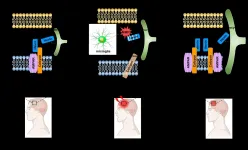
Robot-assisted surgery: Putting the reality in virtual reality
2021-06-19
(Press-News.org) Cardiac surgeons may be able to better plan operations and improve their surgical field view with the help of a robot. Controlled through a virtual reality parallel system as a digital twin, the robot can accurately image a patient through ultrasound without the hand cramping or radiation exposure that hinder human operators. The international research team published their method in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
"Intra-operative ultrasound is especially useful, as it can guide the surgery by providing real-time images of otherwise hidden devices and anatomy," said paper author Fei-Yue Wang, Director of the State Key Laboratory of Management and Control of Complex Systems, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences. "However, the need for highly specialized skills is always a barrier for reliable and repeatable acquisition."
Wang noted that the availability of onsite sonographers can be limited, and that many procedures requiring intra-operative ultrasound also often require X-ray imaging, which could expose the operator to harmful radiation. To mitigate these challenges, Wang and his team developed a platform for robotic intra-operative trans-esophageal echocardiography (TEE), an imaging technique widely used to diagnose heart disease and guide cardiac surgical procedures.
"Our result has indicated the use of robot with a simulation platform could potentially improve the general usability of intra-operative ultrasound and assist operators with less experience," Wang said.
The researchers employed parallel control and intelligence to pair an operator with the robot in a virtual environment that accurately represents the real environment. Equipped with a database of ultrasound images and a digital platform capable of reconstructing anatomy, the robot could navigate the target areas for the operator to better visualize and plan potential surgical corrections in computational experiments.
"Such a system can be used for view definition and optimization to assist pre-planning, as well as algorithm evaluations to facilitate control and navigation in real-time," Wang said.
Next, the researchers plan to further integrate the currently proposed parallel real/virtual system with specific clinical needs to assist the translational research of such imaging robots.
"The ultimate goal is to integrate the virtual system and the physical robot for in-vivo clinical tests, so as to propose a new diagnosis and treatment protocol using parallel intelligence in medical operations," Wang said.
INFORMATION:
S. Y. Wang, J. Housden, T. X. Bai, H. B. Liu, J. Back, D. Singh, K. Rhode, Z.-G. Hou, and F.-Y. Wang, "Robotic intra-operative ultrasound: Virtual environments and parallel systems," IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 1095-1106, May 2021. http://www.ieee-jas.net/en/article/doi/10.1109/JAS.2021.1003985
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica aims to publish high-quality, high-interest, far-reaching research achievements globally, and provide an international forum for the presentation of original ideas and recent results related to all aspects of automation.
The first Impact Factor of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica is 5.129, ranking among Top 17% (11/63, SCI Q1) in the category of Automation & Control Systems, according to the latest Journal Citation Reports released by Clarivate Analytics in 2020. In addition, its latest CiteScore is 11.2, and has entered Q1 in all three categories it belongs to (Information System, Control and Systems Engineering, Artificial Intelligence) since 2018.
Why publish with us: Fast and high quality peer review; Simple and effective online submission system; Widest possible global dissemination of your research; Indexed in SCIE, EI, IEEE, Scopus, Inspec. JAS papers can be found at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=6570654 or http://www.ieee-jas.net
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-19
Patients with brain injury (caused by stroke or trauma) primarily rely on rehabilitation therapy for recovery, as there are no other known effective treatment methods. The rate of recovery from brain injury observed in adults is significantly slower (or the recovery is impossible) than that observed in young children. The consensus among researchers is that the number of excess neural stem cells capable of restoring brain functions is lower in a mature brain than that in the brain of young children.
A Korean research team reported a novel mechanism to describe the brain injury recovery process. The researchers reported that when the animal model experiment was conducted, the time taken to recover from a brain injury could be controlled by ...
2021-06-19
Globally, an estimated 10 million people develop tuberculosis (TB) each year and the disease remains a leading cause of death from a single infectious agent. Standard short-course anti-TB treatment still requires a regimen of at least six months of antimicrobial drugs, and drug-resistant TB is an increasing public health threat. Even after the traces of TB disease are quashed, patients often suffer from significant sequelae, such as lung scarring. TB survivors have approximately three to four times greater mortality than their local population.
In pulmonary TB, the most common form of active TB disease, the ...
