INFORMATION:
New microscopy method reveals single childhood cancer cells in unprecedented detail
2021-06-24
(Press-News.org) A new technique to look at tumors under the microscope has revealed the cellular make-up of Wilm's tumors, a childhood kidney cancer, in unprecedented detail. This new approach could help understand how tumors develop and grow, and fuel research into new treatments for children's cancers.
Scientists at the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology developed a new imaging technique and computational pipeline to study millions of cells in 3D tissue, revealing hundreds of features from each individual cell. Their research was published this month in Nature Biotechnology.
By offering a look at individual cells within an intact organ, the new technique helps scientists analyze the molecular profile of the cells, as well as their shape and position within an organ or tumor.
Other techniques to study individual cells require tissue to be cut up into small pieces, sacrificing important information about how tissue is organized.
Spatial information about cells is key in understanding how large tissues are organized, and the relationships between different cell types - to reveal differences between healthy tissue and childhood tumors. Linking such information to clinical outcome data could in future improve diagnosis.
New group of Wilm's tumor cells
The team led by co-first authors Ravian van Ineveld and Michiel Kleinnijenhuis applied their microscopy technique to compare Wilm's tumor tissue with healthy developing kidney tissue. They found a group of cells with higher levels of a gene called SIX2, linked to keeping cells in an immature state where they keep growing.
Other tumor cells with high SIX2 levels are linked with a poor outcome after chemotherapy treatment. Further research is needed to explore the clinical relevance of this new group of SIX2 Wilm's tumor cells - but this finding shows that the new imaging technique can lead to insights that could in future improve treatment.
More data in less time
Cells can be told apart from each other under the microscope by tagging specific molecules with fluorescent particles in different colors. The new imaging pipeline developed by the Rios group at the Princess Máxima Center (Dream3D Lab) doubles the number of colors that can be tagged at the same time from four to eight - meaning the researchers could distinguish cell types much more precisely.
The team also developed a brand new way of processing the enormous amounts of information generated by the microscopy technique. They cut up the information about the whole organ into smaller 3D blocks. These blocks were sent to many computers at once to analyze the data in parallel. This reduced the time to process the large volume of data from multiple days to about two hours - a requirement for bringing the new technique into practice. In addition, the team used deep learning approaches to identify each individual cell in the large dataset with high accuracy.
Link with clinical outcome
The scientists tested their new technique with different molecular tags to look at biopsy material from a childhood central nervous system tumor, as well as breast tumor tissue, confirming that it can be applied in multiple tissue types.
Next, the researchers aim to use their imaging pipeline to analyze more patient samples. Linking their 3D tissue analysis to clinical outcome could lead to better diagnostic tools for children's cancer.
Dr. Anne Rios, principal investigator at the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology and senior author of the study, said:
'Our new single-cell technology marks a key step forward in unravelling the complexities of the way organs and tumors are organized. With our new microscopy technique, you get the best of both worlds: in-depth characterization of individual cells, in the full context of large-scale 3D tissue analysis.
'I look forward to seeing our new technique used to better understand how tumors develop and grow, and perhaps even discover leads for better treatment and diagnosis.'
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find the adhesions that build the brain's networks
2021-06-24
DURHAM, N.C. - The brain's neurons tend to get most of the scientific attention, but a set of cells around them called astrocytes - literally, star-shaped cells - are increasingly being viewed as crucial players in guiding a brain to become properly organized.
Specifically, astrocytes, which form about half the mass of a human brain, seem to guide the formation of synapses, the connections between neurons that are formed and remodeled as we learn and remember.
A new study from Duke and UNC scientists has discovered a crucial protein involved in the communication and coordination between astrocytes as they build synapses. Lacking this molecule, called hepaCAM, astrocytes aren't as sticky as they ...
A 'tasty' protein may lead to new ways to treat metabolic and immune diseases
2021-06-24
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (June 24, 2021) -- The same taste-sensing molecule that helps you enjoy a meal from your favorite restaurant may one day lead to improved ways to treat diabetes and other metabolic and immune diseases.
TRPM5 is a specialized protein that is concentrated in the taste buds, where it helps relay messages to and from cells. It has long been of interest to researchers due to its roles in taste perception and blood sugar regulation.
Now, a team led by scientists at Van Andel Institute has published the first-ever high-resolution images of TRPM5, which reveal two areas that may serve as targets for new medications. The structures also may aid in the development of low-calorie alternative sweeteners that mimic sugar. The findings were published today in Nature ...
