'Smart' segmented ring device delivers medications to stop HIV transmission
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) Researchers have designed a device that delivers two medications that help stop HIV transmission.
Although condom usage is the best strategy for preventing HIV transmission, the researchers are working to design a device that can be used by sex workers and in situations where women are not in a position to negotiate condom use.
The device is an intravaginal ring (IVR ) that can be inserted into the female genital tract where it will deliver medications known to decrease the transmission of HIV. The researchers examined how effectively their IVR delivered two medications - hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), an FDA approved medication, and a nanomedicine gene therapy developed by the team in previous research. Their results were published in a recent study.
"We've specifically engineered a combination IVR that can deliver two unique medications targeting different aspects of the HIV infection process," said Emmanuel Ho, a professor in the University of Waterloo's School of Pharmacy and study author. "Before, only one drug could be delivered from an intravaginal ring."
The ring is made of medical-grade plastic and contains two segmented sections. One section is solid and coated in a pH-sensitive polymer that releases the customized gene-therapy treatment specifically during sexual intercourse. The other half is a hollow ring with tiny pores that releases HCQ slowly over twenty-five days.
The HCQ is the first line of defence that reduces the immune cell activation - meaning HIV cells have fewer host target cells to interact with. Doing this buys time for the gene therapy treatment which comes in specifically during sexual intercourse to further suppress the expression of cellular receptors that HIV cells attach to.
The team, which has previously partnered with the University of Nairobi in Kenya on related research, recognizes the importance of using medications as judiciously as possible given potentially limited healthcare resources.
The researchers wanted to have a system that can be placed in the vaginal tract but that only acts when there is sexual intercourse. The presence of semen increases the pH of the genital tract. Therefore, they designed the "smart" gene-therapy segment of the IVR to detect that change in pH and to release the nanomedicine at that point in time only.
"This IVR system will help women to protect themselves against HIV infection and greatly reduce drug usage when it is not necessary," says Yannick Traore, a recent Waterloo PhD graduate and lead author on the study. "We are hoping that this will reduce the cost of drug therapy and also prevent users from developing drug resistance."
The unique, segmented design of the IVR is effective. In lab tests, the HCQ segment successfully released the drug slowly and effectively over 25 days and the gene therapy segment responded to the presence of seminal fluid simulant by releasing 20 times more nanomedicine than was released in an environment of only vaginal fluid simulant. The next steps involve testing the IVR in animal models.
INFORMATION:
The study was recently published in the journal Drug Delivery and Translation Research and features authors from Waterloo and the University of Manitoba.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
New research published in BMJ Open shows that community pharmacy could play a 'key clinical role' in the future role of COVID-19 vaccination programmes, according to a study led by Aston University in Birmingham, UK, in collaboration with UK and international researchers.
The team found that community pharmacists, as a 'skilled clinical workforce', could positively contribute, supporting the community in which they serve - by playing a critical role in ongoing COVID-19 vaccination campaigns.
The researchers working on the PERISCOPE study found that community pharmacy is uniquely placed to support individuals, because it is seen by the public as a credible, trustworthy service, which could be key to any future clinical ...
2021-06-17
The role of people infected with malaria without showing symptoms presents a hidden risk to efforts to control the disease after they were found to be responsible for most infections in mosquitoes, according to a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Researchers from the Infectious Diseases Research Collaboration (IDRC), London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), Radboud university medical center and University of California, San Francisco, found asymptomatic children in the Uganda study were the biggest source of malaria parasites transmitted to mosquitoes. This could provide a new opportunity for control efforts by targeting this infectious reservoir. ...
2021-06-17
Corticosteroids may be an effective treatment for children who develop a rare but serious condition after COVID-19 infection.
This is the finding of an international study of 614 children, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, led by Imperial College London.
All children in the study developed a serious disorder following COVID-19 infection. This condition, called multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), is thought to affect 1 in 50,000 children with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The new disorder, which is also called paediatric inflammatory multi-system syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection (PIMS-TS), affects children of all ages but is more common in older children ...
