Study explores how readers at partisan news sites respond to challenging news events
2021-06-23
(Press-News.org) Researchers from Bentley University have been exploring how readers at partisan news sites respond to news events that challenge their worldview.
In a forthcoming paper in the journal ACM Transactions on Social Computing, they report results of a study that examines reader comments on stories surrounding the 2017 Roy Moore Alabama senate race at two partisan news sites: a left-leaning news site (Daily Kos) and a right-leaning news site (Breitbart). They consider the alleged sexual misconduct of Mr. Moore as a challenging news event for the right-leaning readers; and the subsequent nomination of Mr. Moore as the Republican candidate as a challenging news event for the left-leaning readers.
Their analysis identifies the obstacles that readers face as they try to make sense of news events they find challenging. The comments they contribute show that some readers question the motives of different actors in the story, others provide erroneous arguments to diffuse the story, yet others engage in personal attacks. The researchers describe these as breakdowns that prevent a group from acknowledging the new event.
The study adds to our understanding of political discourse and polarization. "We are still trying to understand the causes of disinformation and political echo chambers. Our study provides a window into how deliberation can break down in closed groups," says Dr. Sandeep Purao, one of the lead researchers.
"The processes underlying social representations are difficult to examine. The reader comments allow us this opportunity," says Dr. David Murungi, a professor who also participated in the study. "The reader comments tend to be complex. Although we can judge them to be problematic, it is often hard to name what the problems are," says Dr. David Yates, another professor who participated in the study.
The results of the study are being published in the journal ACM Transactions on Social Computing. The team continues to empirically investigate the problem of disinformation and political discourse, and is moving to explore potential solutions to combat misinformation.
INFORMATION:
Purao, S., Murungi, D., Yates, D. 2021. Deliberative Breakdowns in the Social Representation Process: Evidence from Reader Comments in Partisan News Sites. ACM Transactions on Social Computing. https://doi.org/10.1145/3450143.
http://purao.us/paper-accepted-at-acm-transactions-on-social-computing/
About Bentley University
Bentley University is more than just one of the nation's top business schools. It is a lifelong-learning community that creates successful leaders who make business a force for positive change. With a combination of business and the arts and sciences and a flexible, personalized approach to education, Bentley provides students with critical thinking and practical skills that prepare them to lead successful, rewarding careers. Founded in 1917, the university enrolls 4,200 undergraduate and 1,000 graduate and PhD students and is set on 163 acres in Waltham, Massachusetts, 10 miles west of Boston. For more information, visit http://www.bentley.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-23
NEW YORK CITY, June 23, 2021 -- From amoebas to zebras, all living things evolve. They change over time as pressures from the environment cause individuals with certain traits to become more common in a population while those with other traits become less common.
Cancer is no different. Within a growing tumor, cancer cells with the best ability to compete for resources and withstand environmental stressors will come to dominate in frequency. It's "survival of the fittest" on a microscopic scale.
But fitness -- how well suited any particular individual is to its environment -- isn't set in stone; it can change when the environment changes. The cancer cells that might do best in an environment saturated ...
2021-06-23
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--June 23, 2021--A healthy heart is a pliable, ever-moving organ. But under stress--from injury, cardiovascular disease, or aging--the heart thickens and stiffens in a process known as fibrosis, which involves diffuse scar-like tissue. Slowing or stopping fibrosis to treat and prevent heart failure has long been a goal of cardiologists.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered a master switch for fibrosis in the heart. When the heart is under stress, they found, the gene MEOX1 is turned on in cells called fibroblasts, spurring fibrosis. Their new study, published in the journal Nature, suggests that blocking ...
2021-06-23
HOUSTON - (June 23, 2021) - Bone cancer is hard to treat and prone to metastasis. Research teams at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have a new strategy to attack it.
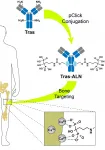
Chemist Han Xiao at Rice and biologist Xiang Zhang at Baylor and their labs have developed an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.
