HKUST scientists develop simple blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-06-28
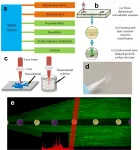
(Press-News.org) An international research team led by HKUST has developed a simple but robust blood test from Chinese patient data for early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease (AD) for the first time, with an accuracy level of over 96%.
Currently, doctors mainly rely on cognitive tests to diagnose a person with AD. Besides clinical assessment, brain imaging and lumbar puncture are the two most commonly used medical procedures to detect changes in the brain caused by AD. However, these methods are expensive, invasive, and frequently unavailable in many countries.
Now, a team led by Prof. Nancy IP, Vice-President for Research and Development at HKUST, has identified 19 out of the 429 plasma proteins associated with AD to form a biomarker panel representative of an "AD signature" in the blood. Based on this panel, the team has developed a scoring system that distinguishes AD patients from healthy people with more than 96% accuracy. This system can also differentiate among the early, intermediate, and late stages of AD, and can be used to monitor the progression of the disease over time. These exciting findings have led to the development of a high-performance, blood-based test for AD, and may also pave the way to novel therapeutic treatments for the disease.
"With the advancement of ultrasensitive blood-based protein detection technology, we have developed a simple, noninvasive, and accurate diagnostic solution for AD, which will greatly facilitate population-scale screening and staging of the disease," said Prof. Nancy Ip, Morningside Professor of Life Science and the Director of the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience at HKUST.
The work was conducted in collaboration with researchers at University College London and clinicians in local hospitals including the Prince of Wales Hospital and Queen Elizabeth Hospital. The discovery was made using the proximity extension assay (PEA) - a cutting-edge ultrasensitive and high-throughput protein measurement technology, to examine the levels of over 1,000 proteins in the plasma of AD patients in Hong Kong.
As the most comprehensive study of blood proteins in AD patients to date, the work has recently been published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, and has also been featured and actively discussed on different scholarly exchange platforms on AD research such as Alzforum.
AD, which affects over 50 million people worldwide, involves the dysfunction and loss of brain cells. Its symptoms include progressive memory loss as well as impaired movement, reasoning, and judgment. While patients often only seek medical attention and are diagnosed when they have memory problems, AD affects the brain at least 10-20 years before symptoms appear.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-28
University of Otago, New Zealand, and UK researchers have developed a world-first weight-loss device to help fight the global obesity epidemic.
DentalSlim Diet Control is an intra-oral device fitted by a dental professional to the upper and lower back teeth. It uses magnetic devices with unique custom-manufactured locking bolts. It allows the wearer to open their mouths only about 2mm, restricting them to a liquid diet, but it allows free speech and doesn't restrict breathing.
Participants in a Dunedin-based trial lost an average of 6.36kg in two weeks and were motivated to continue with their weight loss ...
2021-06-28
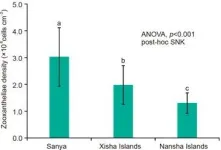
Coral bleaching and the ecological degradation of coral reefs have become increasingly severe due to the global warming and human activities. As "mixotrophic" organisms, scleractinian coral can not only obtain energy through photosynthesis of symbiotic zooxanthellae (autotrophy), but also ingest nutrients in seawater through the coral host (heterotrophy). However, the influence of coral's trophic flexibility on environmental adaptability remains unclear. Coral reefs are widely distributed in the South China Sea (SCS), spanning about 20 latitudes from north to south. The environmental conditions of coral reef areas at different latitudes are significantly different. ...
2021-06-28
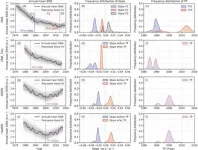
Thousands of scientific papers describing the inner workings of the brain and its dysfunction have been published using resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging (RS-fMRI). This powerful tool allows researchers to look at each cubic millimeter of the brain, in voxels - the 3D version of a pixel. The average brain is well over 1,000,000 cubic mm, so researchers need to perform multiple comparisons correction (MCC) to reduce the possibility of making false claims, i.e., reduce the false positive rates. As part of this MCC, a smaller p value threshold is widely recommended for declaring ...
