Cancer risk in ART children and young adults is not increased
Results from 18-year follow-up of babies born from treatments including ICSI and frozen embryo transfer
2021-06-28
(Press-News.org) 28 June 2021: The risk of cancer in children born as a result of fertility treatment has been found to be no greater than in the general population.
Results presented today at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE from an 18-year median follow up study demonstrate that the overall chance of developing malignant disease did not increase in ART-conceived offspring. Details of the analysis are presented today online by Dr Mandy Spaan from the Amsterdam University Medical Center (UMC) and Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, at the virtual Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
The findings also found no difference in outcomes between ART children and those conceived by sub-fertile women who became pregnant naturally, either with or without fertility drugs to induce ovulation.
Overall, the results are described by Spaan as "quite reassuring, especially for children conceived by IVF" and are an important contribution to the current knowledge about health risks in ART-offspring". They may assist physicians, she explained, to inform parents considering ART about the potential health risks for their children. What's more, Spaan says the findings provide gynaecologists with "evidence-based information about the association between ART and cancer risk in children and adolescents."
As background to the study, Dr Spaan explained there is growing evidence that ART procedures could influence the normal genetic modifications which occur in the embryo prior to its implantation in the womb.(1) Fertility drugs, egg/embryo freezing and thawing, and the type of medium in which embryos are grown could all have an impact.
This report is based on the offspring of women treated in the 13 IVF clinics or two regional fertility centres in the Netherlands.
Data came from the OMEGA cohort, a Netherlands based cohort study of all live-born offspring from subfertile women treated with and without ART between 1980 and 2012. A total of 89,249 children were included - 51,417 born though ART such as IVF, ICSI and frozen embryo transfer (FET) between 1983 and 2012, and 37,832 conceived naturally by subfertile women with/without fertility drugs between 1975 and 2012.
Details on the ART treatment and maternal characteristics were obtained from medical records, the Dutch Perinatal Registry, and questionnaires completed by the mothers. This information - IVF versus ICSI, fresh versus frozen embryo transfer, and cause of subfertility - was compared with cancer incidence ascertained from the Netherlands Cancer Registry.
The analysis showed that 358 cancers were diagnosed in children, of which 157 were in the ART group and 201 in the non-ART group. There was no overall increase in cancer risk for those born after ART compared with those not conceived by ART and the general population.
The chance of developing cancer was not significantly increased for children conceived by IVF compared with non-ART children. ICSI children were more likely to get cancer, but the authors say this was mainly driven by an increased likelihood of melanoma (based on four cases) and may be down to chance.
Children born after FET were not at increased risk compared to those born after a fresh embryo transfer, neither were those aged 18 and above who were conceived by ART compared with non-ART.
INFORMATION:
Presentation 0-077, Monday 28 June 2021
Cancer risk in a nationwide cohort of children and young adults conceived by assisted reproductive technology in 1983-2011
Cancer risk and ART
1. The proportion of children born after intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ISCI) and frozen embryo transfer (FET) has increased dramatically over the past decades. Recent studies have shown (both significantly and non-significantly) increased cancer risks after both these techniques, with the suggestion that fertility drugs and/or ART could trigger cancer through epigenetic changes. Hence, the importance from a public health perspective to investigate cancer risk after ICSI and FET in larger studies like the one presented today.
* When obtaining outside comment, journalists are requested to ensure that their contacts are aware of the embargo on this release.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-28
28 June 2021: Despite continuing controversies over its value in improving birth rates in IVF, testing embryos for their chromosomal content has become routine in many fertility clinics. Embryos with a normal complement of chromosomes (known as "euploid") are known to have a good chance of implanting in the uterus to become a pregnancy, while abnormal embryos (aneuploid) have no chance. Testing embryos for aneuploidy (known as PGT-A*) has so far required a sample single cell or several cells taken from the embryo by biopsy, and this too has raised fears over safety such that a search for non-invasive methods has arisen in recent years.
Now, a new study suggests that euploid embryos can be visually distinguished from ...
2021-06-28
28 June 2021: Only now, more than a year after Covid-19 infection rates first hit peak levels and in the knowledge that receptors for SARS-CoV-2 are present in the ovary, are we able to assess the effect of the virus on reproductive function. Now, a new study has shown that the ovarian reserve of women previously infected with the virus was not adversely affected, and that their chance of success from fertility treatment remained as it was before infection.*
The study, which monitored hormone levels in women having IVF at one of 11 clinics in the IVI group in Spain between May and June 2020, is ...
