Patents help build a global map of new space industry
2021-06-22
(Press-News.org) Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and Serbia have reviewed almost a thousand patents held by some two hundred organizations involved in the New Space economy. The analysis helped draw a comprehensive picture of technology trends in the field. The paper was published in the journal Progress in Aerospace Sciences.
"New Space" is a loosely defined term that encompasses the recent flurry of space-related activities coming from smaller actors rather than a handful of space-faring nations. Put somewhat simply, while the Apollo missions were more traditional, SpaceX, Rocket Lab (launching small satellites from New Zealand) or LeoLabs (a space junk tracking company) are undeniably parts of a new and different space economy. In a 2020 paper, Skoltech Associate Professor Alessandro Golkar and Alejandro Salado of Virginia Tech found three distinguishing traits of New Space companies: explicit customer focus, new product development approaches, and new business models.
"In a nutshell, the main difference relates to how New Space organizations develop their products and how they approach the business. New Space organizations tend to embrace innovative development processes such as agile, have a risk-taker attitude, and focus on profit. This new attitude allows New Space companies to reduce time-to-market and lower the cost of entry to the space business," Skoltech PhD student Nicola Garzaniti says.
Golkar, Garzaniti and their colleagues decided to map New Space to analyze this paradigm shift in the industry. They used the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), a topic modeling algorithm, to analyze patents' data and the global intellectual property landscape, identifying the most prominent technological trends.
"For this project, we employed a data-based approach to analyze the New Space ecosystem. To do so, we employed a topic modeling technique known as Latent Dirichlet Allocation, or LDA. LDA is a generative statistical model used in the natural language processing domain. Put simply, the model "reads" the patents and identifies patterns of words in the collection of patents, allowing to connect documents that exhibit similar patterns," Garzaniti explains.
He notes that startup companies and large system integrators as key stakeholders of New Space do not typically publish academic papers but rather prefer filing for patents to protect their intellectual property.
Having looked at 122 organizations that own 933 active patents and patent applications, the team identified ten topics, from remote sensing and image acquisition and launch systems to antenna systems and space platforms. 62% of the portfolio had to do with data related products and services, making data "the most valuable asset of the New Space ecosystem," the authors note.
"Our society is increasingly hungry for data, and for useful insights deriving from data. New Space ventures are contributing to this need by exploiting space infrastructure to generate, process and distribute a huge amount of data, and making available to end users a set of information possible to get only through space systems," Garzaniti notes.
An analysis of trends over time revealed sharp exponential growth from 2007 onward, making that year a tentative cutoff line for the start of the New Space era. The paper also describes the ecosystem of New Space companies, providing a useful overview of the markets and major players based on the existing academic literature.
"As a direct consequence of this work, we identified key topics in space systems development that represent significant opportunities for research and innovation in the short- and mid-term. For instance, we are now actively looking into the topic of active constellation management, and new paradigms for designing and operating satellite systems. From an innovation perspective, we are increasingly interested in looking at the implications and opportunities that arise from the increasing rate of consolidation of the space value chain through vertical integration," Nicola Garzaniti concludes.
INFORMATION:
Other organizations involved in this research include HSE University Graduate School of Business and the University of Novi Sad.
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology and business, is conducting research in breakthrough fields, and is promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https://www.skoltech.ru/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-22
In 2020, as many states of emergency were declared around the world during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic as there were in the entire previous decade. The influence of neighbouring countries on each other, weak democracies and poor pandemic preparedness are some of the explanations, according to research from the University of Gothenburg and Stockholm University.
A state of emergency is a situation in which a country's ordinary laws and rights are suspended and authorities are given increased powers. A state of emergency is declared by the government of a country, often as a result of war, civil unrest or natural disasters. The introduction of a curfew is ...
2021-06-22
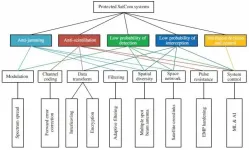
Protected Satellite Communications (SatComs) exhibit specific characteristics such as security, intelligence, anti-jamming, and nuclear disaster survivability. They constitute one of the key research topics in modern communications. Currently, the United States is using the latest Advanced Extremely High-Frequency (AEHF) system to provide protected communications. Other countries are also employing their own protected SatCom systems to meet future operational requirements. Furthermore, in the modern intelligent age, many intelligent-related technologies are introduced into the protected SatCom ...
