Passive smoking and air pollution -- links to arthritis development and poor response to therapy
2021-06-18
(Press-News.org) RA is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that causes pain, swelling and stiffness in the joints. It can also cause fatigue, and the underlying inflammation may affect other body systems. It is more common in women than in men. To date, active smoking has been the most reproducibly reported risk factor for a type of RA called anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) positive RA-particularly in people who carry the HLA-DRB1-shared epitope alleles.
Nguyen and colleagues set out to investigate the relationship between passive smoking and the risk of developing RA in a large prospective cohort of healthy French women.
The E3N-EPIC (Etude Epidémiologique au prèsdes femmes de la Mutuelle générale de l'Education Nationale) has collected data on healthy French women since 1990. RA cases have been identified with specific questionnaires and via the medication reimbursement database. Women were considered to have been exposed to passive smoking in childhood if they self-declared staying in a smoky room several hours a day during childhood, and to passive smoking as an adult if they self-declared being exposed for at least 1 hour a day.
79,806 women were included in the study. Among them, 698 cases of RA were identified. In the whole cohort, 10,810 (13.5%) were exposed to passive smoking as children, and 42,807 (53.6%) to passive smoking as adults.6,581 (8.25%) were exposed to both, and 47,036 (58.9%) were exposed to either.
In the whole population, passive smoking in childhood was positively associated with the risk of RA. When analysed by each person's own smoking status, passive smoking in childhood was associated with RA among women who had never smoked themselves, but not among those who had ever smoked themselves.
When the authors looked at passive smoking in adulthood, there was also a positive risk association in the whole population. But when analysed again by individual smoking status, the association with increased RA risk was only among never-smoking women, not those who had ever themselves been a smoker.
These results suggest that smoking by-products - whether actively or passively inhaled - could generate autoimmunity, at least towards antigens involved in RA pathogenesis.
In a poster examining another link between the lungs and inflammatory arthritis, Adami and colleagues looked at the association between concentration of air pollutants and biologic drug retention rates in people with chronic inflammatory arthritis (CIA) living in the Verona area of Italy.
This was a case-crossover study to compare the exposure to pollutants in the 30?day and 60-day periods preceding a drug switch or swap due to disease progression.
1,286 patients with CIA (888 with RA, 260 with psoriatic arthritis and 138 with ankylosing spondylitis) were included, and 13,636 daily air pollution records were retrieved. The authors found an exposure-dependent relationship between exposure to air pollutants and markers of inflammation in people with CIA. Exposures of greater than 50μg/m3 and greater than 40μg/m3 had a 150% and 65% higher risk of having C-reactive protein (CRP) levels above 5 mg/L, respectively.
If the pollution threshold was set at 30μg/m3(below the European Union health protection limit) there was still a 38% higher risk of having altered CRP (OR 1.383, 95% CI 1.206-1.588).
Air pollutants concentrations were higher before a switch or swap due to drug inefficacy. The authors concluded that environmental air pollution was a determinant of poor response to biologic treatment. Interventions to decrease fossil fuel combustion emissions might have beneficial effects on the persistence rate of biologic treatments in people with inflammatory arthritis.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-18
At the 2021 EULAR congress, Brkic and colleagues presented data from people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)treated at Norwegian rheumatology outpatient clinics between 2010 and 2019.
The project BioRheuma (BIOlogic treatment of patients suffering from inflammatory RHEUMAtic disorders in Norway) aimed to monitor people receiving b/tsDMARDs. Anonymized data files from10 participating centres were merged and analyzed over a 10-year period to show the annual total b/tsDMARD cost, as well as the mean cost per patient for all current users, for all those who started treatment, and for initiating patients naïve to b/tsDMARDs. The cost was calculated based on price offers given at the annual tender process for the different years.
The number of registered RA patients in the databases increased ...
2021-06-18
Murat Torgutalp and colleagues investigated the longitudinal association between radiographic sacroiliitis progression and treatment with TNFi in patients with early axSpA in a long-term inception cohort. The results were shared in an oral session at the 2021 EULAR congress.
Based on the availability of at least two sets of sacroiliac joint (SIJ radiographs), 166 people with non-radiographic axialspondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), and135 with radiographic (r-axSpA), from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (GESPIC) were included in the analysis. Two trained and calibrated ...
