(Press-News.org) As the saying goes, an apple a day keeps the doctor away. But what's the key to growing a quality apple?
Apple trees need access to important nutrients, which come from the soil. However, soil is quite different from orchard to orchard.
Gregory Peck studies how sustainable orchard practices can improve the availability of nutrients. The research was recently shared in Soil Science Society of America Journal, a publication of the Soil Science Society of America.
Farmers are becoming more aware of the environmental impacts of different orchard management practices.
"Apple growers are interested in developing more sustainable nutrient management plans," explains Peck. "They are asking for more information to improve the soil health on their farms."
A healthy soil depends on many factors. One of those factors is the microbial community living in the soil. The community is made up of bacteria, nematodes, and fungi. Some of these microbes convert nutrients in the soil into forms that apple trees can use.
In the soil, microbes and plant roots interact in beneficial partnerships. Plants, like apple trees, release fluids from their roots into the soil. These fluids serve as a food source for the microbial community. In return, the microbes can help the apple trees.
"Bacteria serve many functions in an apple orchard soil," says Peck. "They recycle nutrients, promote plant growth, and even alter plant metabolisms."
In this study, the team applied composts - such as chicken litter and yard waste - to apple orchards.
Researchers found that adding compost increased the number of soil bacteria associated with recycling nutrients. The compost provides additional food for the bacteria to help them thrive.
This larger microbial community means more nutrients are available to the apple trees.
By applying compost, farmers could reduce the amount of fertilizer needed to provide nutrients for apple trees. This could help their pocketbooks and the environment.
Some fertilizers come from non-renewable sources. Adding in compost to a farm's nutrient management plan reduces the dependence on those sources. It also provides a sustainable use for materials otherwise considered to be waste.
On a practical level, this research shows that farmers can successfully integrate compost with quicker release fertilizer sources.
"Although sustainable apple production is not defined by a single practice, we think this research contributes to the long-term goal of increasing farm sustainability," says Peck.
In the future, the team hopes to replicate this study in different regions with different soil characteristics. They would also like to take a deeper look into the roles of fungi in the microbial community of orchard soils.
"We can produce great apples, and apple orchard farmers can supply a huge population with delicious, nutritious food," Peck adds.
INFORMATION:
Gregory Peck is a researcher at Cornell University. This work was supported by Cornell University - College of Agriculture and Life Science, the Virginia Agricultural Council, the Virginia Apple Research Program, the Virginia Agricultural Experiment Station, and Virginia Tech - Department of Horticulture.
A new UC Riverside study finds geckos are fierce hunters whether or not their tails are attached to their bodies.
Geckos and other lizards can distract predators by quickly dropping their tails. The tail vertebrae are perforated, making it easier to disconnect them without any formation of scar tissue or loss of blood. Though this ability can keep lizards from being eaten, the maneuver is performed at a cost.
"Other studies have documented the negative effects of tail loss on lizards' ability to run, jump, mate, and reproduce," said UCR biologist Marina Vollin, lead author of the ...
UJ researchers take a novel step to change hydrogenation into a safe, low energy process. They use a very stable three phase emulsion to transform a toxic waste product into valuable feedstock. The process does not need flammable, compressed hydrogen gas.
The emulsion catalysis hydrogenates nitrobenzene efficiently at room temperature to output aniline. Aniline is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry. The bi-metallic hydrogenation catalyst is fully recovered afterwards.
Without hydrogenation, it would not be possible to manufacture many of ...
Cities must become fully car-free in order to be liveable in the future, according to the UCL experts behind a new modelling report looking at urban car use.
The experts have called for a shift in collective behaviour to reduce the number of private cars in cities. Globally, the number of cars produced is increasing faster than the population; 80m cars were produced in 2019, while the population increased by 78m.
The researchers said future city planning must include a focus on reducing dependence on cars, promoting fewer and shorter trips and encouraging walking and cycling as primary modes of local transport. Public transport should be encouraged for longer journeys, the researchers argued, and cars should only be used for emergencies or special occasions. ...
