INFORMATION:
A novel method for controlling the microstructure and performance of 3D printed human implants
2021-06-28
(Press-News.org) As the average life expectancy of residents increases, there are more and more cases of human bone tissue disease. With the upgrading of treatment methods, more and more bone tissue lesions can be treated with artificial implants for replacement. Due to the huge demand in the field of biophysical therapy, biomedical materials have very broad market prospects. In the past 10 years, the market growth rate of biomedical materials has remained at 20-25%, and the world population is nearly 6.5 billion. Statistics show that there are close to 400 million disabled people, 60 million physically disabled, and about 2 billion dental patients.
At present, there are only 35 million implanters of biomaterial devices, and the annual joint replacement volume is about 1.5 million, which is far from the actual number of replacements. Therefore, the market demand for biomedical materials has great potential. At present, common metal materials such as 316 stainless steel, pure titanium, TC4, cobalt-based alloys and precious metals are widely used in the production of human implants, such as dentures, bone plates, joints.
However, the elastic modulus of the above-mentioned materials is far greater than the Young's modulus of the human bone, and the mismatch between the Young's modulus of the metal implant and the human bone will cause physical discomfort. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an implant material with good biocompatibility, low toxicity or even non-toxicity, resistance to friction and wear, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties that match human bones. Titanium-molybdenum alloy is the preferred choice for human implants due to its non-toxicity and low elastic modulus. As an emerging manufacturing technology, additive manufacturing technology (3D printing) is very suitable for the manufacture of parts with complex shapes, and also very suitable for the preparation of customized human implants. However, the titanium-molybdenum alloy implants directly prepared by laser three-dimensional forming technology have poor uniformity in microstructure and performance.
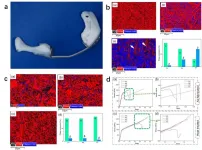
In the Light: Advanced Manufacturing magazine, some scientists from the State Key Laboratory of Coagulation Technology of Northwestern Polytechnical University proposed a way to control the uniformity of microstructure and performance through a heat treatment system, so that the tissue performance of 3D printed human implants and human bones can be achieved. Better matching and better biocompatibility. Aiming at the problem of poor uniformity of tissue properties of directly using 3D printed Ti-Mo alloy human implants, these scientists proposed a new type of triple-cycle heat treatment system, based on the transformation of the heat treatment process, through long-term heat preservation and extraordinary low cooling rate, the non-equilibrium metastable β phase transforms into the equilibrium α phase, which makes the structure of Ti-Mo alloy sample from top to bottom tend to be thermodynamically stable. The change of microstructure improves the mechanical properties of Ti-Mo alloy while maintaining good stability.
Through triple-cycle heat treatment, the microstructure and performance of the 3D printed Ti-Mo alloy are adjusted and controlled, so that the 3D printed Ti-Mo alloy human implant has better microstructure and performance stability, and thus better matches the performance of human bones. This makes 3D printed Ti-Mo alloy human implants more widely used in the biomedical field.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USTC realizes the first on-chip valley-dependent quantum interference
2021-06-28
Research team, led by academician GUO Guangcan from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with researchers from Sun Yat-sen University and Zhejiang University, realized two-photon quantum interference in the structure of valley-dependent topological insulators based on the valley Hall effect.
The study was published in Physical Review Letters on June 11st, 2021.
Topological photonics has a practical application prospect in the research of photonic chips due to its robust energy transport prosperities. The key to topological phase transition is to generate an energy gap at certain degenerate points by breaking either the time-reversal ...
Saturated fatty acid levels increase when making memories
2021-06-28
Saturated fatty acid levels unexpectedly rise in the brain during memory formation, according to END ...
Poor use of science jeopardizes climate lawsuits -- Oxford research
2021-06-28
Newly-available scientific evidence, which could prove critical to the success of climate-related lawsuits, is often not produced in court, according to a new study published today by the Oxford Sustainable Law Programme and Environmental Change Institute.
Filling the evidentiary gap in climate litigation in Nature Climate Change, a leading interdisciplinary science journal, is the first global study on the use and interpretation of climate-science evidence in lawsuits.
The study reveals evidence submitted by litigants in 73 lawsuits across 14 jurisdictions is significantly behind state-of-the-art ...
Model that explains how charged biopolymers enhance protein clustering in amyloid diseases
2021-06-28
(Boston)--Amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, type-2 diabetes and other life-threatening diseases, involve pathologic deposits of normally soluble proteins or peptides as insoluble amyloid fibrils. When this happens in vital organs, such as the brain, kidney, liver and heart, it causes organ damage and, if left untreated, death. Unfortunately, the available treatment options are very limited.
Now a new study from researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) improves our understanding of how heparan sulfate and related biopolymers such as heparin, which is perhaps best known as a blood thinner, can promote amyloid deposition in various organs.
The researchers ...
Understanding black youth suicide: Steps toward prevention
2021-06-28
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - While little research exists on how and why the rates of Black youth suicide are rising, research does show the rate of suicide in Black youth younger than 13 years of age is approximately two times higher compared to white peers. From 2009 to 2019, the percentages of Black youth who considered suicide, made a suicide plan and attempted suicide all increased.
In a statement published in JAMA Pediatrics, researchers at the Nationwide Children's Hospital, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the nonprofit research institute RTI International ...
Changes in opioid prescribing to children, teens, young adults
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: The rates, duration and dosages of opioids prescribed to children, adolescents and young adults from 2006 to 2018 were examined in this study.
Authors: Madeline H. Renny, M.D., of the New York University Grossman School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1832)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
Comparing health care access, quality among US states, high-income countries with universal health insurance
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: Researchers compared health care access and quality scores for the United States with high-income countries with universal health insurance coverage and compared scores among U.S. states with varying insurance coverage.
Authors: Marcia R. Weaver, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14730)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other ...
Mental health of high school students during social distancing, remote schooling during COVID-19
2021-06-28
What The Study Did: High school students in Austria were surveyed about their well-being, sleep quality, eating and symptoms of depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Christoph Pieh, M.D., of Danube University in Krems, Austria, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.14866)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
Gene variant linked to unnecessary bone marrow biopsies in African Americans
2021-06-28
A gene variant that lowers white blood cell levels and is common in individuals with African ancestry contributes to unnecessary bone marrow biopsies, according to a study published June 28 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The findings from three institutions, led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, provide an example of how using genetic data could reduce a health disparity.
"We've essentially created this racial health disparity by not fully considering how genetic variation affects white blood cell levels," said Jonathan Mosley, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine and Biomedical Informatics at VUMC. "Our study supports genotyping African Americans before ...
Face masks that can diagnose COVID-19
2021-06-28
Most people associate the term "wearable" with a fitness tracker, smartwatch, or wireless earbuds. But what if you could wear cutting-edge biotechnology in your clothing, and it could warn you when you were exposed to something dangerous?
A team of researchers from the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has found a way to embed synthetic biology reactions into fabrics, creating wearable biosensors that can be customized to detect pathogens and toxins and alert the wearer.
The team has integrated this technology into standard face masks to detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in a patient's breath. The button-activated mask ...