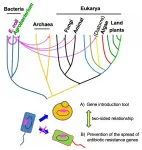
(Press-News.org) Bacteria do not sexually reproduce, but that does not stop them from exchanging genetic information as it evolves and adapts. During conjugal transfer, a bacterium can connect to another bacterium to pass along DNA and proteins. Escherichia coli bacteria, commonly called E. coli, can transfer at least one of these gene-containing plasmids to organisms across taxonomic kingdoms, including to fungi and protists. Now, researchers from Hiroshima University have a better understanding of this genetic hat trick, which has potential applications as a tool to promote desired characteristics or suppress harmful ones across genetic hosts.
They published their results on May 20 in Frontiers in Microbiology.
Plasmids transfer from one bacterium -- the donor -- to another -- the recipient. A particular kind of plasmid, called IncP1, can be hosted by a variety of bacteria and, seemingly as a result of its broad hosts, can transfer DNA to recipients beyond bacteria. The hypothesis is that the plasmid contains genes cultivated from different hosts and donors, resulting in this unique ability.
"Although conjugation factors encoded on plasmids have been extensively analyzed, those on the donor chromosome have not," said paper author Kazuki Moriguchi, associate professor, Program of Basic Biology, Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life, Hiroshima University.
There have been some studies on the various genes, according to Moriguchi, but the function of the genes was not examined, so it is not clear how they were related to the conjugation mechanism.
In this study, the researchers conducted a genome-wide survey on an extensive collection of bacteria mutants as donors to yeast. The mutants were engineered to have specific genes "knocked out" in order to study how the overall system performs without the presence of that specific gene, allowing researchers to infer information about the gene's function.
"We focused on 'up' mutants that have the ability to accelerate conjugative transfer to both prokaryotes and eukaryotes as they could be potent donor strains applicable to gene introduction tools," Moriguchi said, noting how IncP1's ability to transmit genetic material across kingdoms could be used to develop precise tools to introduce genes capable of changing how the bacteria perform certain functions or react to changes in their environments.
Out of 3,884 mutants surveyed, three were identified that could conjugate across E. coli or from E. coli to yeast without accumulating genetic material, indicating that the genes worked together. The researchers analyzed the genes but were unable to elucidate the exact target or targets of conjugation mechanism that allows for cross-kingdom transfer. However, their analysis did reveal how the genes appear to work.
Two of the genes work to repress the unknown target in the E. coli donor. Simultaneously, the third gene is inactivated, allowing another unknown target to resume activity.
"The results suggest that the unknown target factors of these three genes form a complex in order to activate or repress the conjugation, either directly or indirectly at an identical step or steps of the IncP1 conjugation machinery, although the exact mechanism beyond this phenomenon remains unknown," Moriguchi said.
According to Moriguchi, the data collected in this study can help facilitate the breeding of donor strains from various bacteria, each of which carries a high affinity with target organisms in addition to having a high conjugation ability.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Fatin Iffah Rasyiqah Mohamad Zoolkefli, Shinji Yamamoto and Katsunori Suzuki, Department of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science; Suzuki and Kazuya Kiyokawa, Program of Basic Biology, Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life; and Yunjae Cho, Department of Biological Science, Faculty of Science.
The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science funded this work in part.
About Hiroshima University
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 4 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan. English website: https://www.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/en
Young people with poor mental health took a turn for the better during the pandemic but those with good mental health saw a considerable decline, new research reveals.
The first nationally representative evidence regarding the diverse impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on adolescent mental health in the UK was led by researchers at Lancaster University working with the University of British Columbia in Canada.
Adolescents (aged 10 to 16) with better than average mental health before the pandemic experienced an increase in their emotional and conduct problems, hyperactivity, and problems interacting with their peers and friends, but a decrease in their prosocial ...
Scientists have identified key molecular events in the developing human embryo between days 7 and 14 - one of the most mysterious, yet critical, stages of our development.