2021-06-28
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- As their infants and toddlers grow, many parents may wonder if their children are walking, talking and socializing when they're supposed to be.
In fact, nearly a quarter of parents have suspected their child might be delayed in their development, a new national poll finds - but they may not always share these concerns with a doctor.
Among parents who worried that their child was behind in hitting milestones, nearly one in five did not seek advice from a healthcare or childcare provider, according to the University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health.
"Parents may be unsure whether their child is progressing appropriately for their age and are on track with ...
2021-06-28
Arlington, Va., June 28, 2021 - Designed initially for entertainment purposes, escape rooms are proving their value as medical training tools as demonstrated by the Central Texas Veterans Health Care System. Staff there have used the concept for a flu pandemic escape room and is reporting increased staff handwashing and acceptance of flu vaccines as a result.
The escape room is the brainchild of Gracia Boseman, RN, MPH, and Kristy Causey, MSN, RN, who are END ...
2021-06-28
Sophia Antipolis - 28 June 2021: A study in more than 200,000 individuals has found that patients with heart failure are more likely to develop cancer compared to their peers without heart failure. The research is presented today at Heart Failure 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC),1 and published in ESC Heart Failure, a journal of the ESC.2
"This was an observational study and the results do not prove that heart failure causes cancer," said author Dr. Mark Luedde of the Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel and Cardiology Joint Practice Bremerhaven, Germany. "However, the findings do suggest that heart failure patients may benefit from cancer prevention measures."
Heart failure affects around 65 million people ...
2021-06-28
Oncotarget published "The presence of polymorphisms in genes controlling neurotransmitter metabolism and disease prognosis in patients with prostate cancer: a possible link with schizophrenia" reported that polymorphisms of neurotransmitter metabolism genes were studied in patients with prostate cancer (PC) characterized by either reduced or extended serum prostate-specific antigen doubling time corresponding to unfavorable and favorable disease prognosis respectively.
The following gene polymorphisms known to be associated with neuropsychiatric disorders were investigated:
A. ...
2021-06-28
Oncotarget published "Predicting clinical outcomes using cancer progression associated signatures" which reported somatic mutation signatures are an informative facet of cancer aetiology, however they are rarely useful for predicting patient outcome.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the utility of a panel of 142 mutation-signature–associated metrics for predicting cancer progression in patients from a ‘TCGA PanCancer Atlas’ cohort.
Cancer specific machine learning models were built using the output from the P142 panel to predict patient ...
2021-06-28
Oncotarget published "Insulin-like growth factor 1/Child-Turcotte-Pugh composite score as a predictor of treatment outcomes in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib" which reported that this study investigated the association of the IGF/CTP score with overall survival and progression-free survival of HCC patients treated with sorafenib.
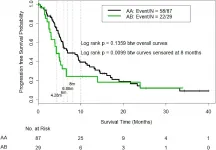
The authors calculated the IGF/CTP score and used the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test to estimate and compare the time-to-event outcomes between patient subgroups.
171 patients were included, 116 of whom were CTP class A. Median ...
2021-06-28
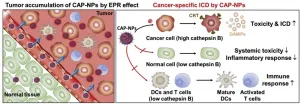
Unlike conventional cancer drugs that attack and kill cancer cells directly, anti-cancer immunotherapy, which kills cancer cells by strengthening the body's immunity, is a novel type of cancer treatment currently attracting increased attention. Unfortunately, a minority of cancer patients who have some degree of pre-existing immunity only benefit from anti-cancer immunotherapy.
Recently, 'doxorubicin', a cancer treatment drug, has been shown to boost patients' immune response by releasing various components when cancer cells are killed. However, as the toxicity and inflammatory responses induced by doxorubicin can affect normal cells in addition to cancer cells, it can lower ...
2021-06-28
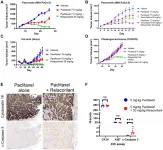
Oncotarget published "Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism promotes apoptosis in solid tumor cells" which reported that to guide studies in cancer patients, relacorilant, an investigational selective GR modulator that antagonizes cortisol activity, was assessed in various tumor types, with multiple cytotoxic combination partners, and in the presence of physiological cortisol concentrations.
In the MIA PaCa-2 cell line, paclitaxel-driven apoptosis was blunted by cortisol and restored by relacorilant.
A screen to identify optimal combination partners for relacorilant showed that microtubule-targeted agents consistently ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cancer risk in ART children and young adults is not increased
Results from 18-year follow-up of babies born from treatments including ICSI and frozen embryo transfer