2021-06-28
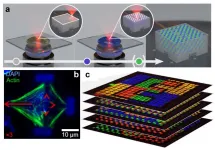
Multi-photon approaches provide printing rates of up to about ten million voxels per second. And, multi-photon-based 3D approaches structure matter with a resolution approaching sub-micrometer and nanometer feature sizes. Such spatial resolution is crucial for many applications in photonics and electronics and is inaccessible to most other 3D additive manufacturing approaches. However, the vast majority of 3D printed objects and devices made along these lines has been composed of only a single polymeric material. Multi-material architectures are much less investigated ...
2021-06-28
The most significant feature of global land surface wind speed (SWS) recently is the long-term weakening trend since the 1960s, that is, the phenomenon known as global terrestrial stilling. Many studies have found that stilling is widespread worldwide. It has seriously affected the ecological environment and social economy, especially restricted the sustainable development of the wind energy industry. It is found that the stilling reversed around 2010 and global SWS is strengthening; then, has the stilling of surface wind speed ended in China? A recent study systematically answered this question. The related paper titled "Has the stilling of the surface wind ...
2021-06-28
In the 1970s, Fleischmann, the scientist in British, discovered that on noble metallic nanostructure, the Raman scattering of pyridine was enhanced hundreds-hold. Then, the scientists attributed the enhancement to the localized electric field highly amplified near the surface of specific noble metallic nanostructures. Thus, this phenomenon was termed surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Currently, although the enhancement mechanism of SERS is still in the debate, the SERS exhibits incomparable abilities of monitoring and sensing with high sensitivity in diverse fields ...
2021-06-28
Human's understanding of the oceans is still limited. The oceans are rich of various kinds of resource which have great exploitation potential and are far away from fully development. Marine biosafety also needs to be noticed. There are not only many animal and plant species undiscovered, but also a much larger and diverse number of microorganisms such as viruses. Traditional studies of marine viruses have focused on bacteriophage represented DNA viruses, and little is known about the genetic diversity, distribution characteristics and transmission patterns of marine invertebrate RNA viruses.
Here, CUI Jie's team have collected a total of 58 marine invertebrate samples from 3 phyla and 6 classes and ...
2021-06-28
The research team led by Prof. XIONG Wei and Prof. CANG Chunlei from Life Science and Medicine of University of Science and Technology of China, realized lysosome typing based on single lysosome metabonomic information for the first time by stablishing a single lysosome metabonomic mass spectrometry detection technology. A deeply explore to the heterogeneity changes of lysosome metabonomics in the process of cellular senescence has been achieved. The result was published on Nature Methods.
Lysosomes are organelles present in almost all eukaryotic cells. Lysosomes are essential for maintaining energy and metabolic homeostasis, signal transduction, and recovery of damaged proteins and organelles. Previous reports indicate that cellular senescence is closely related to lysosomes and their ...
2021-06-28
As the average life expectancy of residents increases, there are more and more cases of human bone tissue disease. With the upgrading of treatment methods, more and more bone tissue lesions can be treated with artificial implants for replacement. Due to the huge demand in the field of biophysical therapy, biomedical materials have very broad market prospects. In the past 10 years, the market growth rate of biomedical materials has remained at 20-25%, and the world population is nearly 6.5 billion. Statistics show that there are close to 400 million disabled people, 60 million physically disabled, and about 2 billion dental patients.
At present, there are only 35 million implanters of biomaterial devices, and the annual joint replacement volume is about 1.5 million, ...
2021-06-28
Research team, led by academician GUO Guangcan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with researchers from Sun Yat-sen University and Zhejiang University, realized two-photon quantum interference in the structure of valley-dependent topological insulators based on the valley Hall effect.
The study was published in Physical Review Letters on June 11st, 2021.
Topological photonics has a practical application prospect in the research of photonic chips due to its robust energy transport prosperities. The key to topological phase transition is to generate an energy gap at certain degenerate points by breaking either the time-reversal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] HKUST scientists develop simple blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease