(Press-News.org) Results of this technique, known as transfer learning, achieved a 99.24 per cent success rate when detecting COVID-19 in chest x-rays.
The study tackles one of the biggest challenges in image recognition machine learning: algorithms needing huge quantities of data, in this case images, to be able to recognise certain attributes accurately.
ECU School of Science researcher END
Researchers are using photos of toasters and fridges to train algorithms to detect COVID
New research using machine learning on images of everyday items is improving the accuracy and speed of detecting respiratory diseases, reducing the need for specialist medical expertise
2021-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A way to surmount supercooling
2021-06-28
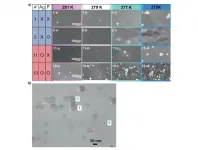
Osaka, Japan - Scientists at Osaka University, Panasonic Corporation, and Waseda University used scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy to determine which additives induce crystallization in supercooled aqueous solutions. This work may lead to the development of new energy storage materials based on latent heat.
If you put a bottle of water into the freezer, you will expect to pull out a solid cylinder of ice after a few hours. However, if the water has very few impurities and left undisturbed, it may not be frozen, and instead remain as a supercooled liquid. Be careful, because this state is very unstable, and the water will crystallize quickly if shaken or impurities are added - as many YouTube videos will attest. ...
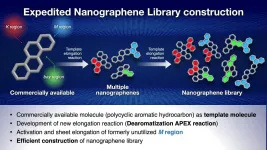
A template for fast synthesis of nanographenes
2021-06-28
A group of researchers at Nagoya University, Japan, have developed a new method for quickly and efficiently synthesizing nanographenes, a type of nanocarbon with great potential as a next generation material.
Nanographenes are the part structures of graphene, which is a sheet of carbon atoms around 3 nanometers thick with particular potential for use in semiconductor development, having electron mobility several hundred times better than current generation materials. Graphene was first isolated in 2004, a discovery which received the 2010 Nobel Prize in physics, making it a very new material which is currently the subject of a great deal of research.
With ...
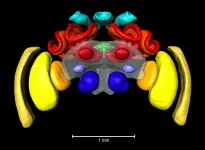
An atlas of the bumblebee brain
2021-06-28
The buff-tailed bumblebee Bombus terrestris is one of the most common bumblebee species in Europe. It is not only active in nature as a pollinator - humans also use it in greenhouses and foil tunnels to get good harvests of tomatoes or strawberries.
The buff-tailed bumblebee is also used in science: "Basic research is increasingly using it as a model organism to analyse learning and memory, the visual system, flight control and navigation abilities," says Dr. Keram Pfeiffer, Professor of neurobiology at the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany.
Pfeiffer investigates the neuronal ...
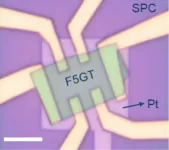
Transforming the layered ferromagnet F5GT for future spintronics
2021-06-28
A RMIT-led international collaboration published this week has achieved record-high electron doping in a layered ferromagnet, causing magnetic phase transition with significant promise for future electronics
Control of magnetism (or spin directions) by electric voltage is vital for developing future, low-energy high-speed nano-electronic and spintronic devices, such as spin-orbit torque devices and spin field-effect transistors.
Ultra-high-charge, doping-induced magnetic phase transition in a layered ferromagnet allows promising applications in antiferromagnetic spintronic devices.
The FLEET collaboration of researchers at RMIT, UNSW, the University of Wollongong and FLEET partner ...
Honey, we shrunk the intense XUV laser
2021-06-28
The invention of the laser has opened the era of nonlinear optics, which today plays an important role in many scientific, industrial and medical applications. These applications all benefit from the availability of compact lasers in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The situation is different at XUV wavelengths, where very large facilities (so called free-electron lasers) have been built to generate intense XUV pulses. One example of these is FLASH in Hamburg that extends over several hundred meters. Smaller intense XUV sources based on HHG have also been developed. However, these sources still have a footprint of tens of meters, and have so far only been demonstrated at a few universities and research institutes worldwide. ...
Sunflower peptide as 'template' for potential analgesic
2021-06-28
A naturally occurring peptide in sunflower seeds was synthetically optimised and has now been identified as a potential drug for treating abdominal pain or inflammation (in the gastrointestinal tract, abdominal area and/or internal organs). That is the finding of an international study led by Christian Gruber from MedUni Vienna's Institute of Pharmacology (Center for Physiology and Pharmacology), which was conducted jointly with the University of Queensland and Flinders University in Australia and has now been published.
The scientific aim of the study is to find analgesics that are only active in the periphery and do not cross the blood-brain barrier, as an alternative to commonly used synthetic opioids. Gruber explains the background: "Morphine was one of the first ...
New tools for pandemic prevention research: DNA sequencing from water and leech
2021-06-28
In a new scientific investigation headed by the German Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW), water from African and Mongolian waterholes as well as bloodmeals from Southeast Asian leeches were assessed for the ability to retrieve mammalian viruses without the need to find and catch the mammals. The scientists analysed the samples using high throughput sequencing to identify known viruses as well as viruses new to science. Both approaches proved to be suitable tools for pandemic prevention research as they allow finding and monitoring reservoirs of wildlife viruses. For example, a novel coronavirus most likely associated with Southeast Asian deer species was identified. The results are ...
HKUST scientists develop simple blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-06-28
An international research team led by HKUST has developed a simple but robust blood test from Chinese patient data for early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease (AD) for the first time, with an accuracy level of over 96%.
Currently, doctors mainly rely on cognitive tests to diagnose a person with AD. Besides clinical assessment, brain imaging and lumbar puncture are the two most commonly used medical procedures to detect changes in the brain caused by AD. However, these methods are expensive, invasive, and frequently unavailable in many countries.
Now, a team led by Prof. Nancy IP, Vice-President for Research and Development at HKUST, has identified 19 out of the 429 plasma proteins associated with AD to form ...
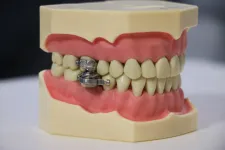
Researchers develop world-first weight loss device
2021-06-28
University of Otago, New Zealand, and UK researchers have developed a world-first weight-loss device to help fight the global obesity epidemic.
DentalSlim Diet Control is an intra-oral device fitted by a dental professional to the upper and lower back teeth. It uses magnetic devices with unique custom-manufactured locking bolts. It allows the wearer to open their mouths only about 2mm, restricting them to a liquid diet, but it allows free speech and doesn't restrict breathing.
Participants in a Dunedin-based trial lost an average of 6.36kg in two weeks and were motivated to continue with their weight loss ...
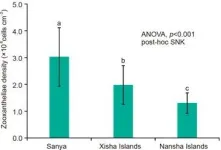
Coral enhance its environmental adaptability by adjusting trophic status
2021-06-28
Coral bleaching and the ecological degradation of coral reefs have become increasingly severe due to the global warming and human activities. As "mixotrophic" organisms, scleractinian coral can not only obtain energy through photosynthesis of symbiotic zooxanthellae (autotrophy), but also ingest nutrients in seawater through the coral host (heterotrophy). However, the influence of coral's trophic flexibility on environmental adaptability remains unclear. Coral reefs are widely distributed in the South China Sea (SCS), spanning about 20 latitudes from north to south. The environmental conditions of coral reef areas at different latitudes are significantly different. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
[Press-News.org] Researchers are using photos of toasters and fridges to train algorithms to detect COVIDNew research using machine learning on images of everyday items is improving the accuracy and speed of detecting respiratory diseases, reducing the need for specialist medical expertise