2021-06-18
RA is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that causes pain, swelling and stiffness in the joints. It can also cause fatigue, and the underlying inflammation may affect other body systems. Dementia is a symptom of damage to the brain, which can be caused by a number of different diseases - for example, Alzeimer's. Symptoms include memory loss, difficulty concentrating, confusion, and mood changes. It is not known what causes all types of dementia, but it is it thought that some of the damage could be caused by other underlying diseases. Heart failure happens when ...
2021-06-18
Uveitis occurs in up to 20% of children with JIA, although this varies depending on the specific type of JIA that each child has. Jens Klotsche and colleagues shared new data at the 2021 EULAR congress analysing the risk of uveitis events after discontinuing disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD) in children with one of two JIA categories: extended oligoarthritis and rheumatoid factor (RF)-negative polyarthritis.
The data for the analysis came from two ongoing biologic registers: the German Biologics in Pediatric Rheumatology (BiKeR) registry, and the Juvenile arthritis Methotrexate/Biologics long-term Observation (JuMBO) study. Adverse events and reports about uveitis events during treatment and after discontinuation of DMARDs were collected. ...
2021-06-18
Fruit flies have found at least two solutions to the problem of sorting their sex chromosomes: a matter of life and death.
Sex determination in animals often depends on the unequal segregation of specific chromosomes. Female cells generally possess two X chromosomes, while male cells contain one X and one Y chromosome. The latter, which is inherited from the male parent, has far fewer genes than the X. In the fruit fly Drosophila, male cells make up for the fact that they have only one X chromosome by boosting the level of expression of all of its genes by a factor of 2. This phenomenon, which is known as dosage compensation, requires that the X chromosome in males be regulated differently from all the others. A team of molecular biologists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) ...
2021-06-18
Professor Konstantin Arutyunov of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM HSE), together with Chinese researchers, has developed a graphene-based mechanical resonator, in which coherent emission of sound energy quanta, or phonons, has been induced. Such devices, called phonon lasers, have wide potential for application in information processing, as well as classical and quantum sensing of materials. The study is published in the journal Optics Express.
Using an analogy with photons, quanta of the electromagnetic spectrum, there are also particles of sound energy, phonons. In fact, these are artificially introduced objects in physics - quasi-particles, which correspond to vibrations ...
2021-06-18
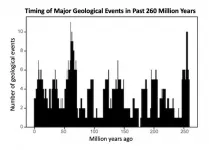
Geologic activity on Earth appears to follow a 27.5-million-year cycle, giving the planet a "pulse," according to a new study published in the journal Geoscience Frontiers.
"Many geologists believe that geological events are random over time. But our study provides statistical evidence for a common cycle, suggesting that these geologic events are correlated and not random," said Michael Rampino, a geologist and professor in New York University's Department of Biology, as well as the study's lead author.
Over the past five decades, researchers have proposed cycles ...
2021-06-18
A new paper in Scientific Reports led by researchers at William & Mary's Virginia Institute of Marine Science challenges increased salinity and seawater temperatures as the established explanation for a decades-long increase in the prevalence and deadliness of a major oyster disease in the coastal waters of the mid-Atlantic.
Dr. Ryan Carnegie, the paper's lead author, says "We present an entirely new lens through which we can view our last 35 years of oyster history in the Chesapeake Bay region. We now know the great intensification of Dermo disease in the 1980s wasn't simply due to drought. It was more fundamentally due to the emergence of a new and highly virulent form of Perkinsus marinus, the parasite that causes Dermo."
In an unusual twist, the team's evidence ...
2021-06-18
The Axial Spondyloarthritis International Federation (ASIF) set out to coordinate a comprehensive evidence-based global review of the factors influencing the current diagnosis delay in axSpA, and to produce a definitive report that shines a light on these barriers, as well as providing a resource that can ultimately empower a range of international stakeholders to reduce this delay.
At the 2021 EULAR congress, Wendy Gerhart and colleagues report the results of a full literature review and two virtual global forum events, involving patients and patient group ...
2021-06-18
Ben Mulhearn and colleagues estimated the incidence of GCA seen during the COVID-19 pandemic and compared it to data from 2019, before the pandemic hit. The two distinct peaks of COVID-19 reflected by UK hospital admissions of COVID-19-positive patients allowed the authors to investigate the relationship in time between COVID-19 and GCA incidence.
At the Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases in Bath, UK, there were 61 probable or definite GCA diagnoses made in 2020 compared to 28 in 2019- representing an excess of 33 cases in 2020, or an increase of 118%.Taking into account the fact that41% of the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Passive smoking and air pollution -- links to arthritis development and poor response to therapy