INFORMATION:
Researchers perform metabolomic profiling of individual enlarged lysosomes
2021-06-28
(Press-News.org) The research team led by Prof. XIONG Wei and Prof. CANG Chunlei from Life Science and Medicine of University of Science and Technology of China, realized lysosome typing based on single lysosome metabonomic information for the first time by stablishing a single lysosome metabonomic mass spectrometry detection technology. A deeply explore to the heterogeneity changes of lysosome metabonomics in the process of cellular senescence has been achieved. The result was published on Nature Methods.
Lysosomes are organelles present in almost all eukaryotic cells. Lysosomes are essential for maintaining energy and metabolic homeostasis, signal transduction, and recovery of damaged proteins and organelles. Previous reports indicate that cellular senescence is closely related to lysosomes and their internal metabolic processes.
There exists variety of lysosomes in a single cell, such as autophagy lysosome, endolysosome and so on. Studying the specificity of different types of lysosomes in the process of aging can provide new possibilities and research approaches for targeted development of drug targets for anti-aging and treatment of aging related diseases. Due to technical limitations, it is not possible to detect single lysosome metabonomics, let alone study cell aging from the perspective of single lysosome metabonomics.
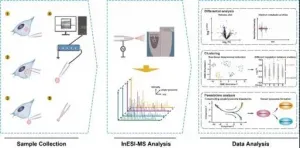
Faced with this, the research group established the first single lysosomal mass spectrometry platform. The platform is based on single lysosome patch clamp combined with ultra-low speed induction electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. It realized the detection of metabolites directly without any pretreatment in cells, and more accurately retained the information of metabolites in lysosomes.
Through the technology platform, the research group conducted in-depth research on the metabolic heterogeneity of various types of lysosomes in the process of cell aging. Based on the single lysosome metabonomics, lysosomes from at least four cell sources were divided into five subgroups, including endocytic lysosomes and autophagic lysosomes and metabolic changes of various lysosomes in the aging process are studied.
In addition, the research group also analyzed the metabolic changes of the five lysosomal subsets in the aging process, and found that the metabonomics changes of each type of lysosomal subsets were different.
This work indicates that there exists lysosome type specificity in the changes of lysosome metabolism in the process of cell aging. Studying the heterogeneity of lysosome changes in the process of aging will attribute to solve the problems of cell aging and related diseases.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel method for controlling the microstructure and performance of 3D printed human implants
2021-06-28
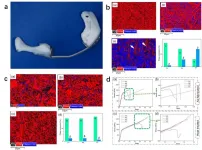
As the average life expectancy of residents increases, there are more and more cases of human bone tissue disease. With the upgrading of treatment methods, more and more bone tissue lesions can be treated with artificial implants for replacement. Due to the huge demand in the field of biophysical therapy, biomedical materials have very broad market prospects. In the past 10 years, the market growth rate of biomedical materials has remained at 20-25%, and the world population is nearly 6.5 billion. Statistics show that there are close to 400 million disabled people, 60 million physically disabled, and about 2 billion dental patients.
At present, there are only 35 million implanters of biomaterial devices, and the annual joint replacement volume is about 1.5 million, ...
USTC realizes the first on-chip valley-dependent quantum interference
2021-06-28
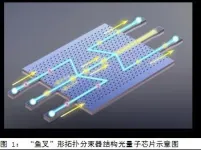
Research team, led by academician GUO Guangcan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with researchers from Sun Yat-sen University and Zhejiang University, realized two-photon quantum interference in the structure of valley-dependent topological insulators based on the valley Hall effect.
The study was published in Physical Review Letters on June 11st, 2021.
Topological photonics has a practical application prospect in the research of photonic chips due to its robust energy transport prosperities. The key to topological phase transition is to generate an energy gap at certain degenerate points by breaking either the time-reversal ...
Saturated fatty acid levels increase when making memories
2021-06-28
Saturated fatty acid levels unexpectedly rise in the brain during memory formation, according to END ...
Poor use of science jeopardizes climate lawsuits -- Oxford research
2021-06-28
Newly-available scientific evidence, which could prove critical to the success of climate-related lawsuits, is often not produced in court, according to a new study published today by the Oxford Sustainable Law Programme and Environmental Change Institute.
Filling the evidentiary gap in climate litigation in Nature Climate Change, a leading interdisciplinary science journal, is the first global study on the use and interpretation of climate-science evidence in lawsuits.
The study reveals evidence submitted by litigants in 73 lawsuits across 14 jurisdictions is significantly behind state-of-the-art ...
Model that explains how charged biopolymers enhance protein clustering in amyloid diseases
2021-06-28
(Boston)--Amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, type-2 diabetes and other life-threatening diseases, involve pathologic deposits of normally soluble proteins or peptides as insoluble amyloid fibrils. When this happens in vital organs, such as the brain, kidney, liver and heart, it causes organ damage and, if left untreated, death. Unfortunately, the available treatment options are very limited.
Now a new study from researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) improves our understanding of how heparan sulfate and related biopolymers such as heparin, which is perhaps best known as a blood thinner, can promote amyloid deposition in various organs.
The researchers ...
Understanding black youth suicide: Steps toward prevention
2021-06-28
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - While little research exists on how and why the rates of Black youth suicide are rising, research does show the rate of suicide in Black youth younger than 13 years of age is approximately two times higher compared to white peers. From 2009 to 2019, the percentages of Black youth who considered suicide, made a suicide plan and attempted suicide all increased.
In a statement published in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers at the Nationwide Children's Hospital, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the nonprofit research institute RTI International ...
Changes in opioid prescribing to children, teens, young adults
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: The rates, duration and dosages of opioids prescribed to children, adolescents and young adults from 2006 to 2018 were examined in this study.
Authors: Madeline H. Renny, M.D., of the New York University Grossman School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1832)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
Comparing health care access, quality among US states, high-income countries with universal health insurance
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: Researchers compared health care access and quality scores for the United States with high-income countries with universal health insurance coverage and compared scores among U.S. states with varying insurance coverage.
Authors: Marcia R. Weaver, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14730)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other ...
Mental health of high school students during social distancing, remote schooling during COVID-19
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: High school students in Austria were surveyed about their well-being, sleep quality, eating and symptoms of depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Christoph Pieh, M.D., of Danube University in Krems, Austria, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14866)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
Gene variant linked to unnecessary bone marrow biopsies in African Americans
2021-06-28
A gene variant that lowers white blood cell levels and is common in individuals with African ancestry contributes to unnecessary bone marrow biopsies, according to a study published June 28 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The findings from three institutions, led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, provide an example of how using genetic data could reduce a health disparity.
"We've essentially created this racial health disparity by not fully considering how genetic variation affects white blood cell levels," said Jonathan Mosley, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine and Biomedical Informatics at VUMC. "Our study supports genotyping African Americans before ...