Most comprehensive RNA-Atlas ever
Researchers have built one of the most comprehensive catalogues of the human transcriptome ever
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) The article 'The RNA Atlas expands the catalog of human non-coding RNAs', published today in Nature Biotechnology, is the result of more than five years of hard work to further unravel the complexity of the human transcriptome. Never before such a comprehensive effort was undertaken to characterize all RNA-molecules in human cells and tissues.
RNAs in all shapes and sizes
Our transcriptome is - analogous to our genome - the sum of all RNA molecules that are transcribed from the DNA strands that make up our genome. However, there's no 1-on-1 relationship with the latter. Firstly, each cell and tissue hasve a unique transcriptomes, with varying RNA production and compositions, including tissue-specific RNAs. Secondly, not all RNAs are transcribed from typical - protein coding - genes that eventually produce proteins. Many of our RNA molecules are not used as a template to build proteins, but originate from what once was called junk DNA: long sequences of DNA with unknown functions.
These non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) come in all kinds of shapes and sizes: short, long, and even circular RNAs. Many of them even lack the tail of adenine-molecules that is typical for protein-coding RNAs.
300 human cell and tissue types and three sequencing methods
"There have been other projects to catalogue our transcriptome but the RNA-Atlas project is unique because of the applied sequencing methods," says prof. Pieter Mestdagh from the Center for Medical Genetics at Ghent University. "Not only did we look at the transcriptome of as many as 300 human cell and tissue types, but most importantly, we did so with three complementary sequencing technologies, one aimed at small RNAs, one aimed at polyadenylated (polyA) RNAs and a technique called total RNA sequencing."
This last sequencing technology led to the discovery of thousands of novel non-coding RNA genes, including a novel class of non-polyadenylated single exon genes and many new circular RNAs. By combining and comparing the results of the different sequencing methods the researchers were able to define for every measured RNA transcript, the abundance in the different cells and tissues, whether it has a polyA-tail or not (it appears that for some genes this can differ from cell type to cell type), and whether it is linear of circular. Moreover, the consortium searched and found important clues in determining the function of some of the ncRNAs. By looking at the abundancy of different RNA's in different cell types they found correlations that indicate regulatory functions, and could determine whether this regulation happens on the transcription level (by preventing or stimulating transcription of protein coding genes) or post-transcriptional (e.g. by breaking down RNAs).
An invaluable resource for biomedical science
All data, analyses and results (equivalent to a few libraries of information) are available for download and interrogation in the R2 web portal, enabling the community to implement this resource as a tool for exploration of non-coding RNA biology and function.
Prof. Pavel Sumazin of the Baylor College of Medicine: "By combining all data in one comprehensive catalogue, we have created a new valuable resource for biomedical scientists around the world studying disease processes. A better understanding of the complexity of the transcriptome is indeed essential to better understand disease processes and uncover novel genes that may serve as therapeutic targets or biomarkers. The age of RNA therapeutics is swiftly rising - we've all witnessed the impressive creation of RNA vaccines, and already the first medicines that target RNA are used in the clinic. I'm sure we'll see lots more of these therapies in the next years and decades."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
Additive manufacturing offers an unprecedented level of design flexibility and expanded functionality, but the quality and process can drastically differ across production machines, according to Hui Yang, a professor of industrial engineering at Penn State. With applications in aerospace, health care and automotive industries with potential for mass customization, additive manufacturing needs quality management.
To address this concern, Yang and a team of researchers from Penn State, University of Nebraska--Lincoln and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) proposed the design, development and implementation of a new data-driven methodology for quality control in additive manufacturing. They published their work in the Proceedings ...
2021-06-17
CAMBRIDGE, MA--Geothermal energy systems have the potential to power the world and become the leading technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions if we can drill down far enough into the Earth to access the conditions necessary for economic viability and release the heat beneath our feet. END ...
2021-06-17
SAN ANTONIO (June 17, 2021) -- Convalescent plasma therapy was associated with better survival in blood cancer patients hospitalized with COVID-19, especially in sicker patients. The findings by the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) are newly published in the peer-reviewed journal JAMA Oncology.
The Mays Cancer Center, home to UT Health San Antonio MD Anderson, is part of the CCC19. The international consortium is composed of 124 medical centers and institutions in North and South America that conduct research to learn how COVID-19 affects cancer patients.
