A new type of gravitational wave detector to find tennis ballsized black holes
A new type of gravitational wave detector to find tennis ballsized black holes straight out of the Big Bang
2021-06-22
(Press-News.org) "Detecting primordial black holes opens up new perspectives to understand the origin of the Universe, because these still hypothetical black holes are supposed to have formed just a few tiny fractions of a second after the Big Bang. Their study is of great interest for research in theoretical physics and cosmology, because they could notably explain the origin of dark matter in the Universe". You can see stars in the eyes of the members of the team led by Professor Fuzfa, astrophysicist at UNamur, when talking about the perspectives of their research. This project is the result of an unprecedented collaboration between the UNamur and ULB, to which the ENS added thanks to the involvement of trainee student Léonard Lehoucq.
The idea was to combine the UNamur expertise in the field of gravitational wave antennas, an idea patented by Professor F?zfa in 2018 and studied by Nicolas Herman as part of his doctorate, with that of ULB in the booming field of primordial black holes, in which Professor Clesse is one of the central players. They have just developed an application of this type of detector in order to observe "small" primordial black holes. Their results have just been published in the journal Physical Review D. "To this day, these primordial black holes are still hypothetical, because it is difficult to make the difference between a black hole resulting from the implosion of a star core and a primordial black hole. Being able to observe smaller black holes, the mass of a planet but a few centimeters in size, would make the difference," the team of researchers says. They carry on: "We are offering experimenters a device that could detect them, by capturing the gravitational waves they emit when merging and which are of much higher frequencies than those currently available".
But what is the technique? A gravitational wave "antenna", composed of a specific metal cavity and suitably immersed in a strong external magnetic field. When the gravitational wave goes through the magnetic field, it generates electromagnetic waves in the cavity. In a way, the gravitational wave makes the cavity "hiss" (resonate), not with sound but with microwaves.
This type of device, just a few meters in size, would be enough to detect fusions of primordial small black holes millions of light years from Earth. It is much more compact than the commonly used detectors (LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA interferometers) which are several kilometers long. The detection method makes it sensitive to very high frequency gravitational waves (in the order of 100 MHz, compared to 10-1000 Hz for LIGO / Virgo / Kagra), which are not produced by ordinary astrophysical sources such as fusions, neutron stars or stellar black holes.
On the other hand, it is ideal for the detection of small black holes, the mass of a planet and its size goes from a small ball to a tennis ball. "Our detector proposal combines well mastered and everyday life technologies such as magnetrons in microwave ovens, MRI magnets and radio antennas. But don't take your household appliances apart right away to start the adventure: read our article first, then order your equipment, understand the device and the signal that awaits you at the output," the researchers say laughingly.
This patented technique is currently at the stage of advanced theoretical modeling, but has all the necessary elements to enter a more concrete phase, with the construction of a prototype. In any case, it paves the way for fundamental research into the origins of our Universe. In addition to primordial black holes, this type of detector could also directly observe the gravitational waves emitted at the time of the Big Bang, and thus probe physics at much higher energies than the ones achieved in particle accelerators.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-22
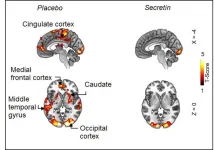
Researchers from the Turku PET Centre and Technical University of Munich have discovered a new mechanism controlling satiation. According to the recently published study, the hormone secretin induces satiation by activating brown adipose tissue.
Brown adipose tissue is known for its ability to generate heat in response to cold exposure. Its activity has been proven to be connected to normal weight and glucose metabolism as well as lesser risks of cardiovascular diseases. Meals have also been shown to increase the thermogenesis in brown fat, but the significance of this phenomenon has been unclear. ...
2021-06-22
Teacher training students who practised teaching virtual pupils developed greater confidence in their teaching ability, according to a study from Linköping University. In the long term, simulation can make the students better prepared for their workforce debut.
Teacher training programmes often have difficulty offering their students sufficient teaching practice for their future profession. Many teaching graduates feel unprepared when they start working, and some decide to change career path, despite good employment prospects caused by a teacher shortage.
A group of researchers at Linköping University investigated whether teaching virtual pupils could make teacher training students better prepared for teaching in a real classroom.
"By ...