The second week of gestation represents a critical stage of embryo development, or embryogenesis. Failure of development during this time is one of the major causes of early pregnancy loss. Understanding more about it will help scientists to understand how it can go wrong, and take steps towards being able to fix problems.
The pre-implantation period, before the developing embryo implants into the mother's womb, has been studied extensively in human embryos ...
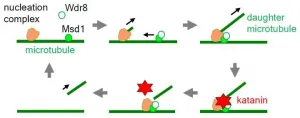
Ikoma, Japan - The katana, a Japanese sword, may be thought of solely as a weapon used by the samurai. But researchers from Japan have discovered that not only do plants wield their own katanas within their cells, they recruit them to specific locations within those cells to do their work.
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology have revealed that the enzyme katanin, which is named after the katana, is used by an anchoring complex to cut microtubules at specific locations of the framework within individual plant cells.
Katanin ...
NEW YORK (June 17, 2021)--New York City neighborhoods that had higher levels of socioeconomic disadvantage experienced more COVID-19 infections and deaths, according to Mount Sinai scientists who created a neighborhood-level COVID-19 inequity index.
The index measured factors that fueled inequities in the residents' lives, such as employment and commuting patterns, population density of their neighborhood, food access, socioeconomic status, and access to health care. This allowed the scientists to compare between neighborhoods the contributions of these social factors in facilitating disease transmission during the first wave of the pandemic in a study published in Nature Communications in June.
"Much of the early rhetoric around COVID-19 ...
As almost all our private information is digitalized, it is increasingly important that we find ways to protect our data and ourselves from being hacked.
Quantum Cryptography is the researchers' answer to this problem, and more specifically a certain kind of qubit - consisting of single photons: particles of light.
Single photons or qubits of light, as they are also called, are extremely difficult to hack.
However, in order for these qubits of light to be stable and work properly they need to be stored at temperatures close to absolute zero - that is minus ...
AI is used in an array of extremely useful applications, such as predicting a machine's lifetime through its vibrations, monitoring the cardiac activity of patients and incorporating facial recognition capabilities into video surveillance systems. The downside is that AI-based technology generally requires a lot of power and, in most cases, must be permanently connected to the cloud, raising issues related to data protection, IT security and energy use.
CSEM engineers may have found a way to get around those issues, thanks to a new system-on-chip they have developed. It runs on a tiny ...
Bottom Line: Genetic mutations indicative of DNA damage were associated with high red meat consumption and increased cancer-related mortality in patients with colorectal cancer.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Marios Giannakis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Background: "We have known for some time that consumption of processed meat and red meat is a risk factor for colorectal cancer," ...
The unique mechanical and optical properties found in the exoskeleton of a humble Asian beetle has the potential to offer a fascinating new insight into how to develop new, effective bio-inspired technologies.
Pioneering new research by a team of international scientists, including Professor Pete Vukusic from the University of Exeter, has revealed a distinctive, and previously unknown property within the carapace of the flower beetle - a member of the scarab beetle family.
The study showed that the beetle has small micropillars within the carapace - or the upper section of the exoskeleton - that give the insect both strength and flexibility to withstand damage very effectively.
Crucially, these micropillars are incorporated into highly regular layering in the exoskeleton ...
Sophia Antipolis - 17 June 2021: People living with obesity who attended a non-judgemental and personalised lifestyle modification programme improved their cardiovascular and mental health during just 10 weeks, according to a study presented today at EuroHeartCare - ACNAP Congress 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Participants lost weight and achieved benefits in anxiety and depression and physical measurements including blood pressure.
"We focus on changing behaviours and improving people's relationship with food," said study ...
The fast-food industry spent $5 billion on advertising in 2019, and the advertisements disproportionately targeted Black and Hispanic youth, according to new research published today by the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity at the University of Connecticut. The new report, Fast Food FACTS 2021, finds that the industry's annual ad spending in 2019 increased by over $400 million since 2012, and that children and teens were viewing on average more than two fast food TV ads per day.
Frequent and widespread exposure to fast-food marketing increases young people's preferences for, and consumption ...