INFORMATION:
The study was published in June in the Oncogene journal, part of the prestigious Nature publishing group, with the full title "Targeting HIF-1 alpha transcriptional activity drives cytotoxic immune effector cells into melanoma and improves combination immunotherapy". The article was listed under the category of 'brief communication', a category reserved for articles of exceptional interest due to their significance and timely contribution to cancer biology.
'Suffocating' cancer: A new headway in melanoma immunotherapy
Disrupting cancer cell ability to adapt to low oxygen conditions shows promise in melanoma
2021-06-21
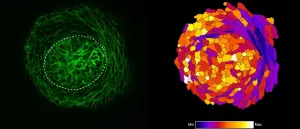
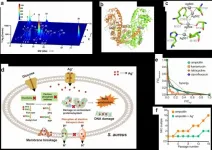
(Press-News.org) Hypoxia, or the inadequate oxygenation of a tissue, is a condition occurring frequently in all solid tumours such as melanoma skin cancer. Melanoma cells are not only able to survive oxygen deprivation, but also to use it to their own advantage by hijacking the anti-tumour immune response and developing resistance mechanisms to conventional anti-cancer therapies. A key gene responsible for cancer cell adaptation to hypoxia is HIF-1α (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 alpha). Led by Dr Bassam Janji, head of the Tumor Immunotherapy and Microenvironment (TIME) research group at the Luxembourg Institute of Health (LIH) and in collaboration with Gustave Roussy Cancer Center in France and the Thumbay Research Institute of Precision Medicine at Gulf Medical University in the United Arab Emirates, the team used gene editing technologies to show how targeting HIF-1α could not only inhibit tumour growth, but also drive cytotoxic (toxic to cells) immune cells to the cancer tissue. This discovery provided a valuable new target to make resistant melanomas more vulnerable to available anti-cancer treatments. Their findings were recently published in the reputable Oncogene Journal.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes, cells that are responsible for the production of pigments. Melanomas become harder to treat if not detected early, with emerging treatment resistance being an important barrier to their effective management. Due to their rapid growth rate and low blood supply, solid tumours including melanoma often exhibit areas of hypoxia. Hypoxia, or the decrease of oxygen in the tumour microenvironment, would normally cause tumour cell death. "However, certain solid tumours have evolved to survive this hostile microenvironment by activating HIF-1α, a gene reported to be a major factor mediating the adaptive response to changes in tissue oxygen level," explains Dr Janji. William G. Kaelin Jr, Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2019 for their discovery of HIF-1? and how cells use it to sense hypoxia. Hypoxia has also been reported to be responsible for the failure of tumour response to conventional anti-cancer therapies and can prevent the infiltration of immune cells into the tumour. It is therefore crucial to understand the mechanisms by which cancer cells overcome this hypoxic environment to improve the effectiveness of available anti-cancer therapies.
In this context, the team led by Dr Janji sought to inactivate the functionality of the HIF-1α gene using CRISPR gene editing technology and investigate the impact of such inactivation on tumour growth, immune cell infiltration and response to immunotherapy in a preclinical melanoma mouse model.
"Our study revealed that blocking the activity of HIF-1α significantly inhibited melanoma growth and amplified the infiltration of immune cells into the tumour microenvironment by increasing the release of CCL5, a well-defined mediator involved in driving cytotoxic immune cells to the tumour battlefield", summarises Dr Audrey Lequeux, first author of the publication. Importantly, the study also showed that combining a drug devised to stop hypoxia significantly improves melanoma immunotherapy. When the results were validated retrospectively in a cohort of 473 melanoma patients, the hypoxic signature of tumours was correlated to worsened outcomes and the lack of immune cell infiltration into tumours, which is considered as a major characteristic of tumour resistance to immunotherapies.
"Together, our data strongly argue that therapeutic strategies disrupting HIF-1α would be able to modulate the tumour microenvironment to permit the infiltration of immune cells. Such strategies could be used to improve vaccine-based and immune checkpoint blockade-based cancer immunotherapies in non-responder melanoma patients," conclude Dr Chouaib and Dr Janji from Gulf Medical University and Luxembourg Institute of Health, respectively.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
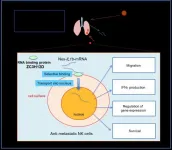
Extracellular mRNA transported to the nucleus shows translation-independent function
2021-06-21
A research group led by Professor Sachie Hiratsuka, Institute for Biomedical Research, Shinshu University, has found that a specific sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA), which exists outside cells, binds to receptors on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells and is taken up into the nucleus. The group found that NK cells with mRNA uptake are able to enhance their migration activity and interferon gamma production. Furthermore, NK cells incorporating the mRNA showed an inhibitory effect on cancer metastasis in animal experiments.
In recent years, the results of cancer treatment have been improving with the increase of medical ...
Cellular mechanisms of early mammary gland development unraveled
2021-06-21
Helsinki University research group used live tissue imaging for the first time to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
Despite long-standing interest, the cellular mechanisms driving the initiation of mammary gland development have remained elusive for decades, mostly due to technical limitations in studying dynamic cell behaviors in live tissues. Recent advances in microscopic methods and availability of various mouse models allowed the research group of Marja Mikkola from HiLIFE Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki to address this question. This is the first time when live tissue imaging has been used to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
Mammary gland is the class-defining organ of mammals, yet we know surprisingly little how its ...
