Water vole genome will help boost conservation of one of UK's most endangered mammals
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) A new tool to help conserve one of the UK's most threatened mammals has been released today, with the publication of the first high-quality reference genome for the European water vole. The genome was generated by scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, in collaboration with animal conservation charity the Wildwood Trust, as part of the Darwin Tree of Life Project.
The genome, published today (24 June 2021) through Wellcome Open Research, is openly available as a reference for researchers seeking to assess water vole population genetics, better understand how the species has evolved and to manage reintroduction efforts.
The European water vole (Arvicola amphibius) is a small semi-aquatic mammal that lives on the banks of freshwater habitats and in wetlands. The species is native to Europe, west Asia, Russia and Kazakhstan. While the water vole's conservation status is 'least concern' worldwide*, populations in the United Kingdom have declined to such an extent that the species is considered nationally endangered. Habitat loss and predation by the American mink, an invasive alien species, have reduced the UK population from 7.3 million in 1990 to an estimated 132,000 in 2018**.
Water voles gained full legal protection in the UK in 2008. There have been a number of conservation projects in the UK aimed at supporting water vole populations, including efforts at habitat restoration and to control the population of American mink. There are also efforts to reintroduce the water vole in a number of restored urban and wild habitats, as well as mitigate the impact of new development***.
European water voles returned to Britain from ice-free refuges in Iberia and Eastern Europe after the last ice age, with these two clades contributing to genetic diversity in UK populations. This diversity may be apparent in certain traits, such as the black fur of Scottish water voles, which is distinct from those in England that tend to have brown fur. But the full wealth of genetic diversity cannot be estimated by appearance alone. It is also unknown how much diversity has been lost as a result of the recent population crash.
Hazel Ryan, Senior Conservation Officer at the Wildwood Trust, said: "Water voles are amazing animals and we don't fully understand what ecosystems lose without them. They are industrious habitat managers, almost like miniature beavers in the way they fell stems, make burrows and alter the landscape. We suspect that some water vole populations have become inbred in recent decades owing to shrinking numbers and the fragmentation of populations through habitat loss. The reference genome offers us a way to better understand genetic diversity for reintroductions and consider mixing individuals to ensure populations have the best chance to thrive."
To sequence the European water vole reference genome, a blood sample was taken from a live male A. amphibius individual that was part of the captive breeding population of the Wildwood Trust in Kent, UK. DNA was extracted from this sample and sequenced by scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute on Pacific Biosciences SEQUEL I and Illumina HiSeq X instruments.
Professor Rob Ogden, Director of Conservation Science at the University of Edinburgh, said: "Understanding the genetic diversity and structure of water vole populations is an important aspect of their conservation in the UK, and is central to international guidelines on the movement of wildlife for conservation management. The release of the water vole genome provides a comprehensive set of genetic tools to support the future sustainability of the species in the UK."
The water vole genome is published as part of the Darwin Tree of Life Project, which will see partner organisations sequence and assemble the genomes of 70,000 animal, plant, fungal and protist species across Britain and Ireland.
Professor Mark Blaxter, Programme Lead for the Darwin Tree of Life project at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: "The European water vole is a prime example of a British species whose genetic diversity we're in danger of losing before we've had chance to fully record it. This high-quality Arvicola amphibius reference genome will allow us to do that, as well as support ongoing conservation efforts to preserve existing populations and reintroduce new ones in a way that ensures these populations are genetically robust."
INFORMATION:
Contact details:
Dr Matthew Midgley
Press Office
Wellcome Sanger Institute
Cambridge, CB10 1SA
Phone: 01223 494856
Email: press.office@sanger.ac.uk
Notes to Editors:
* IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
** Population estimate by Natural England
*** For more information, visit the Wildwood Trust website
Publication:
Angus I. Carpenter, Michelle Smith and Craig Corton. (2021). The genome sequence of the European water vole, Arvicola amphibius Linnaeus 1758. Wellcome Open Research. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16753.1
Funding:
The Darwin Tree of Life Project is funded by Wellcome.
Selected websites:
About Wildwood Trust
Wildwood Trust opened in 1999 as a centre of excellence for the conservation of British wildlife, and was established as a registered charity in 2002. Wildwood is Kent's best British wildlife park. Home to over 200 native animals, past and present and set in 40 acres of beautiful ancient woodland where visitors can see bears, wolves, bison, deer, owls, foxes, red squirrels, wild boar, lynx, wild horses, badgers and beavers plus many more.
As one of the leading British animal conservation charities in the UK, Wildwood Trust is dedicated to saving Britain's most threatened wildlife. Wildwood Trust has taken part in many ground-breaking conservation programmes to date, which include, saving the water vole, using wild horses to help restore Kent's most precious nature reserves, bringing the extinct European beaver back to Britain and returning the hazel dormouse & red squirrel to areas where they have been made extinct.
The Wellcome Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Sanger Institute is a world leading genomics research centre. We undertake large-scale research that forms the foundations of knowledge in biology and medicine. We are open and collaborative; our data, results, tools and technologies are shared across the globe to advance science. Our ambition is vast - we take on projects that are not possible anywhere else. We use the power of genome sequencing to understand and harness the information in DNA. Funded by Wellcome, we have the freedom and support to push the boundaries of genomics. Our findings are used to improve health and to understand life on Earth. Find out more at http://www.sanger.ac.uk or follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and on our Blog.
