There's more to genes than DNA: how Mum and Dad add something extra, just for you
Biologists in the UK and Austria have discovered 71 new imprinted genes in the mouse genome
2021-06-21
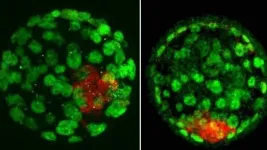
(Press-News.org) Biologists at the Universities of Bath and Vienna have discovered 71 new 'imprinted' genes in the mouse genome, a finding that takes them a step closer to unravelling some of the mysteries of epigenetics - an area of science that describes how genes are switched on (and off) in different cells, at different stages in development and adulthood.
To understand the importance of imprinted genes to inheritance, we need to step back and ask how inheritance works in general. Most of the thirty trillion cells in a person's body contain genes that come from both their mother and father, with each parent contributing one version of each gene. The unique combination of genes goes part of the way to making an individual unique. Usually, each gene in a pair is equally active or inactive in a given cell. This is not the case for imprinted genes. These genes - which make up less than one percent of the total of 20,000+ genes - tend to be more active (sometimes much more active) in one parental version than the other.
Until now, researchers were aware of around 130 well-documented imprinted genes in the mouse genome - the new additions take this number to over 200.
Professor Tony Perry, who led the research from the Department of Biology & Biochemistry at Bath in the UK, said: "Imprinting affects an important family of genes, with different implications for health and disease, so the seventy-plus new ones add an important piece of the jigsaw."
THE IMPORTANCE OF HISTONES
Close examination of the newly identified genes has allowed Professor Perry and his colleagues to make a second important discovery: the switching on and off of imprinted genes is not always related to DNA methylation, where methyl groups are added to genomic DNA- a process that is known to repress gene activity, switching them off). DNA methylation was the first known type of imprint, and was discovered around thirty years ago. From the results of the new work, it seems that a greater contribution to imprinting is made by histones - structures that are wrapped up with genomic DNA in chromosomes.
Although scientists have known for some time that histones act as 'dimmer' switches for genes, fading them off (or back on), until now it was thought that DNA methylation provided the major switch for imprinted gene activity. The findings from the new study cast doubt on this assumption: many of the newly identified genes were found to be associated with changes to the histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3), and only a minority with DNA methylation.
WHY IMPRINTING MATTERS
Scientists have yet to work out how one parental version of a given gene can be switched (or faded) on or off and maintained that way while the other is in the opposite state. It is known that much of the on/off switching occurs during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg), but the precise mechanisms remain unclear. This new study points to the intriguing possibility that some imprinted genes may not be marked in gametes, but become active later in development, or even in adulthood.
Although it only involves a small proportion of genes, imprinting is important in later life. If it goes wrong, and the imprinted gene copy from one parent is switched on when it should be off (or vice versa), disease or death occur. Faulty imprinted genes are associated with many diseases, including neurological and metabolic disorders, and cancer.
"We may underestimate how important the relationship between imprinting and disease is, as well as the relationship of imprinting to the inheritance of parentally-acquired disease, such as obesity," said Professor Perry. "Hopefully, this improved picture of imprinting will increase our understanding of disease."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
Fat biomolecules in the blood, called "serum lipids," are necessary evils. They play important roles in the lipid metabolism and are integral for the normal functioning of the body. However, they have a darker side; according to several studies, they are associated with various cancers. The medical community has fathoms to go before truly understanding the implications of different serum lipid levels in cancer.
As a major step in this direction, a group of scientists from the Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research, Laboratory of Genetics, Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute; Hua County People's Hospital; and Anyang Cancer Hospital, have successfully determined that a family history ...
2021-06-21
(BOSTON) - Research collaborators from the VA, Boston University, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation (CLF) published an inspiring new report today, "1,000 Reasons for Hope," which exclusively details the first 1,000 brain donors studied at the VA-BU-CLF Brain Bank since 2008 and how they have advanced research on concussions and CTE. The report also explains how the next 1,000 brain donors will answer critical questions that take us closer to preventing, diagnosing, and treating CTE, as well as the long-term consequences of concussion and traumatic brain injury.
"Our understanding ...
