Creating cooler cities
Pitt civil engineers examine urban cooling strategies using reflective surfaces
2021-06-21
(Press-News.org) If you've ever been in a city's central core in the middle of summer, you know the heat can be brutal--and much hotter than in the surrounding region.
Temperatures in cities tend to be several degrees warmer than in its rural areas, a phenomenon called the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. Many cities have been observed to be 2-4ºC warmer than the countryside in virtually every inhabited continent. This phenomenon occurs because urban infrastructure, especially pavements, absorbs a lot of heat as compared to natural vegetated surfaces. This heat pollution causes higher air conditioning and water costs, while also posing a public health hazard.
One mitigation strategy called gray infrastructure involves the modification of impermeable surfaces (walls, roofs, and pavements) to counter their conventional heating effect. Typical urban surfaces have a solar reflectance (albedo) of 0.20, which means they reflect just 20 percent of sunlight and absorb as much as 80 percent. By contrast, reflective concrete and coatings can be designed to reflect 30-50 percent or more. Cities like Los Angeles have already used reflective coatings on major streets to combat heat pollution, although the solution can be expensive to implement city-wide.
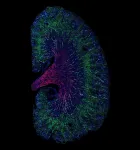
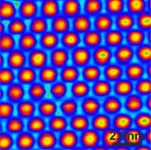
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering used a Computational Fluid Dynamics model to find ways to decrease cost and increase usage of cooler surfaces. The paper, published in the journal Nature Communications, examined the possibility of applying cooler surfaces to just half the surfaces in a city.
"This could be an effective solution if the surfaces selected were upstream of the dominant wind direction," said lead author Sushobhan Sen, postdoctoral associate in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. "A 'barrier' of cool surfaces preemptively cools the warm air, which then cools the rest of the city at a fraction of the cost. On the other hand, if the surfaces are not strategically selected, their effectiveness can decline substantially."
This research gives urban planners and civil engineers an additional way to build resilient and sustainable infrastructure using limited resources.
"It's important for the health of the planet and its people that we find a way to mitigate the heat produced by urban infrastructure," said coauthor Lev Khazanovich, the department's Anthony Gill Chair Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering. "Strategically placed reflective surfaces could maximize the mitigation of heat pollution while using minimal resources."
INFORMATION:
The paper, titled "Limited application of reflective surfaces can mitigate urban heat pollution," (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23634-7) was coauthored by Sen and Khazanovich. The paper was recently featured by Nature Communications in the Editors' Highlight page on climate change impacts.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
NEW YORK, NY--COVID vaccine surveillance efforts are a global priority, but safety monitoring for vaccines should not reflect a single population. The largest, most extensive international study of the background rates of adverse events of special interest (AESI) that are being tracked in vaccine surveillance efforts show that adverse event rates vary substantially by age, sex, and method of data capture.
Led by researchers at Oxford University, Columbia University, Erasmus MC, UCLA, and Janssen, an international team of collaborators from the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network provided a timely reference of the background rates of AESIs in a new study published ...
2021-06-21
A research team led by the University of Arizona has reconstructed in unprecedented detail the history of a dust grain that formed during the birth of the solar system more than 4.5 billion years ago. The findings provide insights into the fundamental processes underlying the formation of planetary systems, many of which are still shrouded in mystery.
For the study, the team developed a new type of framework, which combines quantum mechanics and thermodynamics, to simulate the conditions to which the grain was exposed during its formation, when the solar system was a swirling disk of gas ...
2021-06-21
The USC Stem Cell laboratory of Andy McMahon has identified a type of injured cell that might contribute to the transition from an acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease, as described in a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The same issue of PNAS also features an accompanying Q&A with McMahon to mark his recent election as a member of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Acute kidney injury can be a common side effect of surgery, sepsis or certain prescription drugs, and there is no effective treatment," said McMahon, who is the W.M. Keck Provost and University Professor of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, and Biological Sciences at USC. "Even a mild or moderate injury can progress into chronic ...
2021-06-21
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. - Women who lose local or state elections are just as likely to run for office again as men, suggesting the recent surge in women running for office may have a long-term impact on women's political representation, according to a new study by researchers from Harvard and the University of California, Davis.
Pundits and scholars have argued that women are more likely to abandon politics after a losing campaign than men, citing evidence that women are more risk-averse and more likely to avoid competition than men.
Political scientists Rachel Bernhard, assistant professor at UC-Davis, and Justin de Benedictis-Kessner, assistant professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School, ...
2021-06-21
Team used Argonne's GREET model to simulate changes, predict outcomes.
Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory participated in a study that shows innovation in technologies and agricultural practices could reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from grain production by up to 70% within the next 15 years.
Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, the study identifies a combination of readily adoptable technological innovations that can significantly reduce emissions and fit within current production systems and established grain markets.
The study, "Novel ...
2021-06-21
A species of butterfly found in Sub-Saharan Africa is able to migrate thousands of miles to Europe, crossing the Saharan Desert, in years when weather conditions are favourable, scientists have found.
The striking Painted Lady (Vanessa cardui) butterfly has been shown for the first time to be capable of making the 12,000-14,000km round trip - the longest insect migration known so far - in greater numbers, when wetter conditions in the desert help the plants on which it lays eggs.
The international research team's findings increase understanding of how insects, including pollinators, pests and the diseases they carry could spread between continents in ...
2021-06-21
Lead levels in London's atmosphere have dropped drastically since lead additives in petrol were phased out, and currently meet UK air quality targets. However despite this drop, airborne particles in London are still highly lead-enriched compared to natural background levels, according to new Imperial research published today in PNAS.
The study found that up to 40 per cent of lead in airborne particles today comes from the legacy of leaded petrol. The researchers say this highlights the long-term persistence of contaminants introduced by human activities in the environment.
Lead author of the study Dr Eléonore Resongles, who carried out the work at Imperial's Department of Earth Science and Engineering, said: "Petrol-derived lead deposited decades ago remains an important ...
2021-06-21
One vision that is currently driving material scientists is to combine organic molecules (and their diverse functionalities) with the technological possibilities offered by extremely sophisticated semiconductor electronics. Thanks to modern methods of micro- and nanotechnology, the latter designs ever more efficient electronic components for a wide variety of applications. However, it is also increasingly reaching its physical limits: Ever smaller structures for functionalizing semiconductor materials such as silicon cannot be produced using the approaches of classical technology. Scientists ...
2021-06-21
Think about how many different pieces of technology the average household has purchased in the last decade. Phones, TVs, computers, tablets, and game consoles don't last forever, and repairing them is difficult and often as expensive as simply buying a replacement.
Electronics are integral to modern society, but electronic waste (e-waste) presents a complex and growing challenge in the path toward a circular economy--a more sustainable economic system that focuses on recycling materials and minimizing waste. Adding to the global waste challenge is the prevalence of dishonest recycling practices by companies who claim to be recycling electronics but actually dispose of them by other means, such as in ...
2021-06-21
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, June 21, 2021 - A team of scientists at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have invented an artificial nose that is capable of continuous bacterial monitoring, which has never been previously achieved and could be useful in multiple medical, environmental and food applications.
The study was published in Nano-Micro Letters.
"We invented an artificial nose based on unique carbon nanoparticles ("carbon dots") capable of sensing gas molecules and detecting bacteria through the volatile metabolites the emit into the air," says lead researcher Prof. Raz Jelinek, BGU vice president ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Creating cooler cities
Pitt civil engineers examine urban cooling strategies using reflective surfaces