INFORMATION:
More than 16 million Americans undiagnosed with COVID-19 during first wave, estimates antibody analysis
2021-06-22
(Press-News.org) As many as 16.8 million Americans had undiagnosed SARS-CoV-2 infections - 5 times the rate of diagnosed infections - by the end of July of 2020, according to an analysis of antibodies from more than 8,000 previously undiagnosed adults collected during the pandemic's first wave. The authors calculated that almost 5% of the undiagnosed U.S. population harbored SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, with the highest positivity rates among African Americans, those under the age of 45, urban dwellers, and women. The results suggest a larger spread of COVID-19 in the U.S. than originally suspected in previous reports. SARS-CoV-2 can stealthily cause asymptomatic infections in some individuals, who can still spread the disease to others. This property has frustrated health authorities' efforts to track down the true number of infected people, especially during the pandemic's early stages in the spring and summer of 2020. Here, Heather Kalish and colleagues posed survey questions to, and analyzed blood samples from, 8,058 undiagnosed adults reflecting the makeup of the U.S. population, which the team mostly gathered from early May to the end of July in 2020. They ensured a representative sample by using quota sampling with a much larger pool of more than 460,000 volunteers, allowing the scientists to make estimates about the general population. Kalish et al. found that 304 of the participants harbored antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and its receptor binding domain, leading them to estimate that 4.6% of the U.S. population harbored undiagnosed infections. The team also found differences in seropositivity across regions, gender, and ethnicity: rates were highest in the Mid-Atlantic (8.6%), in women (5.5%), and in African-Americans (14.2%), while lower in people working from home (3%) and in patients with chronic conditions such as heart disease. "Our findings have implications for understanding SARS-CoV-2 spread ... and prevalence in different communities and could have a potential impact on decisions involved in vaccine rollout," the authors conclude.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vaccine side effects should be welcomed as a sign of efficacy, immunologists say in new focus
2021-06-22
The rapid development of safe and efficacious vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 has offered hope that the global COVID-19 pandemic may soon be under control. However, vaccinations remain incomplete in many developed nations, and lag further still in the developing world. In a new Focus, Jonathan Sprent and Cecile King posit that vaccine hesitancy, motivated in part by fear of side effects documented in scientific journals and the popular media, could hold back the global population from reaching herd immunity. Seeking to reassure those with reservations, Sprent and King suggest that "it is highly likely ...
Does bubble cascade form only in a glass of Guinness beer?
2021-06-22
Osaka, Japan - As far back as 1959, brewers at Guinness developed a system that fundamentally altered the texture of their draught beer. Now, researchers from Japan have solved the physics of Guinness' cascading flow, which will have widespread applications to technology in life and environmental sciences.
In a study recently published in Physical Review E, researchers from Osaka University have revealed why the nitrogen bubbles of Guinness draught beer flow similarly to a fluid.
The bubbles of many just-opened carbonated beverages simply move upwards, following Archimedes' principle. Much of the appeal of the draught from Guinness beer is that the bubbles sink and flow collectively, known as "bubble cascade." ...
Gestational diabetes increases the risk of fetal hypoxia during labor
2021-06-22
In Finland, every fifth mother was diagnosed with gestational diabetes in 2019. The condition increases the mother's risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, the most significant consequence of gestational diabetes is fetal macrosomia, or excessive growth of the fetus. Macrosomia increases birth injuries for both the child and the mother, causes fetal hypoxia, that is, a lack of oxygen in the fetus, and increases labour-related complications for the newborn.
A research group active at the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital demonstrated that the mother's gestational diabetes ...
Illuminating the mechanism behind how plants regulate starch synthesis
2021-06-22
In a world-first, a Kobe University research group led by Associate Professor FUKAYAMA Hiroshi of the Graduate School of Agricultural Science has used rice to successfully illuminate the mechanism by which plants regulate the amount of starch produced via photosynthesis. This knowledge could contribute towards improving the quality and yield of agricultural crops.
These research results were published in the international scientific journal Plant, Cell & Environment on May 14, 2021.
Main Points
Plants convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic substances ...
Sports: Men and women react differently to a missing audience
2021-06-22
Without an audience, men run slower and women faster: The lack of spectators during the coronavirus pandemic appears to have had a noticeable effect on the performance of athletes at the 2020 Biathlon World Cup, a new study by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in Psychology of Sport and Exercise shows. According to the new analysis, women also performed better in complex tasks, such as shooting, when an audience was present while men did not.
Social facilitation theory states that a person's performance is impacted if other people watch them. The mere presence of an audience improves the performance of simple tasks, especially those that require stamina. "The studies have been relatively clear so far, but the results are more heterogeneous when it comes to more complex ...
USC study shows inherited risk of early-onset cancer is higher among minority families
2021-06-22
Increased risk of cancer due to a genetic predisposition in first- and second-degree relatives is long-established but has previously only been studied in white or European populations.
Now, a new study published in eLife is the first to demonstrate that the inherited risk of early-onset cancer is significantly higher among Latino and African American families for solid tumors, and Asian/Pacific Islander families for blood-based cancers, compared to non-Latino white families in California.
"Cancer clustering within families, meaning the devastating diagnosis of more than one early-onset cancer within the same family, usually points ...
Mushroom growing out of fossilized ant reveals new genus and species of fungal parasite
2021-06-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University research has identified the oldest known specimen of a fungus parasitizing an ant, and the fossil also represents a new fungal genus and species.
"It's a mushroom growing out of a carpenter ant," said OSU's George Poinar Jr., an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn about the biology and ecology of the distant past.
A mushroom is the reproductive structure of many fungi, including the ones you find growing in your yard, and Poinar and a collaborator in France named their discovery Allocordyceps baltica. They found the ...
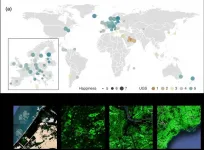
'Urban green space affects citizens' happiness'
2021-06-22
A recent study revealed that as a city becomes more economically developed, its citizens' happiness becomes more directly related to the area of urban green space.
A joint research project by Professor Meeyoung Cha of the School of Computing and her collaborators studied the relationship between green space and citizen happiness by analyzing big data from satellite images of 60 different countries.
Urban green space, including parks, gardens, and riversides not only provides aesthetic pleasure, but also positively affects our health by promoting ...
Urban green space brings happiness when money can't buy it anymore
2021-06-22
Urban green spaces, such as parks, backyards, riverbanks, and urban farmlands, are thought to contribute to citizen happiness by promoting physical and mental health. While a number of previous studies have reported the mental bene?ts of green space, most had been conducted in the affluent parts of the world like the United States and Europe, and only a few involved a multi-country setting.
Lack of data had been the main limitation in carrying out these studies because there is no global medical dataset that can provide reliable and standardized mental health surveys from different countries. Another challenge involves a systematic method to measure the amount of green space across countries. Various methods of measuring ...
Future of perovskite solar cells shines a little brighter
2021-06-22
Solar cells, which convert sunlight to electricity, have long been part of the global vision for renewable energy. Although individual cells are very small, when upscaled to modules, they can be used to charge batteries and power lights. If laid side-by-side, they could, one day, be the primary energy source for buildings. But the solar cells currently on the market utilize silicon, which makes them expensive to fabricate when compared to more traditional power sources.
That's where another, relatively new-to-science, material comes in - metal halide perovskite. When nestled at the center of a solar cell, this crystalline structure also ...