Updated analysis of US COVID-19 deaths shows drops, disparities in average lifespans
In the US, COVID-19 reduced overall life expectancy by over 1.3 years, with the effects on Black and Latino populations 2 to 3 times those for the white population
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) An updated analysis of American COVID-19 deaths throughout 2020 reveals an even bigger drop in average life expectancy as well as still-substantial disparities by race and ethnicity.
Lead author Theresa Andrasfay, a postdoctoral scholar at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology, and coauthor Noreen Goldman of Princeton University first examined the pandemic's effect on American life expectancy in October 2020. Their initial study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in January 2021, showed the largest single-year decline in life expectancy in at least 40 years and the lowest life expectancy estimated since 2003.
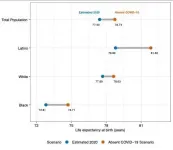
The updated analysis, which included the more than 380,000 US COVID-19 deaths in 2020 and used 2018 life expectancies as a comparison, indicates that COVID-19 reduced overall life expectancy by 1.31 years (up from the initial estimate of 1.13 years lost) to 77.43 years. The reductions in average lifespan are more than three times as large for Latinos (3.03 years) and twice as large for the Black population (1.90 years) compared to whites (0.94 years).
"Impacts on life expectancy are likely to be even larger once excess mortality from other causes is taken into account." Andrasfay cautioned.
The changing geography of the pandemic's impact since last fall has made a significant difference in total average life expectancy loss as well as for whites, who were previously projected to lose 0.68 years on average.
"Since our October 2020 projections, disproportionately white Midwestern and Mountain states experienced surges in COVID-19 cases and deaths," Andrasfay explained. "As a result, the disparities are not quite as large as we initially projected, but are still striking."
As noted in the previous study, Black and Latino Americans have experienced a disproportionate burden of coronavirus infections and deaths, reflecting persistent structural inequalities that heighten risk of exposure to and death from COVID-19. The particularly large decrease in average life expectancy among Latinos likely stems from social and economic inequities that result in both higher exposure to infection and higher fatality among those infected. Compared to Black and white populations, Latinos have lower rates of health insurance, are more likely to live in multi-generational or crowded households and are more likely to hold frontline jobs with COVID-19 exposure risks, Andrasfay noted.
"Life expectancy is a metric of population-level mortality in a given year, and it is sensitive to deaths at younger ages," Andrasfay explained. "Though COVID-19 disproportionately killed older Americans, substantial numbers of younger Black and Latino Americans had their lives taken by COVID-19, which contributed to greater life expectancy reductions for these populations."
Andrasfay and Goldman also examined data from the first few months of 2021, which showed that average life expectancy is still affected by the pandemic.
"Though it is too early to estimate 2021 life expectancy, the deaths that occurred in just the first three months of 2021 already indicate that 2021 will have reduced life expectancy compared to pre-pandemic levels, and substantial racial and ethnic disparities in these reductions will persist," Andrasfay said. "The ultimate impact of COVID-19 on 2021 US life expectancy will depend on whether there is sufficient and equitable vaccination across the US. Looking to the future beyond COVID-19, reducing racial disparities in life expectancy requires investments beyond healthcare, including a commitment to make the economy more equitable."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-24
When cancers metastasize, cells from the primary tumor break away, travel through the blood or lymph system,
and form new tumors in other body parts. Although metastasis are responsible for more than 90% of all cancer
deaths, limited progress has been made in treating cancers that have spread.
Besides DNA, RNA is the other molecule of life. For several years now, RNA has become just as important as DNA in understanding the book of life. Especially, messenger RNA (mRNA), the basis of the Covid-19 vaccines, has been put in the spotlight. Just as with DNA, in addition to the 4 well known letters (A, U, G, C), there are further letters defining the RNA alphabet or ...
2021-06-24
Discovering and engineering nanobodies with properties suitable for treating human diseases ranging from cancer to COVID-19 is a time-consuming, laborious process.
To that end, University of Michigan researchers found a simple method for identifying nanobodies with drug-like properties suitable for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infections. They demonstrated the approach by generating nanobodies that neutralized the SARS-CoV-2 virus more potently than an antibody isolated from an infected patient and a nanobody isolated from an immunized animal.