2021-06-22
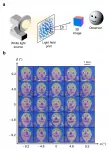
Wouldn't it be amazing if printed images can look three-dimensional (3D)? Unfortunately, conventional prints like photographs display two-dimensional (2D) images with a fixed appearance as they contain only intensity and colour information. These prints are unable to display a 3D image because they lack directional control of light rays, hence resulting in the loss of depth information.
To address this problem, a team of researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) used a nanoscale 3D printing technique to create high-resolution light field prints ...
2021-06-22
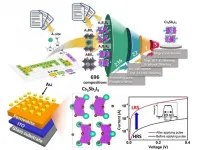
A research team led by Professor Jang-Sik Lee of Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has successfully developed the halide perovskite-based memory with ultra-fast switching speed. The findings from this study were published in Nature Communications on June 10, 2021.
Resistive switching memory is a promising contender for next-generation memory device due to its advantages of simple structure and low power consumption. Various materials have been previously studied for resistive switching memory. Among them, halide perovskites are receiving much attention for use in the memory because of low operation voltage and high on/off ratio. However, halide perovskite-based ...
2021-06-22
People who have contact with other social groups are more likely to be committed to social justice. However, an international study led by the University of Zurich has shown that for this to be the case, power relations and discrimination must be actively addressed and group-specific needs must be met. It is important that disadvantaged group members, such as racial minorities and LGBTIQ+ individuals, are given a voice, and that those who belong to advantaged groups do not feel labeled as biased.
People who are socially disadvantaged or discriminated against because they belong to a particular group often join forces with other disadvantaged people to fight together for better rights. Prominent examples of such political engagement are the women's rights movement, Black Lives ...
2021-06-22
Rather than levelling inequality, as the Great Depression did, the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated inequalities around the world allowing some wealthy investors to benefit from the crisis and make a fortune on the misfortune of others.
During March to December last year, U.S. billionaires increased their wealth by over one-third, to one trillion dollars, while millions of Americans faced deep financial hardship.
New research from Copenhagen Business School has examined how American "shadow banks"- which are less regulated and include private credit intermediaries such as private equity, venture capital, and hedge fund firms - have invested in ways that extract profit from the misfortunes of frontline workers, struggling companies, ...
2021-06-22
People who have experienced childhood trauma get a more pleasurable "high" from morphine, new research suggests.
University of Exeter scientists compared the effects of morphine on 52 healthy people - 27 with a history of childhood abuse and neglect, and 25 who reported no such experiences in childhood.
Those with childhood trauma liked morphine (an opioid drug) more, felt more euphoric and had a stronger desire for another dose.
Those with no childhood trauma were more likely to dislike the effects and feel dizzy or nauseous.
"There are high rates of childhood trauma in people with addictions. Our findings ...
2021-06-22
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is gaining attention in the asphalt industry as an eco-friendly and sustainable technology. WMA reduces energy consumption while simultaneously minimizing vapors and greenhouse gas emissions during the production of asphalt mixtures in comparison to conventional asphalt. However, high moisture susceptibility and ageing of asphalt make WMA less durable on the roads.
To address both issues in WMA technology, a team from the Energy Safety Research Institute (ESRI) at Swansea University and Braunschweig Pavement Engineering Centre (ISBS) at the Technical University of Braunschweig have discovered ...
2021-06-22
Listening to music while running might be the key to improving people's performance when they feel mentally fatigued a study suggests.
The performance of runners who listened to a self-selected playlist after completing a demanding thinking task was at the same level as when they were not mentally fatigued, the research found.
The study is the first to investigate the effect of listening to music playlists on endurance running capacity and performance when mentally fatigued.
Researchers at the University of Edinburgh used two tests to study how listening to music affected the running performance of ...
2021-06-22
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and Serbia have reviewed almost a thousand patents held by some two hundred organizations involved in the New Space economy. The analysis helped draw a comprehensive picture of technology trends in the field. The paper was published in the journal Progress in Aerospace Sciences.
"New Space" is a loosely defined term that encompasses the recent flurry of space-related activities coming from smaller actors rather than a handful of space-faring nations. Put somewhat simply, while the Apollo missions were more traditional, SpaceX, Rocket Lab (launching small satellites from New Zealand) or LeoLabs (a space junk tracking company) are undeniably parts of a new and different ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new type of gravitational wave detector to find tennis ballsized black holes
A new type of gravitational wave detector to find tennis ballsized black holes straight out of the Big Bang