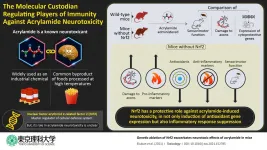
Nrf2: The custodian regulating oxidative stress and immunity against acrylamide toxicity
2021-06-21
Acrylamide is a toxic chemical compound that affects the nervous system. Not only is it widely used in industries such as paper production, plastics, and wastewater management, but it is also a byproduct of commonly used food processing methods, which makes human exposure to acrylamide inevitable. Therefore, many studies have focused on understanding the toxic effects of acrylamide and our body's response to them. Generally, in response to toxicity, the body's cells release protective factors and antioxidants to remedy the damage. This response is activated by various cellular machinery. One such activator is a protein called "nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2" (Nrf2), ...
There's no cheating old age
2021-06-21
Special diets, exercise programs, supplements and vitamins, there is everywhere something supposed to help us live longer. Whether it actually works has not always been shown, but the average life expectancy of people has increased over the last 150 years. A study by an international team of researchers, including Claudia Fichtel and Peter Kappeler, scientists in the Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology Unit at the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen, indicates that we probably cannot slow down aging. The comparative studies with humans and non-human primates, indicates that it is not the rate at which humans age that slows ...
Twenty-year study links childhood depression to disrupted adult health and functioning
2021-06-21
Washington, DC, June 21, 2021 - Depression in youth, between the ages of 10 and 24 years, is both a leading cause of stress and a possible risk factor for future diseases and impairment. Now, a study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, confirms that depression in childhood or adolescence is associated with higher levels of adult anxiety and substance use disorders, worse health and social functioning, less financial and educational achievement, and increased criminality.
The findings are based on the Great Smoky Mountains Study, an ongoing longitudinal ...
RedHill announces presentation of positive oral opaganib phase 2 data in COVID-19
2021-06-21
TEL AVIV, Israel and RALEIGH, NC, June 21, 2021, RedHill Biopharma Ltd. (Nasdaq: RDHL) ("RedHill" or the "Company"), a specialty biopharmaceutical company, today announced presentation of the positive Phase 2 safety and efficacy data for oral opaganib (Yeliva®, ABC294640) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia at the World Microbe Forum (WMF) 2021 (poster #: 5574).
Results and post hoc analyses of data from the 40-patient U.S. Phase 2 study were presented in a poster entitled, "Opaganib, an Oral Sphingosine Kinase-2 (SK2) Inhibitor in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Phase 2A Study, in ...
HKU physics Ph.D. student obtained the Higgs mode via dimensional crossover in quantum magnets revealing importance of dimensions in many-body systems
2021-06-21
In 2013, François ENGLERT and Peter HIGGS won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, which was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle by the A Toroidal LHC Apparatus (ATLAS) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiments at The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)'s Large Hadron Collider in 2012. The Higgs mode or the Anderson-Higgs mechanism (named after another Nobel Laureate Philip W ANDERSON), has widespread influence ...
Ancient bones provide clues about Kangaroo Island's past and future
2021-06-21
A Curtin University-led study of ancient bones on South Australia's Kangaroo Island has provided new information about the Island's past fauna and an insight into how species may live there in the future.
Published in Quaternary Science Reviews, the researchers analysed around 2,000 bone fragments with the aim of eventually being able to establish a more complete picture of past biodiversity on the Island.
Lead researcher Dr Frederik Seersholm from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said DNA studies on such a large scale have never been done on the Island before.
"We identified 33 species, 10 of which are extinct on the island today. We also found DNA traces from both the ...
HKU scientists reveal silver-based antimicrobials can be utilized as antibiotic adjuvants to combat antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
2021-06-21
A research team led by Professor Hongzhe SUN, Norman & Cecilia Yip Professor in Bioinorganic Chemistry and Chair Professor from Research Divison for Chemistry and Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, in collaboration with Dr Richard Yi-Ysun KAO, Associate Professor from the Department of Microbiology, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, and Dr Aixin YAN, Associate Professor from School of Biological Sciences, the University of Hong Kong (HKU), discovers that silver (Ag)-based antimicrobials can effectively combat antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus by targeting multiple biological pathways via functional disruption of key proteins and can be further exploited to enhance the efficacy of conventional antibiotics ...
Ramanome Database can help mining microalgal cell factories for reducing carbon emissions
2021-06-21
Microalgae are "simple" organisms of single cells, yet they pack a mighty potential punch when it comes to helping humanity achieve carbon neutrality, according to researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Their metabolic activities play fundamental roles in global carbon cycling and convert carbon dioxide into a wide variety of high-value macromolecules.
Now, the QIBEBT researchers have developed a way to rapidly determine exactly which microalgae -- out of the millions of variations -- can most readily convert carbon dioxide into valuable compounds that can be used for fuels, food and drugs. They published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
[Press-News.org] 'Suffocating' cancer: A new headway in melanoma immunotherapyDisrupting cancer cell ability to adapt to low oxygen conditions shows promise in melanoma