength of our bones, allowing them to identify several genes not previously known to influence bone density and, ultimately, our risk of fracture.
The work offers important insights into osteoporosis, a condition that affects 10 million Americans, and it provides scientists potential new targets in their battle against the brittle-bone disease.
Importantly, the approach uses a newly created population of laboratory mice that allows researchers to identify relevant genes and overcome limitations of human studies. Identifying such genes has been very difficult but is key to using genetic discoveries to improve ...
Icebergs drifting from Canada to southern Florida
2021-06-16
Woods Hole, MA (June 16, 2021) -- Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) climate modeler Dr. Alan Condron and United States Geological Survey (USGS) research geologist Dr. Jenna Hill have found evidence that massive icebergs from roughly 31,000 years ago drifted more than 5000km (> 3,000 miles) along the eastern United States coast from Northeast Canada all the way to southern Florida. These findings were published today in Nature Communications.
Using high resolution seafloor mapping, radiocarbon dating and a new iceberg model, the team analyzed about 700 iceberg scours ("plow marks" on the seafloor left behind by the bottom parts of icebergs dragging through marine sediment ) from Cape Hatteras, North Carolina to the Florida Keys. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Online mental health therapy significantly aids the isolated, immunosuppressed in pandemicResearchers say the support program could be extended to many patient populations