New in Ethics & Human Research, May-June 2021
Underrepresented populations in clinical research, and more
2021-06-16
(Press-News.org) American Indian and Alaska Native Enrollment in Clinical Studies in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program
Dejonna Vigil, Ninet Sinaji, and Barbara Karp
This is the first study to provide data about the inclusion of American Indians and Alaska Natives in the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program (NIH-IRP), which provides eligible individuals with access to innovative research treatments that may not otherwise be available. The program's mission is to include all Americans. This study analyzed data from more than 1,800 NIH-IRP protocols active in 2014 and 2017. While the number of American Indian/Alaska Native enrollees increased, it remained at 1% of all participants, a disproportionately low level. The number of clinical studies that enrolled American Indian/Alaska Native individuals also did not change. The authors outline their plans for further research to aid in the ethical inclusion of American Indian and Alaska Native enrollees in clinical research.
Also in the May-June 2021 issue:
"Advance Research Directives: Dementia Researchers' Views on a Prototype Directive and Implementation Strategies," Nola Ries, Elise Mansfield
"Stakeholder Experiences with the Single IRB Review Process and Recommendations for Food and Drug Administration Guidance," Amy Corneli, Carrie B. Domeck, Kevin McKenna, Sara B. Calvert
"SARS-CoV-2 Human Challenge Trials: Rethinking the Recruitment of Health Young Adults First," Kenji Matsui, Yusuke Inoue, Keiichiro Yamamoto
Commentary: "Human Infection Challenge Experiments: Then and Now," Franklin G. Miller, Jonathan D. Moreno
INFORMATION:
For more information, contact:
Susan Gilbert
Director of Communications
The Hastings Center
gilberts@thehastingscenter.org
845-424-4040 x 244
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
When someone bumps their elbow against a wall, they not only feel pain but also might experience bruising. Robots and prosthetic limbs don't have these warning signs, which could lead to further injury. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed an artificial skin that senses force through ionic signals and also changes color from yellow to a bruise-like purple, providing a visual cue that damage has occurred.
Scientists have developed many different types of electronic skins, or e-skins, that can sense stimuli through electron transmission. However, these electrical conductors are not always biocompatible, which could limit their use in some types of prosthetics. In contrast, ionic skins, or I-skins, ...
2021-06-16
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden found industrial chemicals in the organs of fetuses conceived decades after many countries had banned the substances. In a study published in the journal Chemosphere, the researchers urge decision makers to consider the combined impact of the mix of chemicals that accumulate in people and nature.
"These are important findings that call for regulators to consider the collective impact of exposure to multiple chemicals rather than evaluating just one chemical at a time," says first author Richelle Duque Björvang, PhD student at the Department of Clinical ...
2021-06-16
As consumers and corporations alike become more environmentally conscious, the chemical industry is working to find solutions to the plastic waste crisis. One idea is to use biodegradable polymers known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) as replacements for traditional plastic packaging and other materials. A feature article in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explores the possibilities and pitfalls of PHA.
PHA is not a new human invention; this class of polymers can be found in nature and is used to store cellular energy, writes Senior Editor Alex Tullo. Commercially, it is manufactured through the industrial fermentation of sugars or lipids. As cities ...
2021-06-16
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have demonstrated a technology that rapidly detects pollutants in water by measuring their impacts on swimming microorganisms.
Their proof-of-concept, published in Scientific Reports, does not require any chemicals, reagents or laboratory equipment. Instead, it leverages the regular camera of a smartphone as well as microorganisms called Paramecia that are ubiquitous in water bodies--making it especially suitable for assessing water drinkability in underdeveloped regions.
Typically, levels of environmental pollutants are measured by assessing their impact on a given population. Though such impacts may be visible after several days for microorganisms, it takes several years for the true scale to be ...
2021-06-16
People with a rare autoimmune disease, who likely experience more serious isolation during a global pandemic, saw their anxiety and depression improve after receiving online mental health intervention through an international study involving investigators from Michigan Medicine.
The paper, END ...
2021-06-16
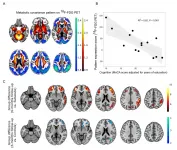
Reston, VA--The effects of COVID-19 on the brain can be accurately measured with positron emission tomography (PET), according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2021 Annual Meeting. In the study, newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients, who required inpatient treatment and underwent PET brain scans, were found to have deficits in neuronal function and accompanying cognitive impairment, and in some, this impairment continued six months after their diagnosis. The detailed depiction of areas of cognitive impairment, neurological symptoms and comparison of impairment over a six-month time frame has been selected as SNMMI's 2021 Image of the Year.
Each year, SNMMI chooses an image that best exemplifies the most promising ...
2021-06-16
LMU researchers have identified the 14-3-3sigma gene as an important suppressor of carcinogenesis in the gastrointestinal tract.
Intestinal cancers, also known as colorectal cancer, are among the most prevalent forms of malignancy worldwide. If detected early enough, tumors can be surgically excised. However, as cancer growth progresses, cells may escape from the primary tumor, which can then establish metastatic tumors in other organs. Once such satellite tumors have formed, survival rates fall significantly. Formation of the initial tumor can be triggered by mutations in any of a number of genes. Together with postdocs ...
2021-06-16
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Health care workers often don't adopt new guidelines for best practices in medical care until well after those guidelines are established. A team of researchers led by Eunice E. Santos, the dean of the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has developed a new computational modeling and simulation framework to analyze decision-making and identify effective dissemination strategies for medical guidelines.
The research team examined guidelines for Type 2 diabetes that were established in 2012 and were still not adopted years later. The researchers found that health ...
2021-06-16
The lush forests and more than 7,000 islands of the Philippines hold a rich diversity of life, with 258 bird species who live nowhere but the Philippine archipelago. A new study from University of Utah researchers suggests that, due to deforestation and habitat degradation, more bird species may be endangered that previously thought - including species that may not have been discovered yet. The study is published in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
"Our study provides a roadmap for not only which species may warrant heightened conservation attention," says Kyle Kittelberger, a doctoral student in the University of Utah School of Biological Sciences, "but which traits ...
2021-06-16
An algorithm can predict when narwhals hunt - a task once nearly impossible to gain insight into. Mathematicians and computer scientists at the University of Copenhagen, together with marine biologists in Greenland, have made progress in gathering knowledge about this enigmatic Arctic whale at a time when climate change is pressuring them.
The small whale, known for its distinctively spiraled tusk, is under mounting pressure due to warming waters and the subsequent increase in Arctic shipping traffic. To better care for narwhals, we need to learn more about their foraging behaviour - and how these may change as a result of human disturbances and global warming. Biologists know almost nothing about this. Because narwhals live in isolated Arctic regions and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New in Ethics & Human Research, May-June 2021
Underrepresented populations in clinical research, and more