Dimpy Shah, MD, PhD, is an epidemiologist and assistant professor of population health sciences at The University of Texas Health ...
2021-06-17
Forest fires have crept higher up mountains over the past few decades, scorching areas previously too wet to burn, according to researchers from McGill University. As wildfires advance uphill, a staggering 11% of all Western U.S. forests are now at risk.
"Climate change and drought conditions in the West are drying out high-elevation forests, making them particularly susceptible to blazes," says lead author Mohammad Reza Alizadeh, a PhD student at McGill University under the supervision of Professor Jan Adamowski. "This creates new dangers for mountain communities, with impacts on downstream water supplies and the plants and wildlife that call these forests home."
Climate warming has diminished 'flammability barrier'
In ...
2021-06-17
If the genome is the recipe of life, base pairs are the individual ingredients listed. These chemical structures form DNA, and every living organism on Earth has just four. The specific arrangements of these four base pairs -- A, T, C, G -- make us who and what we are.
So it was a big surprise when Scripps Research scientists revealed in 2014 that they could introduce two new, unnatural base pairs (they called them X and Y for short) into the genetic code of living bacteria in the lab. It was like two never-seen-before ingredients tossed into the recipe, hypothetically expanding the variety of dishes a cell can whip up.
Researchers immediately saw the potential applications: With more control and selection, they ...
2021-06-17
In a bid to find or refine laboratory research models for cancer that better compare with what happens in living people, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists report they have developed a new computer-based technique showing that human cancer cells grown in culture dishes are the least genetically similar to their human sources.
The finding, they say, should help focus more resources on cancer research models such as genetically engineered mice and 3D balls of human tissue known as "tumoroids" to better evaluate human cancer biology and treatments, and the genetic errors ...
2021-06-17
An algorithm designed by researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Computational Biology Department and St. Petersburg State University in Russia could help scientists identify unknown molecules. The algorithm, called MolDiscovery, uses mass spectrometry data from molecules to predict the identity of unknown substances, telling scientists early in their research whether they have stumbled on something new or merely rediscovered something already known.
This development could save time and money in the search for new naturally occurring products that could be used in medicine.
"Scientists waste a lot of time isolating molecules that are already known, essentially rediscovering penicillin," said Hosein Mohimani, an assistant ...
2021-06-17
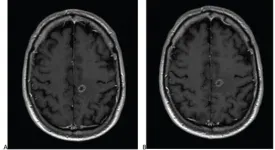
Leesburg, VA, June 17, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a reduced dose of gadobutrol is non-inferior to 100%-standard dose of gadoterate for contrast-enhanced brain MRI.
"A 25% reduced gadobutrol dose demonstrated non-inferior efficacy versus standard dose gadoterate for contrast-enhanced brain MRI," corresponding author Jan Endrikat of Germany's University Medical School of Saarland elaborated, "warranting particular consideration in patients undergoing multiple contrast-enhanced examinations."
In this international, prospective, multicenter, open-label, crossover trial (LEADER-75), 141 patients (78 men, 63 women; mean age, 58.5 years) with known or suspected CNS pathology ...
2021-06-17
Type 1 diabetes is a disorder in which the immune system inappropriately targets a class of cells in the pancreas known as β cells that produce the hormone insulin, which plays an important role in regulating bloodstream glucose levels and the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. The loss of insulin causes a range of health problems for people with type 1 diabetes, and patients become dependent on insulin injections for their survival. Even with insulin therapy, people with type 1 diabetes have shortened lifespans and are at an elevated risk of developing myriad complications.
Previous studies have identified numerous genetic risk factors for type 1 diabetes. One notable finding is the importance of the HLA region, a part of the human ...
2021-06-17
New technologies allow users to do things like race their real bikes against other real people in a virtual world, and a new study outlines what motivates people to use these online platforms. The findings offer insights for future iterations of these technologies - and how to market them.
At issue are "mixed-reality sports": augmented reality platforms that incorporate virtual, online elements and real-world athletic endeavors. For example, Zwift is a platform that allows users to ride their real bicycles, but transfers their efforts to a virtual space depicting real-world courses - allowing them to race against other cyclists who are not physically present.
"We ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Most comprehensive RNA-Atlas ever
Researchers have built one of the most comprehensive catalogues of the human transcriptome ever