An overview of protected satellite communications in the intelligent age
2021-06-22
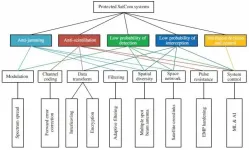
(Press-News.org) Protected Satellite Communications (SatComs) exhibit specific characteristics such as security, intelligence, anti-jamming, and nuclear disaster survivability. They constitute one of the key research topics in modern communications. Currently, the United States is using the latest Advanced Extremely High-Frequency (AEHF) system to provide protected communications. Other countries are also employing their own protected SatCom systems to meet future operational requirements. Furthermore, in the modern intelligent age, many intelligent-related technologies are introduced into the protected SatCom systems to provide more secure and efficient communication services.
Recently, a survey under the title "An overview of protected satellite communications in the intelligent age" is published in Science China Information Sciences (vol.64, no.6) by Changhong Wang, Zhongshan Zhang, Jiayi Wu, Chaofan Chen, and Fei Gao from Beijing Institute of Technology.
In this paper, a comprehensive overview of the protected SatCom systems is presented. The critical technologies used in the protected SatCom systems were investigated and compared. Based on the previous discussion, several practical application scenarios were fully elaborated. Finally, the authors discuss the remaining challenges and look forward to future research directions.
It is obvious that a protected SatCom system is one of the most significant elements in military communications, and it will be a hot topic both now and in the future.
INFORMATION:
This paper was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1836201).
More details can be referred to:
Wang C H, Zhang Z S, Wu J Y, et al. An overview of protected satellite communications in intelligent age. Sci China Inf Sci, 2021, 64(6): 161301.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11432-019-2928-9
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-22
New York, NY (June 22, 2021) - A new class of drugs that inhibits a "master switch" involved in the vast majority of cases of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), a fatal subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, has been discovered by researchers at Mount Sinai.
In a study in Clinical Cancer Research published in June, the team reported that the drugs, known as small-molecule inhibitors of the SOX 11 oncogene, are toxic to MCL tumor development in human cells studied outside the body. If the effect is replicated in living patients, the discovery could lead to new therapies for a disease that is highly resistant to existing treatments.
"The SOX 11 protein, which is expressed in up to 90 percent of mantle cell lymphoma patients, is an attractive target for therapy," said senior author Samir Parekh, MD, ...
2021-06-22
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Scientists at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health have developed a universal vaccine that protected mice not just against COVID-19 but also other coronaviruses and triggered the immune system to fight off a dangerous variant.
While no one knows which virus may cause the next outbreak, coronaviruses remain a threat after causing the SARS outbreak in 2003 and the global COVID-19 pandemic.
To prevent a future coronavirus pandemic, UNC-Chapel Hill researchers designed the vaccine to provide protection from the current SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus and a group of coronaviruses known to make the jump from animals to humans.
The findings were published ...
2021-06-22
As many as 16.8 million Americans had undiagnosed SARS-CoV-2 infections - 5 times the rate of diagnosed infections - by the end of July of 2020, according to an analysis of antibodies from more than 8,000 previously undiagnosed adults collected during the pandemic's first wave. The authors calculated that almost 5% of the undiagnosed U.S. population harbored SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, with the highest positivity rates among African Americans, those under the age of 45, urban dwellers, and women. The results suggest a larger spread of COVID-19 in the U.S. than originally suspected in previous reports. SARS-CoV-2 can stealthily cause asymptomatic ...
2021-06-22
The rapid development of safe and efficacious vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 has offered hope that the global COVID-19 pandemic may soon be under control. However, vaccinations remain incomplete in many developed nations, and lag further still in the developing world. In a new Focus, Jonathan Sprent and Cecile King posit that vaccine hesitancy, motivated in part by fear of side effects documented in scientific journals and the popular media, could hold back the global population from reaching herd immunity. Seeking to reassure those with reservations, Sprent and King suggest that "it is highly likely ...
2021-06-22
Osaka, Japan - As far back as 1959, brewers at Guinness developed a system that fundamentally altered the texture of their draught beer. Now, researchers from Japan have solved the physics of Guinness' cascading flow, which will have widespread applications to technology in life and environmental sciences.
In a study recently published in Physical Review E, researchers from Osaka University have revealed why the nitrogen bubbles of Guinness draught beer flow similarly to a fluid.
The bubbles of many just-opened carbonated beverages simply move upwards, following Archimedes' principle. Much of the appeal of the draught from Guinness beer is that the bubbles sink and flow collectively, known as "bubble cascade." ...
2021-06-22
In Finland, every fifth mother was diagnosed with gestational diabetes in 2019. The condition increases the mother's risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, the most significant consequence of gestational diabetes is fetal macrosomia, or excessive growth of the fetus. Macrosomia increases birth injuries for both the child and the mother, causes fetal hypoxia, that is, a lack of oxygen in the fetus, and increases labour-related complications for the newborn.
A research group active at the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital demonstrated that the mother's gestational diabetes ...
2021-06-22
In a world-first, a Kobe University research group led by Associate Professor FUKAYAMA Hiroshi of the Graduate School of Agricultural Science has used rice to successfully illuminate the mechanism by which plants regulate the amount of starch produced via photosynthesis. This knowledge could contribute towards improving the quality and yield of agricultural crops.
These research results were published in the international scientific journal Plant, Cell & Environment on May 14, 2021.
Main Points
Plants convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic substances ...
2021-06-22
Without an audience, men run slower and women faster: The lack of spectators during the coronavirus pandemic appears to have had a noticeable effect on the performance of athletes at the 2020 Biathlon World Cup, a new study by Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in Psychology of Sport and Exercise shows. According to the new analysis, women also performed better in complex tasks, such as shooting, when an audience was present while men did not.
Social facilitation theory states that a person's performance is impacted if other people watch them. The mere presence of an audience improves the performance of simple tasks, especially those that require stamina. "The studies have been relatively clear so far, but the results are more heterogeneous when it comes to more complex ...
2021-06-22
Increased risk of cancer due to a genetic predisposition in first- and second-degree relatives is long-established but has previously only been studied in white or European populations.
Now, a new study published in eLife is the first to demonstrate that the inherited risk of early-onset cancer is significantly higher among Latino and African American families for solid tumors, and Asian/Pacific Islander families for blood-based cancers, compared to non-Latino white families in California.
"Cancer clustering within families, meaning the devastating diagnosis of more than one early-onset cancer within the same family, usually points ...
2021-06-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University research has identified the oldest known specimen of a fungus parasitizing an ant, and the fossil also represents a new fungal genus and species.
"It's a mushroom growing out of a carpenter ant," said OSU's George Poinar Jr., an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn about the biology and ecology of the distant past.
A mushroom is the reproductive structure of many fungi, including the ones you find growing in your yard, and Poinar and a collaborator in France named their discovery Allocordyceps baltica. They found the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An overview of protected satellite communications in the intelligent age