Mushroom growing out of fossilized ant reveals new genus and species of fungal parasite
2021-06-22
(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University research has identified the oldest known specimen of a fungus parasitizing an ant, and the fossil also represents a new fungal genus and species.
"It's a mushroom growing out of a carpenter ant," said OSU's George Poinar Jr., an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn about the biology and ecology of the distant past.
A mushroom is the reproductive structure of many fungi, including the ones you find growing in your yard, and Poinar and a collaborator in France named their discovery Allocordyceps baltica. They found the new type of Ascomycota fungi in an ant preserved in 50-million-year-old amber from Europe's Baltic region.
"Ants are hosts to a number of intriguing parasites, some of which modify the insects' behavior to benefit the parasites' development and dispersion," said Poinar, who has a courtesy appointment in the OSU College of Science. "Ants of the tribe Camponotini, commonly known as carpenter ants, seem especially susceptible to fungal pathogens of the genus Ophiocordyceps, including one species that compels infected ants to bite into various erect plant parts just before they die."
Doing so, he explains, puts the ants in a favorable position for allowing fungal spores to be released from cup-shaped ascomata - the fungi's fruiting body -protruding from the ants' head and neck. Carpenter ants usually make their nests in trees, rotting logs and stumps.
The new fungal genus and species shares certain features with Ophiocordyceps but also displays several developmental stages not previously reported, Poinar said. To name the genus, placed in the order Hypocreales, Poinar and fellow researcher Yves-Marie Maltier combined the Greek word for new - alloios - with the name of known genus Cordyceps.
"We can see a large, orange, cup-shaped ascoma with developing perithecia - flask-shaped structures that let the spores out - emerging from rectum of the ant," Poinar said. "The vegetative part of the fungus is coming out of the abdomen and the base of the neck. We see freestanding fungal bodies also bearing what look like perithecia, and in addition we see what look like the sacs where spores develop. All of the stages, those attached to the ant and the freestanding ones, are of the same species."
The fungus could not be placed in the known ant-infecting genus Ophiocordyceps because ascomata in those species usually come out the neck or head of an ant, Poinar said, and not the rectum.
"There is no doubt that Allocordyceps represents a fungal infection of a Camponotus ant," he said. "This is the first fossil record of a member of the Hypocreales order emerging from the body of an ant. And as the earliest fossil record of fungal parasitism of ants, it can be used in future studies as a reference point regarding the origin of the fungus-ant association."
INFORMATION:
Findings were published in Fungal Biology.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-22
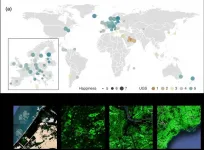
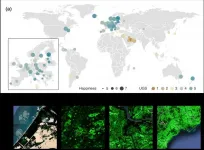
A recent study revealed that as a city becomes more economically developed, its citizens' happiness becomes more directly related to the area of urban green space.
A joint research project by Professor Meeyoung Cha of the School of Computing and her collaborators studied the relationship between green space and citizen happiness by analyzing big data from satellite images of 60 different countries.
Urban green space, including parks, gardens, and riversides not only provides aesthetic pleasure, but also positively affects our health by promoting ...
2021-06-22
Urban green spaces, such as parks, backyards, riverbanks, and urban farmlands, are thought to contribute to citizen happiness by promoting physical and mental health. While a number of previous studies have reported the mental bene?ts of green space, most had been conducted in the affluent parts of the world like the United States and Europe, and only a few involved a multi-country setting.
Lack of data had been the main limitation in carrying out these studies because there is no global medical dataset that can provide reliable and standardized mental health surveys from different countries. Another challenge involves a systematic method to measure the amount of green space across countries. Various methods of measuring ...
2021-06-22
Solar cells, which convert sunlight to electricity, have long been part of the global vision for renewable energy. Although individual cells are very small, when upscaled to modules, they can be used to charge batteries and power lights. If laid side-by-side, they could, one day, be the primary energy source for buildings. But the solar cells currently on the market utilize silicon, which makes them expensive to fabricate when compared to more traditional power sources.