2021-06-19
(Vienna, Saturday, 19 June 2021) Music by Mozart has been shown to have an anti-epileptic effect on the brain and may be a possible treatment to prevent epileptic seizures, according to new research presented today at the 7th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN).
Researchers believe that the acoustic (physical) properties within the music are responsible for this effect.
Listening to the famous 18th century composer's Sonata for Two Pianos K448 led to a 32% reduction in epileptiform discharges (EDs). These are electrical brain waves associated with epilepsy and can cause seizures or bursts of electrical activity that temporarily affect how the brain works.
A team led by Professor Ivan Rektor, from the Epilepsy Centre ...
2021-06-19
Highlights
Primary nephrotic syndrome is characterized by high urinary excretion of protein, low protein in the blood, high cholesterol, and swelling in the arms and legs.
A new analysis highlights the high risk of kidney failure and different cardiovascular complications in patients with primary nephrotic syndrome.
Washington, DC (June 18, 2021) -- A form of kidney disease called primary nephrotic syndrome is characterized by high urinary excretion of protein, low protein in the blood, high cholesterol, and swelling in the arms and legs. Patients may face a range of negative health outcomes, but the extent of these effects are unknown. In a study appearing in an upcoming ...
2021-06-19
Highlights
In a study of patients waiting for a kidney transplant, those who experienced various symptoms had a higher risk of dying while on the waitlist.
Symptoms tended to increase or remain unchanged between transplant evaluation and transplantation; however, at 3 months after transplantation, 9 of 11 symptoms lessened.
Washington, DC (June 18, 2021) -- Investigators have examined how various symptoms experienced by individuals with kidney failure are impacted by kidney transplantation. The findings will appear in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
People with kidney failure must often deal with numerous symptoms, such as fatigue, cramping, muscle soreness, numbness, dizziness, and loss of appetite. Although kidney transplantation ...
2021-06-19
New findings published this week in Physical Review Letters suggest that carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen cosmic rays travel through the galaxy toward Earth in a similar way, but, surprisingly, that iron arrives at Earth differently. Learning more about how cosmic rays move through the galaxy helps address a fundamental, lingering question in astrophysics: How is matter generated and distributed across the universe?
"So what does this finding mean?" asks John Krizmanic, a senior scientist with UMBC's Center for Space Science and Technology (CSST). "These are indicators of something interesting happening. And what that ...
2021-06-18
Just as the skeleton and muscles move the human body and hold its shape, all the cells of the body are stabilised and moved by a cellular skeleton. Unlike our skeleton, this cellular skeleton is a very dynamic structure, constantly changing and renewing itself. It consists of different types of protein filaments, which include intermediate filaments and microtubules. Now, a research team from the University of Göttingen is the first to succeed in observing a direct interaction between microtubules and intermediate filaments outside the cell, and also in quantitatively measuring this interaction. The results of the study were published in Nature Communications.
Microtubules are dynamic filaments ...
2021-06-18
Study Highlights
New research reveals how key proteins interact to regulate the body's response to stress
Targeting these proteins may help treat or prevent stress-related psychiatric disorders
The biological mechanisms behind stress-related psychiatric conditions, including major depressive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are poorly understood.
New research now details the interplay between proteins involved in controlling the body's stress response and points to potential therapeutic targets when this response goes awry. The study, which was conducted by an international team led by investigators at McLean Hospital, appears in ...
2021-06-18
BOSTON - Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have discovered a biological mechanism that transforms cells exposed to carcinogens from environmental factors like smoking and ultraviolet light into immunogenic cells that can be harnessed therapeutically to fight treatment-resistant cancers. As reported in Science Advances, that mechanism involves spurring the release of small proteins known as chemokines which, in turn, recruit antitumor immune cells (CD8+ T cells) to the tumor site to block metastasis, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of a new generation of immunotherapies.
"Immunotherapeutics ...
2021-06-18
CHICAGO --- Scientists have long known the brain's hippocampus is crucial for long-term memory. Now a new Northwestern Medicine study has found the hippocampus also plays a role in short-term memory and helps guide decision-making.
The findings shed light on how the hippocampus contributes to memory and exploration, potentially leading to therapies that restore hippocampal function, which is impacted in memory-related aging and neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia, the study authors said.
In the study, scientists monitored participants' brain activity and tracked their eye movements while looking at different complex pictures. The scientists discovered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Robot-assisted surgery: Putting the reality in virtual reality