If you listen to songbirds, you will recognize repeated melodies or phrases. Each phrase is made up of distinct sounds, strung together. A study from researchers at McGill University has found that the song phrases of many songbird species follow patterns that are similar to those used in human speech. At least in some respects.
The songbirds the researchers studied, like humans---no matter what language they speak---tend to use shorter elements (whether these are words or sounds) when they are putting together longer phrases. Linguists speculate that this pattern, known as Menzerath's Law, may make communication more efficient by making things easier to understand or say.
But the McGill team suggest ...
New York, NY--June 22, 2021--Because corporations and governments rely on computers and the internet to run everything from the electric grid, healthcare, and water systems, computer security is extremely important to all of us. It is increasingly being breached: Numerous security hacks just this past month include the Colonial Pipeline security breach and the JBS Foods ransomware attacks where hackers took over the organization's computer systems and demanded payment to unlock and release it back to the owners. The White House is strongly urging companies to take ransomware threats seriously and update their systems to protect themselves. Yet these attacks continue to threaten all of us on an almost daily basis.
Columbia Engineering researchers ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Communities surrounding the Salton Sea, the inland body of water straddling California's Riverside and Imperial counties, show high rates of asthma due, possibly, to high aerosol dust levels resulting from the sea shrinking over time.
Scientists suspect, however, the Salton Sea plays an additional role in pulmonary health.
A University of California, Riverside study performed on mice has found Salton Sea aerosol turns on nonallergic inflammation genes and may also promote lung inflammation. For comparison, aerosolized fungal allergen (Alternaria) -- a common household fungal allergen -- produces an allergic inflammation in the lungs of mice.
"Our ...
A group of health care leaders, including a University of Massachusetts Amherst nurse innovator, has published a national call to action to prevent non-ventilator-associated, hospital-acquired pneumonia (NVHAP).
This call to action was developed by a joint task force of key national healthcare stakeholders, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Veterans Health Administration, The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations, the American Dental Association, the Patient Safety Movement Foundation, Oral Health Nursing Education and Practice, Teaching Oral-Systemic Health and academia.
In a commentary paper published in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology (ICHE), the joint ...
In a first-of-its-kind study in the world conducted at Tel Aviv University, researchers found that water generated from the air in the heart of an urban area, the city of Tel Aviv, complied with all of the strict drinking water standards set both by the State of Israel and by the World Health Organization. The researchers examined the quality of the water produced from the water vapor in the urban atmosphere, which is characterized by industry and massive construction, and found that it was suitable for drinking. The test was performed using a dedicated facility of the Israeli company Watergen, which partnered in the study.
The study was conducted by a team of experts from the hydrochemistry laboratory at the Porter ...
As you drive down the highway, you may notice an increasing number of hybrid and electric vehicles. Alternative energy automobiles are on the rise contributing to the global effort to reduce carbon emissions. As we move together down this road, researchers are looking to determine new solutions to this ongoing problem.
Dr. Muzammil Arshad, instructional assistant professor for the Department of Multidisciplinary Engineering at Texas A&M University, and a team of multidisciplinary student researchers conducted a study to analyze the performance of hydrogen-enriched fuel on spark engine performance and efficiency. This solution could make significant contributions to helping automobiles ...
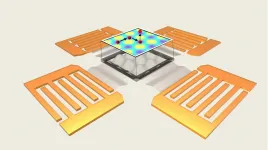
Engineers at Duke University have devised a system for manipulating particles approaching the miniscule 2.5 nanometer diameter of DNA using sound-induced electric fields. Dubbed "acoustoelectronic nanotweezers," the approach provides a label-free, dynamically controllable method of moving and trapping nanoparticles over a large area. The technology holds promise for applications in the fields ranging from condensed matter physics to biomedicine.
The research appears online on June 22 in Nature Communications.
Precisely controlling nanoparticles is a crucial ...