2021-06-17
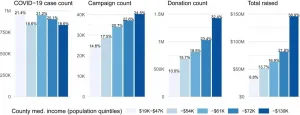
During the first several months of the pandemic -- when communities locked down, jobs were lost, PPE was scarce and store shelves were cleared --thousands of people turned to online crowdfunding to meet their needs.
But a new University of Washington analysis of requests and donations to the popular crowdfunding site GoFundMe, along with Census data, shows stark inequities in where the money went and how much was donated.
A study published June 15 in Social Science & Medicine found more than 175,000 COVID-19-related GoFundMe campaigns in the U.S., raising more than $416 million, from January through July 2020. Researchers found that affluent and educated ...
2021-06-16
'God forbid we need this, but we'll be ready'
Medication would be taken early in the disease, so you don't get as sick
Future drug could also treat common cold
CHICAGO --- Scientists are already preparing for a possible next coronavirus pandemic to strike, keeping with the seven-year pattern since 2004.
In future-looking research, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine scientists have identified a novel target for a drug to treat SARS-CoV-2 that also could impact a new emerging coronavirus.
"God forbid we need this, but we will be ready," said Karla Satchell, professor of microbiology-immunology at Feinberg, who leads an international team of scientists to analyze the important structures of the virus. The Northwestern team previously ...
2021-06-16
An innovative underwater robot known as Mesobot is providing researchers with deeper insight into the vast mid-ocean region known as the "twilight zone." Capable of tracking and recording high-resolution images of slow-moving and fragile zooplankton, gelatinous animals, and particles, Mesobot greatly expands scientists' ability to observe creatures in their mesopelagic habitat with minimal disturbance. This advance in engineering will enable greater understanding of the role these creatures play in transporting carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to the deep sea, as well as how commercial exploitation of twilight ...
2021-06-16
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Human-caused wildfire ignitions in Central Oregon are expected to remain steady over the next four decades and lightning-caused ignitions are expected to decline, but the average size of a blaze from either cause is expected to rise, Oregon State University modeling suggests.
Scientists including Meg Krawchuk of the OSU College of Forestry and former OSU research associate Ana Barros, now of the Washington Department of Natural Resources, say the findings can help local decision-makers understand how a changing climate might affect natural and human-caused fire regimes differently and inform ...
2021-06-16
Researchers at the National Eye Institute (NEI) have determined how certain short protein fragments, called peptides, can protect neuronal cells found in the light-sensing retina layer at the back of the eye. The peptides might someday be used to treat degenerative retinal diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The study published today in the Journal of Neurochemistry. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
A team led by Patricia Becerra, Ph.D., chief of the NEI Section on Protein Structure and Function, had previously derived these peptides from a protein called pigment epithelium-derived ...
2021-06-16
A study of young immigrant mothers who are survivors of sex trafficking found that the trauma affected how they parented: it made them overprotective parents in a world perceived to be unsafe, it fueled emotional withdrawal when struggling with stress and mental health symptoms, and was a barrier to building confidence as mothers. Yet, they coped with such challenges finding meaning in the birth of their child and through social support and faith.
Results of the community-based participatory research study by researchers at Columbia University ...
2021-06-16
An alternate-day intermittent fasting schedule offered less fat-reducing benefits than a matched "traditional" diet that restricts daily energy intake, according to a new, 3-week randomized trial involving 36 participants. The study, which is one of the first to tease apart the effects of fasting and daily energy restriction in lean individuals, indicates that alternate-day fasting may offer no fasting-specific health or metabolic benefits over a standard daily diet. However, the authors caution that longer studies with larger groups are needed. Intermittent fasting, which involves cycling through voluntary fasting and non-fasting periods, has become one of the most popular approaches to losing weight. There ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Smart' segmented ring device delivers medications to stop HIV transmission