That's where another, relatively new-to-science, material comes in - metal halide perovskite. When nestled at the center of a solar cell, this crystalline structure also ...
2021-06-22
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and the University of the Ryukyus has recently identified and described a bizarre new genus and species of xanthid crab found in Okinawa Island, Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Named Mabui calculus, it is unique among the 7,800 species of known crabs in having strongly asymmetrical male and female reproductive structures!
"Male crabs have a pair of reproductive parts called gonopods while females have a pair of vulvae. All crabs mate in the 'missionary position', so the gonopods pump sperm into females for internal fertilisation of the eggs. This was the accepted orthodoxy until our discovery - a small Japanese crab has evolved to do this very differently!" explained Professor Peter Ng, a world-leading expert in ...
2021-06-22
Recent studies show that, in the future, the mercury concentration of fish in Finnish Lapland can shift closer to the level found in lakes located below the Arctic Circle. According to researchers, mercury content should be increasingly carefully investigated and monitored in fish and food webs, as the climate and land use change.
Mercury is a heavy metal found in nature. Methylmercury, a particularly toxic form of the metal, accumulates in fish and is biomagnified in food webs. Humans are exposed to methylmercury especially through fish-based diets.
Researchers investigated the joint effects of the climate and land ...
2021-06-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists are pursuing a new strategy in the protracted fight against the SARS-CoV-2 virus by engineering nanobodies that can neutralize virus variants in two different ways.
In lab studies, researchers identified two groups of molecules that were effective against virus variants. Using different mechanisms, nanobodies in each group bypassed mutations and disabled the virus's ability to bind to the receptor that lets it enter host cells.
Though vaccination is enabling the resumption of some pre-pandemic activities in parts of the world, ...
2021-06-22
MISSOULA - The map of Montana Kayla Irish pulls up is peppered with red circles, each cluster providing details behind one of today's timely topics - childhood vaccination.
The project, led by Dr. Sophia Newcomer in the University of Montana's Center for Population Health Research, is the first spatial scan analysis to identify hotspots of undervaccinated children across Montana and evaluate whether they are due to social or geographic barriers.
CPHR is funded through the National Institutes of Health, and the analysis is part of a collaborative ...
2021-06-22
Irvine, Calif., June 21, 2021 -- Cancer immunotherapy involving drugs that inhibit CTLA-4 also activates an unwanted response that may self-limit its efficacy in fighting tumors, according to a new study led by Francesco Marangoni, Ph.D., assistant professor of physiology & biophysics and member of the Institute for Immunology at the University of California, Irvine. Study results are published online in the journal Cell.
Using a person's own immune system - immunotherapy - to treat cancer may also stimulate T regulatory cells, which are essential for preventing autoimmunity, in which the body attacks healthy cells and tissue, but limit tumor control. Some anticancer drugs of the checkpoint inhibitor family block the molecule CTLA-4 and activate ...
2021-06-22
Every year in Canada, six trillion litres of municipal wastewater are partially treated and released into the environment, while another 150 billion litres of untreated sewage are discharged straight into pristine surface waters.
Now researchers have found a way to stem that flow: by filtering the waste through the roots of willow trees. Experimenting with a plantation in Quebec, the scientists estimate that over 30 million litres of primary wastewater per hectare can be treated using 'bio-refinery' annually.
Their results were published June 14 in the journal ...
2021-06-22
[Brooklyn, New York] - [June 21, 2021] - Applied Biological Laboratories (Applied Bio), a biopharmaceutical company focused on the respiratory disease market, announced that its study published online in Immunology, Inflammation and Disease was able to determine the mechanism behind respiratory inflammation and treat it effectively with Biovanta(TM), a 100% naturally derived, over-the-counter (OTC) drug for cold, cough and sore throat.
The study results also showed that almost all of the leading OTC products on the market can damage the upper respiratory cells and may prolong illness. This research study and its findings represent one of the first major breakthroughs in decades for the cold and flu market.
The study, titled ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mushroom growing out of fossilized ant reveals new genus and species of fungal parasite