COVID-19 patients recover faster with metabolic activator treatment, study shows
2021-06-28
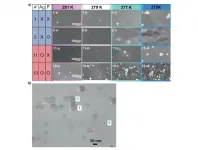
(Press-News.org) Metabolic activators were found to reduce recovery time by as many as 3.5 days in patients with mild-to-moderate Covid-19, according to a Swedish-British study published today in Advanced Science.
The researchers also found that treatment with the metabolic activators improved liver health and decreased the levels of inflammation, as shown by inflammatory markers.
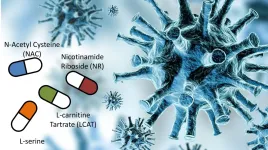
Conducted by researchers at Science for Life Laboratory at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, in collaboration with the Sahlgrenska Academy in Gothenburg and King's College, London, the human phase three clinical study showed that patients with mild-to-moderate Covid-19--who were also receiving standard care--experienced a 3.5 day reduction in recovery time when receiving the combination of metabolic activators, nicotinamide riboside (NR), L-serine, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), and L-carnitine tartrate. All four activators are aimed at improving mitochondrial function. The results of the study build on findings from phase two clinical data.
Through a randomized, placebo controlled, double blind phase three clinical trial, 309 outpatients at Umraniye Teaching and Research Hospital, University of Health Sciences, Istanbul, Turkey were randomly assigned on a 3:1 basis to receive the metabolic activators or placebo. Patients received the combined activators or placebo twice a day for 14 days and clinical status was evaluated through daily telephone check-ins.
"Our phase three data shows that metabolic activators significantly improve the recovery, liver health, and markers of inflammation of patients with COVID-19," says the study's lead author, Adil Mardinoglu, professor at KTH and Kings College and research fellow at Science for Life Laboratory.
"Dysfunctional mitochondria have been implicated in worsened progression for Covid-19, and we are pleased to find that the combination of these metabolic activators helps to remedy the stress put on the body of an infected patient."
INFORMATION:
The study was conducted in partnership with Stockholm-based ScandiBio Therapeutics AB and California-based ChromaDex (NASDAQ:CDXC), which provided one of the four ingredients (nicotinamide riboside) through the ChromaDex External Research Program (CERP). Together with the strategic partner Viscoran (Turkey), a submission for drug approval has been submitted to the Ministry of Health in Turkey.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-28
Want to have a happy relationship? Make sure both partners feel they can decide on issues that are important to them. Objective power measured by income, for example, doesn't seem to play a big role, according to a new study in the "Journal of Social and Personal relationships" by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Bamberg. Instead, how lovers perceive power dynamics in their relationship is most important for relationship satisfaction.
Power is about being able to influence people and successfully resist the attempts of others to influence you. "It sounds like a dog-eat-dog world or the world of business. ...
2021-06-28
The examined tissue does not need to be marked for this. The analysis only takes around half an hour. "This is a major step that shows that infrared imaging can be a promising methodology in future diagnostic testing and treatment prediction," says Professor Klaus Gerwert, director of PRODI. The study is published in the American Journal of Pathology on 1 July 2021.
Treatment decision by means of a genetic mutation analysis
Lung tumours are divided into various types, such as small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Many rare tumour types and sub-types also exist. This diversity hampers reliable rapid diagnostic methods in everyday clinical ...
2021-06-28
There are spiders that eat snakes. Observations of snake-eating spiders have been reported around the world. Two researchers from Basel and the US consolidated and analyzed over 300 reports of this unusual predation strategy.
Spiders are primarily insectivores, but they occasionally expand their menu by catching and eating small snakes. Dr. Martin Nyffeler, arachnologist at the University of Basel, and American herpetologist Professor Whitfield Gibbons of the University of Georgia, USA, got to the bottom of this phenomenon in a meta-analysis. Their findings from ...
2021-06-28
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this article the authors Chunxiong Zheng, Mingqiang Li and Jianxun Ding from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China and Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Changchun, China discuss the challenges and opportunities of nanomedicines in clinical translation.
Researchers are rapidly gaining a much deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities of nanomedicines allowing for improvements in disease treatment and improved patient survival.
Deep exploration of the connections between preclinical and clinical ...
2021-06-28
In March 2020, daily life in the United States changed in an instant as the country locked down to deal with the initial wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. New research reveals how residents in one community returned to their routines as the restrictions lifted, according to a team of Penn State scientists.
"We used sound signals captured by underground fiber-optic sensors to understand how COVID measures impacted human activities," said Junzhu Shen, a graduate student in geosciences at Penn State. "These sensors provide very accurate, high-resolution data that can help us understand what's happening in our communities."
The scientists analyzed sound data recorded from March through June 2020 in and around the Penn State University Park campus and State College, ...
2021-06-28
Researchers have developed smart wound dressings with built-in nanosensors that glow to alert patients when a wound is not healing properly.
The multifunctional, antimicrobial dressings feature fluorescent sensors that glow brightly under UV light if infection starts to set in and can be used to monitor healing progress.
The smart dressings, developed by a team of scientists and engineers at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, harness the powerful antibacterial and antifungal properties of magnesium hydroxide.
They are cheaper to produce than silver-based dressings but equally as effective in fighting bacteria and fungi, with their antimicrobial power lasting up to a week.
Project leader Dr Vi Khanh Truong said the development of cost-effective antimicrobial ...
2021-06-28
Results of this technique, known as transfer learning, achieved a 99.24 per cent success rate when detecting COVID-19 in chest x-rays.
The study tackles one of the biggest challenges in image recognition machine learning: algorithms needing huge quantities of data, in this case images, to be able to recognise certain attributes accurately.
ECU School of Science researcher END ...
2021-06-28
Osaka, Japan - Scientists at Osaka University, Panasonic Corporation, and Waseda University used scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy to determine which additives induce crystallization in supercooled aqueous solutions. This work may lead to the development of new energy storage materials based on latent heat.
If you put a bottle of water into the freezer, you will expect to pull out a solid cylinder of ice after a few hours. However, if the water has very few impurities and left undisturbed, it may not be frozen, and instead remain as a supercooled liquid. Be careful, because this state is very unstable, and the water will crystallize quickly if shaken or impurities are added - as many YouTube videos will attest. ...
2021-06-28
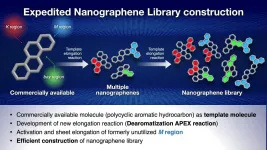
A group of researchers at Nagoya University, Japan, have developed a new method for quickly and efficiently synthesizing nanographenes, a type of nanocarbon with great potential as a next generation material.
Nanographenes are the part structures of graphene, which is a sheet of carbon atoms around 3 nanometers thick with particular potential for use in semiconductor development, having electron mobility several hundred times better than current generation materials. Graphene was first isolated in 2004, a discovery which received the 2010 Nobel Prize in physics, making it a very new material which is currently the subject of a great deal of research.
With ...
2021-06-28
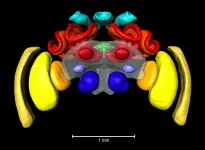
The buff-tailed bumblebee Bombus terrestris is one of the most common bumblebee species in Europe. It is not only active in nature as a pollinator - humans also use it in greenhouses and foil tunnels to get good harvests of tomatoes or strawberries.
The buff-tailed bumblebee is also used in science: "Basic research is increasingly using it as a model organism to analyse learning and memory, the visual system, flight control and navigation abilities," says Dr. Keram Pfeiffer, Professor of neurobiology at the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany.
Pfeiffer investigates the neuronal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 patients recover faster with metabolic activator treatment, study shows