About Wellcome
Wellcome supports science to solve the urgent health challenges facing everyone. We support discovery research into life, health and wellbeing, and we're taking on three worldwide health challenges: mental health, global heating and infectious diseases. https://wellcome.org/
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-24
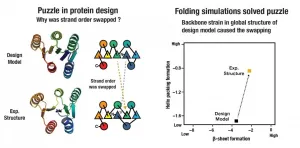
A team from Japan and the United States has identified the design principles for creating large "ideal" proteins from scratch, paving the way for the design of proteins with new biochemical functions.
Their results appear June 24, 2021, in Nature Communications.
The team had previously developed principles to design small versions of what they call "ideal proteins," which are structures without internal energetic frustration.
Such proteins are typically designed with a molecular feature called beta strands, which serve a key structural role for the molecules. In ...
2021-06-24
Our planet's strongest ocean current, which circulates around Antarctica, plays a major role in determining the transport of heat, salt and nutrients in the ocean. An international research team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute has now evaluated sediment samples from the Drake Passage. Their findings: during the last interglacial period, the water flowed more rapidly than it does today. This could be a blueprint for the future and have global consequences. For example, the Southern Ocean's capacity to absorb CO2 could decrease, which would in turn intensify climate change. The study has now been published in the journal Nature Communications.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is the world's strongest ocean ...
2021-06-24
Indonesia's volcanoes are among the world's most dangerous. Why? Through chemical analyses of tiny minerals in lava from Bali and Java, researchers from Uppsala University and elsewhere have found new clues. They now understand better how the Earth's mantle is composed in that particular region and how the magma changes before an eruption. The study is published in Nature Communications.
Frances Deegan, the study's first author and a researcher at Uppsala University's Department of Earth Sciences, summarises the findings.
"Magma is formed in the mantle, and the composition of the mantle under Indonesia used to be only partly known. ...
2021-06-24
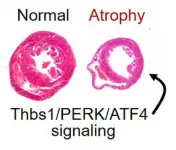
In many situations, heart muscle cells do not respond to external stresses in the same ways that skeletal muscle cells do. But under some conditions, heart and skeletal muscles can both waste away at fatally rapid rates, according to a new study led by experts at Cincinnati Children's.
The new findings, based on studies of mouse models, represent an important milestone in a long effort to prevent or even reverse cardiac atrophy, which can lead to fatal heart failure when the body loses large amounts of weight or experiences extended periods of weightlessness in space. Detailed findings were published online June 24, 2021, in Nature Communications.
"NASA is very interested in cardiac atrophy," says Jeffery Molkentin, PhD, Co-Director ...
2021-06-24
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO
TORONTO, ON - A new study from researchers at the University of Toronto found that 63% of Canadians with migraine headaches are able to flourish, despite the painful condition.
"This research provides a very hopeful message for individuals struggling with migraines, their families and health professionals," says lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, who spent the last decade publishing on negative mental health outcomes associated with migraines, including suicide attempts, anxiety disorders and depression. "The findings of our study have contributed to a major paradigm shift for me. There are important lessons to be learned from those who are flourishing."
A migraine headache, which afflicts ...
2021-06-24
A recent study finds states that exhibit higher levels of systemic racism also have pronounced racial disparities regarding access to health care. In short, the more racist a state was, the better access white people had - and the worse access Black people had.
"This study highlights the extent to which health care inequities are intertwined with other social inequities, such as employment and education," says Vanessa Volpe, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "This helps explain why health inequities are so intractable. Tackling health care inequities will require us to address broader social systems that significantly benefit white people ...
2021-06-24
"Red flag" gun laws--which allow law enforcement to temporarily remove firearms from a person at risk of harming themselves or others--are gaining attention at the state and federal levels, but are under scrutiny by legislators who deem them unconstitutional. A new analysis by legal scholars at NYU School of Global Public Health describes the state-by-state landscape for red flag legislation and how it may be an effective tool to reduce gun violence, while simultaneously protecting individuals' constitutional rights.
Gun violence is a significant public health problem in the U.S., with more than 38,000 people killed by firearms each year. Following several mass shootings this spring, President Biden urged ...
2021-06-24
WHO Frank A. J. L. Scheer, PhD, MSc, Neuroscientist and Marta Garaulet, PhD, Visiting Scientist, both of the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders, Departments of Medicine and Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital. Drs. Scheer and Garaulet are co-corresponding authors of a new paper published in The FASEB Journal.
WHAT Eating milk chocolate every day may sound like a recipe for weight gain, but a new study of postmenopausal women has found that eating a concentrated amount of chocolate during a narrow window of time in the morning may help the body burn fat and decrease blood sugar levels.
To find out about the effects of eating milk chocolate at different times of day, researchers from the Brigham collaborated ...
2021-06-24
Philadelphia, June 24, 2021 - Women with depression and other mood disorders are generally advised to continue taking antidepressant medications during pregnancy. The drugs are widely considered safe, but the effect of these medications on the unborn fetus has remained a topic of some concern. Now, researchers have found that maternal psychiatric conditions - but not the use of serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) - increased the risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and developmental delay (DD) in offspring.
The study appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
Previous studies had found links between SSRI use and ASD in offspring, and ASD is associated with disrupted serotonergic pathways. But the question of whether ...
2021-06-24
With age, a diet lacking in the essential amino acid tryptophan -- which has a key role in our mood, energy level and immune response -- makes the gut microbiome less protective and increases inflammation body-wide, investigators report.
In a normally reciprocal relationship that appears to go awry with age, sufficient tryptophan, which we consume in foods like milk, turkey, chicken and oats, helps keep our microbiota healthy.
A healthy microbiota in turn helps ensure that tryptophan mainly results in good things for us like producing the neurotransmitter serotonin, which reduces depression risk, and melatonin, which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Water vole genome will help boost conservation of one of UK's most endangered mammals