Has the stilling of the surface wind speed ended in China?
2021-06-28
(Press-News.org) The most significant feature of global land surface wind speed (SWS) recently is the long-term weakening trend since the 1960s, that is, the phenomenon known as global terrestrial stilling. Many studies have found that stilling is widespread worldwide. It has seriously affected the ecological environment and social economy, especially restricted the sustainable development of the wind energy industry. It is found that the stilling reversed around 2010 and global SWS is strengthening; then, has the stilling of surface wind speed ended in China? A recent study systematically answered this question. The related paper titled "Has the stilling of the surface wind speed ended in China?" was recently published in Science China Earth Sciences in 2021. The paper was completed by Yang Qing et al., from Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
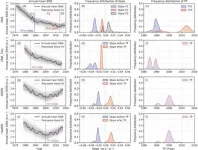
Based on observational SWS data from 1971 to 2019, results showed that annual mean SWS in China underwent a reversal from a continuous weakening trend to a significant strengthening trend around 2014 (Figure 1), implying that stilling may have ended in 2014. Note that the reversal had obvious regional and seasonal variations. For example, in Northeast China, Western Xinjiang and on the Tibetan Plateau, the years when both annual and seasonal mean SWS changed from a weakening to a strengthening trend were around 2013/2014, 1993/1994 and 2000, respectively; however, stilling is ongoing in the eastern and southern coastal areas, North China and Eastern Xinjiang.
In addition, by comparing the SWS data observed by China's stations with the wind speed data obtained from global surface database (GSOD and HadISD), it is found that GSOD and HadISD may have some uncertainties in characterizing the trend changes of SWS in China. The GSOD/HadISD-based results could be considered with some cautions.
Wind power is an integral part of China's strategy to achieve the carbon emission reduction targets set in the Paris Agreement. The results can provide scientific support for the layout of China's wind power industry.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0600404), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41705073, 41530532, 41506040), and the Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for
Climate Change.
See the article:
Yang Q, Li M, Zu Z, Ma Z. 2021. Has the stilling of the surface wind speed ended in China? Science China Earth Sciences, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9738-4
https://www.sciengine.com/publisher/scp/journal/SCES/64/1/10.1007/s11430-020-9738-4?slug=fulltext
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-28
In the 1970s, Fleischmann, the scientist in British, discovered that on noble metallic nanostructure, the Raman scattering of pyridine was enhanced hundreds-hold. Then, the scientists attributed the enhancement to the localized electric field highly amplified near the surface of specific noble metallic nanostructures. Thus, this phenomenon was termed surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Currently, although the enhancement mechanism of SERS is still in the debate, the SERS exhibits incomparable abilities of monitoring and sensing with high sensitivity in diverse fields ...
2021-06-28
Human's understanding of the oceans is still limited. The oceans are rich of various kinds of resource which have great exploitation potential and are far away from fully development. Marine biosafety also needs to be noticed. There are not only many animal and plant species undiscovered, but also a much larger and diverse number of microorganisms such as viruses. Traditional studies of marine viruses have focused on bacteriophage represented DNA viruses, and little is known about the genetic diversity, distribution characteristics and transmission patterns of marine invertebrate RNA viruses.
Here, CUI Jie's team have collected a total of 58 marine invertebrate samples from 3 phyla and 6 classes and ...
2021-06-28
The research team led by Prof. XIONG Wei and Prof. CANG Chunlei from Life Science and Medicine of University of Science and Technology of China, realized lysosome typing based on single lysosome metabonomic information for the first time by stablishing a single lysosome metabonomic mass spectrometry detection technology. A deeply explore to the heterogeneity changes of lysosome metabonomics in the process of cellular senescence has been achieved. The result was published on Nature Methods.
Lysosomes are organelles present in almost all eukaryotic cells. Lysosomes are essential for maintaining energy and metabolic homeostasis, signal transduction, and recovery of damaged proteins and organelles. Previous reports indicate that cellular senescence is closely related to lysosomes and their ...
2021-06-28
As the average life expectancy of residents increases, there are more and more cases of human bone tissue disease. With the upgrading of treatment methods, more and more bone tissue lesions can be treated with artificial implants for replacement. Due to the huge demand in the field of biophysical therapy, biomedical materials have very broad market prospects. In the past 10 years, the market growth rate of biomedical materials has remained at 20-25%, and the world population is nearly 6.5 billion. Statistics show that there are close to 400 million disabled people, 60 million physically disabled, and about 2 billion dental patients.
At present, there are only 35 million implanters of biomaterial devices, and the annual joint replacement volume is about 1.5 million, ...
2021-06-28
Research team, led by academician GUO Guangcan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with researchers from Sun Yat-sen University and Zhejiang University, realized two-photon quantum interference in the structure of valley-dependent topological insulators based on the valley Hall effect.
The study was published in Physical Review Letters on June 11st, 2021.
Topological photonics has a practical application prospect in the research of photonic chips due to its robust energy transport prosperities. The key to topological phase transition is to generate an energy gap at certain degenerate points by breaking either the time-reversal ...
2021-06-28
Saturated fatty acid levels unexpectedly rise in the brain during memory formation, according to END ...
2021-06-28
Newly-available scientific evidence, which could prove critical to the success of climate-related lawsuits, is often not produced in court, according to a new study published today by the Oxford Sustainable Law Programme and Environmental Change Institute.
Filling the evidentiary gap in climate litigation in Nature Climate Change, a leading interdisciplinary science journal, is the first global study on the use and interpretation of climate-science evidence in lawsuits.
The study reveals evidence submitted by litigants in 73 lawsuits across 14 jurisdictions is significantly behind state-of-the-art ...
2021-06-28
(Boston)--Amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, type-2 diabetes and other life-threatening diseases, involve pathologic deposits of normally soluble proteins or peptides as insoluble amyloid fibrils. When this happens in vital organs, such as the brain, kidney, liver and heart, it causes organ damage and, if left untreated, death. Unfortunately, the available treatment options are very limited.
Now a new study from researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) improves our understanding of how heparan sulfate and related biopolymers such as heparin, which is perhaps best known as a blood thinner, can promote amyloid deposition in various organs.
The researchers ...
2021-06-28
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - While little research exists on how and why the rates of Black youth suicide are rising, research does show the rate of suicide in Black youth younger than 13 years of age is approximately two times higher compared to white peers. From 2009 to 2019, the percentages of Black youth who considered suicide, made a suicide plan and attempted suicide all increased.
In a statement published in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers at the Nationwide Children's Hospital, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the nonprofit research institute RTI International ...
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: The rates, duration and dosages of opioids prescribed to children, adolescents and young adults from 2006 to 2018 were examined in this study.
Authors: Madeline H. Renny, M.D., of the New York University Grossman School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1832)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Has the stilling of the surface wind speed ended in China?