Their open-access study, which appears in Science Advances, shows how Xiao's pClick technology can be used to link bone-targeting antibodies and therapeutic molecules.
In experiments, they used pClick to couple a molecule used to treat osteoporosis, alendronate, with the HER2-targeting antibody trastuzumab used to treat breast cancer and found it significantly enhanced the concentration ...
2021-06-23
Most survivors of squamous cell head and neck cancers report that their sense of taste is dulled, changed or lost during radiation treatment, causing them to lose interest in eating and diminishing their quality of life.
In a study of taste and smell dysfunction with 40 cancer survivors, scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign found that the tips of these individuals' tongues were significantly less sensitive to bitter, salty or sweet tastes than peers in the control group who had never been diagnosed with cancer.
In a paper published in the journal Chemical Senses, the U. of I. team said this diminished taste sensitivity suggested that the taste ...
2021-06-23
In New England, constraints in the supply of natural gas have led to nearly a quarter of all unscheduled power plant outages. In a new study, researchers used data from power plant failures in the 2010s to develop a supply curve of the costs required for generators to mitigate fuel shortages in the region. The study found that storing both oil and gas on-site could reduce dependence by power plants on gas grids in geographic areas with few pipelines.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), The Pennsylvania State University, and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation. It is published in The Electricity Journal.
"Gas ...
2021-06-23
Toronto - Last winter, Goldman Sachs reported it was working to make things better after a group of junior analysts revolted against 100-hour work weeks.
That's a smart thing to do, suggests a new study from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management. Drawing from more than 6,000 employee reviews of their workplaces and data on their firms' forecasting accuracy, the research shows that making improvements to hardworking analysts' work-life balance produces dividends for the company and for the analysts' careers.
"There is a lot of anecdotal evidence, but here we provide large-scale evidence that supports the recent push to grant these employees at least some reprieve from the extremes of their jobs," said Ole-Kristian Hope, who is the Deloitte Professor of Accounting ...
2021-06-23
The Gerontological Society of America's highly cited, peer-reviewed journals are continuing to publish scientific articles on COVID-19. The following were published between May 4 and June 14; all are free to access: Cardiometabolic therapy and mortality in very old patients with diabetes hospitalized due to COVID-19: Research article in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences by Jose Manuel Ramos-Rincón, MD, PhD, Luis M. Pérez-Belmonte, MD, PhD, Francisco Javier Carrasco-Sánchez, MD, PhD, Sergio Jansen-Chaparro, MD, PhD, Mercedes De-Sousa-Baena, MD, José Bueno-Fonseca, MD, ...
2021-06-23
Best known for its presence in house cats and a tendency to infect and alter the behaviors of rodents and humans, the parasite Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is also associated with bold behavior among wild hyena cubs and risk of death during interactions with lions, finds new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
The findings, published this week in Nature Communications, reinforce previous research which has found the parasite can prompt profound behavioral changes in its hosts, and potentially in the 2 billion people worldwide estimated to be infected by it. While T. gondii has been well studied in laboratory settings with humans and wild-caught ...
2021-06-23
Researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the University of California in San Francisco were able to show for the first time that a very low calorie diet significantly alters the composition of the microbiota present in the human gut. In a current Nature* publication, the researchers report that dieting results in an increase of specific bacteria - notably Clostridioides difficile, which is associated with antibiotic-induced diarrhea and colitis. These bacteria apparently affect the body's energy balance by exerting an influence on the absorption of nutrients ...
2021-06-23
WHAT:
National Institutes of Health scientists and their collaborators have identified an internal communication network in mammals that may regulate tissue repair and inflammation, providing new insights on how diseases such as obesity and inflammatory skin disorders develop. The new research is published in Cell.
The billions of organisms living on body surfaces such as the skin of mammals--collectively called microbiota--communicate with each other and the host immune system in a sophisticated network. According to the study, viruses integrated in the host genome, remnants of previous infections called endogenous retroviruses, can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study explores how readers at partisan news sites respond to challenging news events