Nanobodies are small antibody fragments ...
2021-06-24
Many people don't realize that the trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi residing within the gastrointestinal tract--collectively called the gut microbiome-- are connected to overall health, and specifically to cancer.
Manipulating the gut microbiome to produce "beneficial" commensal microbes, which protect the host from pathogens and can boost immune responses, among other things, could potentially help patients respond better to cancer drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors, a type of immunotherapy.
To that end, researchers at the University of Michigan have developed ...
2021-06-24
Migrating storms and local weather systems known as cyclones and anticyclones were thought to contribute to behaviors and properties of our global weather system. However, the means to probe cyclones and anticyclones were limited. For the first time, researchers demonstrated a new three-dimensional analytical methodology that can quantify the way individual cyclones and anticyclones impact broader weather systems. This study aids longer-term circulation and climate studies, including how storm characteristics may change in the future.
To many people, the term cyclone probably conjures up images of ferocious storm ...
2021-06-24
A study published on 21 May in Child Development shows that the early production of beat gestures with the hands (i.e., gestures normally associated with emphasis that do not represent the semantic content of speech) by infants between 14 and 58 months of age in natural interactions with their carers predicts that in their later development, nearing the age of five, these children obtain better results insofar as their oral narrative skills.
The authors analysed the predictive value of beat gestures, compared with flip gestures of the hands and iconic gestures
However, the study did ...
2021-06-24
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with colleagues from Spanish universities have offered a simple method how to enhance the responsivity of terahertz radiation detectors by 3.5 folds using a small Teflon cube. The 1 mm cube must be put on the surface of the detector without changing the inner design of the detector.
Such detectors are applied, for instance, in a full-body scanner, spectrometer, in medical devices for diagnosing skin cancer, burn injuries, pathological changes in blood. The research findings are published in the Optics Letters academic journal (IF: 3,714; Q1).
Terahertz range lies between ...
2021-06-24
Coastal bays are momentous transition zones connecting terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Xiangshan Bay is a typically eutrophic and semi-enclosed bay in the East China Sea. A recent study took Xiangshan Bay as an example, revealing the sources and transformation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in this eutrophic bay.
Dissolved organic matter (DOM), consisting of a vast of complex compounds, has received much attention due to its significant contribution to the largest reduced organic carbon pool in the ocean, which is sizable to the atmosphere CO2 reservoir.
Coastal bays are known as semi-enclosed signature and long water retention ...
2021-06-24
Monocultures dominate arable land today, with vast areas given over to single elite varieties that promise a high yield. But planting arable land with just one type of crop has its disadvantages: these areas are easy game for fungal and insect pests, posing a threat to crops. To keep pests at bay, farmers are having to use resistant varieties and various pesticides.
Mixed cultures present a potential alternative to monocultures. Rather than having large expanses of land planted with just one species or variety, several species or varieties are sown alongside each other. However, as little research has been done ...
2021-06-24
A cluster of comet fragments believed to have hit Earth nearly 13,000 years ago may have shaped the origins of human civilisation, research suggests.
Possibly the most devastating cosmic impact since the extinction of the dinosaurs, it appears to coincide with major shifts in how human societies organised themselves, researchers say.
Their analysis backs up claims that an impact occurred prior to start of the Neolithic period in the so-called Fertile Crescent of southwest Asia.
During that time, humans in the region - which spans parts of modern-day countries such as Egypt, Iraq and Lebanon - switched from hunter-gatherer lifestyles to ones centred on agriculture and the creation of permanent settlements.
It is thought that the comet strike ...
2021-06-24
The Third Pole centered on the Tibetan Plateau is home to the headwaters of multiple rivers in Asia. Despite the importance of these rivers, scientists have not known exactly how much water flows out of the mountains of the Third Pole as river runoff.
Now, however, researchers from the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research (ITP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have quantified the total river runoff of 13 major rivers in the region.
The study was published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society and was based on data from an observational network of "water meters" at mountain outlets in the Third Pole.
The network generates comprehensive discharge data for 13 major Third Pole ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Updated analysis of US COVID-19 deaths shows drops, disparities in average lifespans
In the US, COVID-19 reduced overall life expectancy by over 1.3 years, with the effects on Black and Latino populations 2 to 3 times those for the white population