2021-06-22
New York, NY (June 22, 2021) - A new class of drugs that inhibits a "master switch" involved in the vast majority of cases of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), a fatal subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, has been discovered by researchers at Mount Sinai.
In a study in Clinical Cancer Research published in June, the team reported that the drugs, known as small-molecule inhibitors of the SOX 11 oncogene, are toxic to MCL tumor development in human cells studied outside the body. If the effect is replicated in living patients, the discovery could lead to new therapies for a disease that is highly resistant to existing treatments.
"The SOX 11 protein, which is expressed in up to 90 percent of mantle cell lymphoma patients, is an attractive target for therapy," said senior author Samir Parekh, MD, ...
2021-06-22
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Scientists at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health have developed a universal vaccine that protected mice not just against COVID-19 but also other coronaviruses and triggered the immune system to fight off a dangerous variant.
While no one knows which virus may cause the next outbreak, coronaviruses remain a threat after causing the SARS outbreak in 2003 and the global COVID-19 pandemic.
To prevent a future coronavirus pandemic, UNC-Chapel Hill researchers designed the vaccine to provide protection from the current SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus and a group of coronaviruses known to make the jump from animals to humans.
The findings were published ...
2021-06-22
As many as 16.8 million Americans had undiagnosed SARS-CoV-2 infections - 5 times the rate of diagnosed infections - by the end of July of 2020, according to an analysis of antibodies from more than 8,000 previously undiagnosed adults collected during the pandemic's first wave. The authors calculated that almost 5% of the undiagnosed U.S. population harbored SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, with the highest positivity rates among African Americans, those under the age of 45, urban dwellers, and women. The results suggest a larger spread of COVID-19 in the U.S. than originally suspected in previous reports. SARS-CoV-2 can stealthily cause asymptomatic ...
2021-06-22
The rapid development of safe and efficacious vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 has offered hope that the global COVID-19 pandemic may soon be under control. However, vaccinations remain incomplete in many developed nations, and lag further still in the developing world. In a new Focus, Jonathan Sprent and Cecile King posit that vaccine hesitancy, motivated in part by fear of side effects documented in scientific journals and the popular media, could hold back the global population from reaching herd immunity. Seeking to reassure those with reservations, Sprent and King suggest that "it is highly likely ...
2021-06-22
Osaka, Japan - As far back as 1959, brewers at Guinness developed a system that fundamentally altered the texture of their draught beer. Now, researchers from Japan have solved the physics of Guinness' cascading flow, which will have widespread applications to technology in life and environmental sciences.
In a study recently published in Physical Review E, researchers from Osaka University have revealed why the nitrogen bubbles of Guinness draught beer flow similarly to a fluid.
The bubbles of many just-opened carbonated beverages simply move upwards, following Archimedes' principle. Much of the appeal of the draught from Guinness beer is that the bubbles sink and flow collectively, known as "bubble cascade." ...
2021-06-22
In Finland, every fifth mother was diagnosed with gestational diabetes in 2019. The condition increases the mother's risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, the most significant consequence of gestational diabetes is fetal macrosomia, or excessive growth of the fetus. Macrosomia increases birth injuries for both the child and the mother, causes fetal hypoxia, that is, a lack of oxygen in the fetus, and increases labour-related complications for the newborn.
A research group active at the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital demonstrated that the mother's gestational diabetes ...
2021-06-22
In a world-first, a Kobe University research group led by Associate Professor FUKAYAMA Hiroshi of the Graduate School of Agricultural Science has used rice to successfully illuminate the mechanism by which plants regulate the amount of starch produced via photosynthesis. This knowledge could contribute towards improving the quality and yield of agricultural crops.
These research results were published in the international scientific journal Plant, Cell & Environment on May 14, 2021.
Main Points
Plants convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic substances ...
2021-06-22
Without an audience, men run slower and women faster: The lack of spectators during the coronavirus pandemic appears to have had a noticeable effect on the performance of athletes at the 2020 Biathlon World Cup, a new study by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in Psychology of Sport and Exercise shows. According to the new analysis, women also performed better in complex tasks, such as shooting, when an audience was present while men did not.
Social facilitation theory states that a person's performance is impacted if other people watch them. The mere presence of an audience improves the performance of simple tasks, especially those that require stamina. "The studies have been relatively clear so far, but the results are more heterogeneous when it comes to more complex ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Patents help build a global map of new space industry