INFORMATION:
Mongooses solve inequality problem
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) A fair society has evolved in banded mongooses because parents don't know which pups are their own, new research shows.
Mothers in banded mongoose groups all give birth on the same night, creating a "veil of ignorance" over parentage in their communal crèche of pups.
In the new study, led by the universities of Exeter and Roehampton, half of the pregnant mothers in wild mongoose groups were regularly given extra food, leading to increased inequality in the birth weight of pups.
But after giving birth, well-fed mothers gave extra care to the smaller pups born to the unfed mothers - rather than their own pups - and the pup size differences quickly disappeared.
Dr Harry Marshall, of the Department of Life Sciences at the University of Roehampton, said: "In most of the natural world, parents favour their own young.
"However, in banded mongooses, the evolution of remarkable birth synchrony has led to the unusual situation that mothers don't know which pups are their own, and therefore cannot choose to give them extra care.
"Our study shows that this ignorance leads to a fairer allocation of resources - in effect, a fairer society."
The study examined seven groups of banded mongooses in Uganda. Half of the pregnant females in each group were given 50g of cooked egg each day, while the other half were not given extra food.
Inequality at birth (measured by weight) was wider in breeding periods when food was provided than in periods where no extra food was given.
Professor Michael Cant, of the University of Exeter said: "We predicted that a 'veil of ignorance' would cause females to focus their care on the pups most in need - and this is what we found.
"Those most able to help offer it to the most needy, and in doing so minimise the risk that their own offspring will face a disadvantage.
"This redistributive form of care 'levelled up' initial size disparities, and equalised the chances of pups surviving to adulthood.
"Our results suggest that the veil of ignorance, a classic philosophical idea to achieve fairness in human societies, also applies in this non-human society."
The research team included Professor Rufus Johnstone, from the University of Cambridge.
Funding for the study came from the European Research Council and the Natural Environment Research Council.
The paper, published in the journal Nature Communications, is entitled: "A veil of ignorance can promote fairness in a mammal society."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change makes arctic ozone loss worse
2021-06-23
Results of the MOSAiC expedition show: the expected recovery of the ozone layer may fail to happen anytime soon, if global warming is not slowed down
In spring 2020, the MOSAiC expedition documented an unparalleled loss of ozone in the Arctic stratosphere. As an evaluation of meteorological data and model-based simulations by the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) now indicates, ozone depletion in the Arctic polar vortex could intensify by the end of the century unless global greenhouse gases are rapidly and systematically reduced. In the future, this could also mean more UV radiation exposure in Europe, North America and Asia when parts ...
Low-cost method for finding new coronavirus variants
2021-06-23
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed a technology for cost-effective surveillance of the global spread of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. The technique is presented in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Since the onset of the pandemic, thousands of viral genomes have been sequenced to reconstruct the evolution and global spread of the coronavirus. This is important for the identification of particularly concerning variants that are more contagious, pathogenic, or resistant to the existing vaccines.
For global surveillance of the SARS-CoV-2 genome, it is crucial to sequence and analyse many samples in a cost-effective way. Therefore, researchers in the Bienko-Crosetto laboratory at Karolinska Institutet and Science for Life Laboratory (SciLifeLab) ...
Cellular signatures of kidney tumours discovered
2021-06-23
The origins of seven types of kidney cancer, including several rare subtypes, have been identified by researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH), the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology and Oncode Institute. The findings confirm that these cancers have their origin in specific forms of developmental cells present in the maturing fetus.
The study, published today (23 June) in Nature Communications, used computational methods to analyse existing datasets and pinpoint the 'cellular signals' given off by different cancers as they emerge. This method holds promise as a tool for diagnosing patients with rare cancers - in the study, one patient's cryptic kidney cancer was identified as ...
Rising greenhouse gases pose continued threat to Arctic ozone layer
2021-06-23
There is a race going on high in the atmosphere above the Arctic, and the ozone layer that protects Earth from damaging ultraviolet (UV) radiation will lose the race if greenhouse gas emissions aren't reduced quickly enough.
A new study from an international team of scientists, including University of Maryland Professor Ross Salawitch, shows that extremely low winter temperatures high in the atmosphere over the arctic are becoming more frequent and more extreme because of climate patterns associated with global warming. The study also shows that those extreme low temperatures are causing reactions among chemicals humans pumped into the air decades ago, leading to greater ozone losses.
The new findings call into question ...
Recycling of the eye's light sensors is faulty in progressive blindness of older adults
2021-06-23
With the National Eye Institute reporting that about 11 million older adults in the U.S. endure a condition that leads to progressive blindness, known as age-related macular degeneration, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers are starting to understand what goes wrong in the disease, in order to develop new therapies to treat it.
Using human tissue and mice in their new study, published on June 23 in
Nature Communications, they showed that the process which removes the eye's old, damaged light sensors is disrupted in macular degeneration.
Although more than 50 genes have been ...
Using virtual populations for clinical trials
2021-06-23
Digital trial replicated and expanded upon results of traditional clinical trials
Developing virtual patient populations can speed up trials process
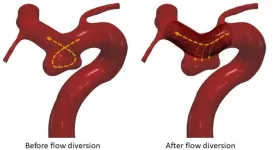
A study involving virtual rather than real patients was as effective as traditional clinical trials in evaluating a medical device used to treat brain aneurysms, according to new research.
The findings are proof of concept for what are called in-silico trials, where instead of recruiting people to a real-life clinical trial, researchers build digital simulations of patient groups, loosely akin to the way virtual populations are built in The Sims ...
How does the one-humped Arabian camel survive without drinking?
2021-06-23
Research led by scientists at the University of Bristol has shed new light on how the kidneys of the one-humped Arabian camel play an important role in helping it to cope with extremes.
In a new paper published today in the journal Communications Biology, they have studied the response of the camel's kidneys to dehydration and rapid rehydration stresses.
Camelus dromedarius is the most important livestock animal in the arid and semi-arid regions of North and East Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Iran, and continues to provide basic needs to millions of people.
Thought to have been domesticated 3,000 to 6,000 years ago in the Arabian Peninsula, the camel has been used ...
Review shows minimal, high-quality evidence dietary supplements lead to weight loss
2021-06-23
SILVER SPRING, Md.-- Although Americans spend billions on them, published research shows a lack of strong evidence that dietary supplements and alternative therapies help adults lose weight, according to a new study published in Obesity, the flagship journal of The Obesity Society (TOS).
There are hundreds of weight-loss supplements like green tea extract, chitosan, guar gum and conjugated linoleic acid, and an estimated 34% of Americans who are trying to lose weight have used one.
For the study, researchers completed a comprehensive review of 315 existing clinical trials of weight loss supplements and therapies, and most of the studies showed the supplements did not produce weight loss among users.
"Our findings are important ...
Universal health care benefited colon cancer survival
2021-06-23
PHILADELPHIA - Patients with colon cancer enrolled in the U.S. military's universal health care system experienced improved survival compared with patients in the general population, according to results published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Colorectal cancer has the third highest death rate out of all cancers in the U.S. Therefore, it is highly important to improve survival of patients with colon cancer," said study author Craig D. Shriver, MD, FACS, FSSO, retired U.S. Army colonel and professor and director of the Murtha Cancer Center Research ...
Research may help identify more dangerous strains of the virus that causes COVID-19
2021-06-23
Viral mutations during the COVID-19 pandemic could cause the SARS-CoV-2 virus to become more dangerous. A new study published in END ...