2021-06-21
Johan Gaume, an EPFL expert in avalanches and geomechanics, has turned his attention to ice. His goal is to better understand the correlation between the size of an iceberg and the amplitude of the tsunami that results from its calving. Gaume, along with a team of scientists from other research institutes, has just unveiled a new method for modeling these events. Their work appears in Communications Earth & Environment, a new journal from Nature Research.
These scientists are the first to simulate the phenomena of both glacier fracture and wave formation when the iceberg falls into the water. "Our goal was to model the explicit interaction between water and ice - but that has a substantial cost in terms of computing time. We therefore decided ...
2021-06-21
An increasing number of studies on artificial intelligence (AI) are published in the dental and oral sciences but aspects of these studies suffer from a range of limitations. Standards towards reporting, like the recently published CONSORT-AI extension, can help to improve studies in this emerging field. Watch authors Falk Schwendicke and Joachim Krois of the Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, discuss the Journal of Dental Research (JDR) article "Better Reporting of Studies on Artificial Intelligence: CONSORT-AI and Beyond," moderated by JDR Editor-in-Chief Nicholas Jakubovics, Newcastle ...
2021-06-21
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit during the winter of 2020, locking down entire countries and leaving people isolated in their homes without outside contact for weeks at a time, many relationship experts wondered what that kind of stress would do to romantic couples. What they found was that when couples blamed the pandemic for their stress, they were happier in their relationships.
The findings are outlined in a paper out today in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science.
Previous research has shown that romantic partners tend to be more critical toward each other when experiencing ...
2021-06-21
Forces of nature have been outsmarting the materials we use to build our infrastructure since we started producing them. Ice and snow turn major roads into rubble every year; foundations of houses crack and crumble, in spite of sturdy construction. In addition to the tons of waste produced by broken bits of concrete, each lane-mile of road costs the U.S. approximately $24,000 per year to keep it in good repair.
Engineers tackling this issue with smart materials typically enhance the function of materials by increasing the amount of carbon, but doing so makes materials lose some mechanical performance. By introducing nanoparticles into ordinary cement, Northwestern University ...
2021-06-21
TAMPA, Fla (June 21, 2021) -- A blood gene profile associated with a high risk of dying from a severe lung disease can also predict poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19, a multicenter retrospective study led by the University of South Florida Health (USF Health) demonstrated. The risk profile based on 50 genes could help customize how COVID-19 is treated, improve allocation of limited health care resources such as intensive care beds and ventilators, and potentially save lives.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a disease of unknown cause, affects the lung interstitium or the space between the lung sacs and the bloodstream, leading ...
2021-06-21
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Using solar energy to inexpensively harvest hydrogen from water could help replace carbon-based fuel sources and shrink the world's carbon footprint. However, finding materials that could boost hydrogen production so that it could compete economically with carbon-based fuels has been, as yet, an insurmountable challenge.
In a study, a Penn State-led team of researchers reports it has taken a step toward overcoming the challenge of inexpensive hydrogen production by using supercomputers to find materials that could help accelerate hydrogen separation when water is exposed to light, a process called photocatalysis.
Both electricity and solar energy can be used to separate hydrogen from water, ...
2021-06-21
Sperm size varies dramatically among different animal species. But why is sperm size so variable when they share the same job - to fertilize eggs? In a new article published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, researchers from Stockholm University show that animal sperm evolution become supercharged only when sperm swim inside females.
Sperm are the most variable cell type known, ranging in size from 0.002 millimeters in a freshwater rotifer to nearly 6 centimeters in a fruit fly. Explaining why sperm are so variable has been a major focus in evolutionary ...
2021-06-21
One in three patients who dies in a hospital has sepsis, a severe inflammatory response to an infection, marked by organ dysfunction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This heavy toll makes predicting which patients are at risk for developing the devastating condition a top priority for clinicians.
Additional motivation to identify and treat sepsis cases lies in the fact that sepsis serves as a system-level quality measure, with hospitals judged by both the by the federal Department of Health and Human Services and the CDC on their sepsis rates. Complicating efforts to reduce sepsis is how difficult it can be to diagnose--both accurately and quickly.
"Sepsis is something we can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] There's more to genes than DNA: how Mum and Dad add something extra, just for you
Biologists in the UK and Austria have discovered 71 new imprinted genes in the mouse genome