Collection of starshade research helps advance exoplanet imaging by space telescopes
2021-06-24
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA - The open access Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (JATIS) has published END ...
Searching for the cell of origin of childhood brain cancer
2021-06-24
The study was conducted by an international collaboration involving the research team led by Luca Tiberi of the Armenise-Harvard Laboratory of Brain Cancer at the Department of Cellular, computational and integrative biology - Cibio of UniTrento, the Paris Brain Institute-Institut du Cerveau at Sorbonne Université in Paris, the Hopp Children´s Cancer Center (KiTZ) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Sapienza University in Rome. It was supported by Fondazione Armenise-Harvard, Fondazione Airc (Italian Association for Cancer Research) and Fondazione Caritro from Trento. The findings of the study, published in Science Advances, could lead to better and more effective treatments.
The team of researchers is proud of the results achieved. Luca Tiberi, coordinator of the study and corresponding ...
Scientists explain the behaviour of the optical emission of blazars
2021-06-24
Dmitry Blinov is a co-author of the article and Senior Research Associate in the Department of Astrophysics, St Petersburg University. He notes that researchers have been studying the optical polarisation from active galactic nuclei for more than 50 years. Some of the first academic papers on this topic were published back in the 1960s by Vladimir Hagen-Thorn, Professor in the Department of Astrophysics, St Petersburg University, and Viktor Dombrovskiy, Associate Professor in the Department of Astrophysics, Leningrad State University.
In the Universe, the main material is concentrated in galaxies with hundreds of billions of stars: there are about 200-400 of them in the Milky Way. At the centre of galaxies there are supermassive ...
Decoding humans' survival from coronaviruses
2021-06-24
An international team of researchers co-led by the University of Adelaide and the University of Arizona has analysed the genomes of more than 2,500 modern humans from 26 worldwide populations, to better understand how humans have adapted to historical coronavirus outbreaks.
In a paper published in Current Biology, the researchers used cutting-edge computational methods to uncover genetic traces of adaptation to coronaviruses, the family of viruses responsible for three major outbreaks in the last 20 years, including the ongoing pandemic.
"Modern human genomes contain evolutionary ...
Repurposing rheumatology drugs for COVID-19
2021-06-24
Rheumatologists are familiar with the everyday use of immunomodulatory drugs. These are designed to treat the inflammation caused by autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. A EULAR taskforce was set up to develop a set of new points to consider to give guidance and advice on the best way to use these medicines to treat COVID-19. The taskforce included rheumatologists, immunologists, haematologists, paediatricians, patients and other health professionals. They looked at the published evidence on the use of immunomodulatory therapies to treat severe COVID-19.
In total, there are two overarching principles and 14 points to consider. The principles stress that the picture of SARS-CoV-2 infection can be very different in different people. Infections range from asymptomatic ...
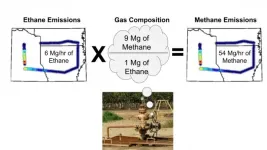
Ethane proxies for methane in oil and gas emissions
2021-06-24
Measuring ethane in the atmosphere shows that the amounts of methane going into the atmosphere from oil and gas wells and contributing to greenhouse warming is higher than suggested by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, according to an international team of scientists who spent three years flying over three areas of the U.S. during all four seasons.
"Ethane is a gas that is related only to certain sources of methane," said Zachary R. Barkley, researcher in meteorology and atmospheric science, Penn State. "Methane, however, is produced by oil, ...
Points to consider for studies of work participation in people with inflammatory arthritis
2021-06-24
Understanding work participation is important, but the way in which this is defined and measured in clinical trials is not always the same, which has made it hard to compare data. EULAR set up a taskforce to draft points to consider when designing studies that use work participation as a measure. The taskforce included doctors, experts and patients from 11 countries. They used the published evidence to draw up a set of points to consider.
Two overarching principles and nine points to consider were developed. The principles say that work participation is important for people with inflammatory arthritis, their ...
Mount Sinai study finds that rotator cuff injuries account for nearly half of shoulder injuries among collegiate baseball players, identifies other risks
2021-06-24
Paper Title: Analysis of Common Shoulder Injuries in Collegiate Baseball Players
Journal: The Physician and Sportsmedicine (June 23, 2021, online edition)
Authors: Alexis Chiang Colvin, MD, Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Daniel A. Charen, MD, Resident, Department of Orthopedic Surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; and other coauthors.
Bottom Line: Baseball players are highly susceptible to shoulder injuries due to significant microtrauma including repetitive overhead throwing. Mount Sinai researchers investigated men's National Collegiate ...