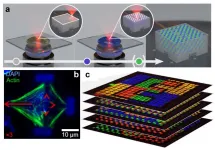
(Press-News.org) A RMIT-led international collaboration published this week has achieved record-high electron doping in a layered ferromagnet, causing magnetic phase transition with significant promise for future electronics
Control of magnetism (or spin directions) by electric voltage is vital for developing future, low-energy high-speed nano-electronic and spintronic devices, such as spin-orbit torque devices and spin field-effect transistors.
Ultra-high-charge, doping-induced magnetic phase transition in a layered ferromagnet allows promising applications in antiferromagnetic spintronic devices.
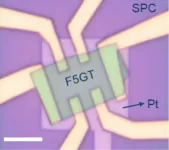
The FLEET collaboration of researchers at RMIT, UNSW, the University of Wollongong and FLEET partner High Magnetic Field Laboratory (China) demonstrates for the first time that ultra-high electron doping concentration (above 1021 cm-3) can be induced in the layered van der Waals (vdW) metallic material Fe5GeTe2 by proton intercalation, and can further cause a transition of the magnetic ground state from ferromagnetism to antiferromagnetism.
TUNING MAGNETISM IN THE VDW FERROMAGNET Fe5GeTe2 (F5GT)
The emergence of layered, vdW magnetic materials has expedited a growing search for novel vdW spintronic devices.
Compared to itinerant ferromagnets, antiferromagnets (AFMs) have unique advantages as building blocks of such future spintronic devices. Their robustness to stray magnetic fields makes them suitable for memory devices, and the AFM-based spin-orbit torque devices require a lower current density than that in ferromagnets.
However currently vdW itinerant antiferromagnets are still scarce.
Besides directly synthesizing a vdW antiferromagnet, another possible method toward this function is to induce a magnetic phase transition in an existing vdW itinerant ferromagnet.
"We chose to work with newly synthesised vdW itinerant ferromagnet Fe5GeTe2 (F5GT)" says the study's first author, FLEET Research Fellow Dr Cheng Tan (RMIT).
"Our previous experience on Fe3GeTe2 ( END
Transforming the layered ferromagnet F5GT for future spintronics
Record-high electron doping in a layered ferromagnet
2021-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Honey, we shrunk the intense XUV laser
2021-06-28
The invention of the laser has opened the era of nonlinear optics, which today plays an important role in many scientific, industrial and medical applications. These applications all benefit from the availability of compact lasers in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The situation is different at XUV wavelengths, where very large facilities (so called free-electron lasers) have been built to generate intense XUV pulses. One example of these is FLASH in Hamburg that extends over several hundred meters. Smaller intense XUV sources based on HHG have also been developed. However, these sources still have a footprint of tens of meters, and have so far only been demonstrated at a few universities and research institutes worldwide. ...
Sunflower peptide as 'template' for potential analgesic
2021-06-28
A naturally occurring peptide in sunflower seeds was synthetically optimised and has now been identified as a potential drug for treating abdominal pain or inflammation (in the gastrointestinal tract, abdominal area and/or internal organs). That is the finding of an international study led by Christian Gruber from MedUni Vienna's Institute of Pharmacology (Center for Physiology and Pharmacology), which was conducted jointly with the University of Queensland and Flinders University in Australia and has now been published.
The scientific aim of the study is to find analgesics that are only active in the periphery and do not cross the blood-brain barrier, as an alternative to commonly used synthetic opioids. Gruber explains the background: "Morphine was one of the first ...
New tools for pandemic prevention research: DNA sequencing from water and leech
2021-06-28
In a new scientific investigation headed by the German Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW), water from African and Mongolian waterholes as well as bloodmeals from Southeast Asian leeches were assessed for the ability to retrieve mammalian viruses without the need to find and catch the mammals. The scientists analysed the samples using high throughput sequencing to identify known viruses as well as viruses new to science. Both approaches proved to be suitable tools for pandemic prevention research as they allow finding and monitoring reservoirs of wildlife viruses. For example, a novel coronavirus most likely associated with Southeast Asian deer species was identified. The results are ...
HKUST scientists develop simple blood test for early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2021-06-28
An international research team led by HKUST has developed a simple but robust blood test from Chinese patient data for early detection and screening of Alzheimer's disease (AD) for the first time, with an accuracy level of over 96%.
Currently, doctors mainly rely on cognitive tests to diagnose a person with AD. Besides clinical assessment, brain imaging and lumbar puncture are the two most commonly used medical procedures to detect changes in the brain caused by AD. However, these methods are expensive, invasive, and frequently unavailable in many countries.
Now, a team led by Prof. Nancy IP, Vice-President for Research and Development at HKUST, has identified 19 out of the 429 plasma proteins associated with AD to form ...
Researchers develop world-first weight loss device
2021-06-28
University of Otago, New Zealand, and UK researchers have developed a world-first weight-loss device to help fight the global obesity epidemic.
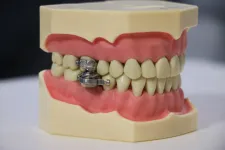
DentalSlim Diet Control is an intra-oral device fitted by a dental professional to the upper and lower back teeth. It uses magnetic devices with unique custom-manufactured locking bolts. It allows the wearer to open their mouths only about 2mm, restricting them to a liquid diet, but it allows free speech and doesn't restrict breathing.
Participants in a Dunedin-based trial lost an average of 6.36kg in two weeks and were motivated to continue with their weight loss ...
Coral enhance its environmental adaptability by adjusting trophic status
2021-06-28
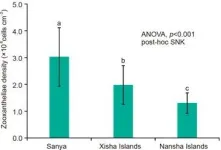
Coral bleaching and the ecological degradation of coral reefs have become increasingly severe due to the global warming and human activities. As "mixotrophic" organisms, scleractinian coral can not only obtain energy through photosynthesis of symbiotic zooxanthellae (autotrophy), but also ingest nutrients in seawater through the coral host (heterotrophy). However, the influence of coral's trophic flexibility on environmental adaptability remains unclear. Coral reefs are widely distributed in the South China Sea (SCS), spanning about 20 latitudes from north to south. The environmental conditions of coral reef areas at different latitudes are significantly different. ...
Small p values may not yield robust findings: An example using REST-meta-PD
2021-06-28
Thousands of scientific papers describing the inner workings of the brain and its dysfunction have been published using resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging (RS-fMRI). This powerful tool allows researchers to look at each cubic millimeter of the brain, in voxels - the 3D version of a pixel. The average brain is well over 1,000,000 cubic mm, so researchers need to perform multiple comparisons correction (MCC) to reduce the possibility of making false claims, i.e., reduce the false positive rates. As part of this MCC, a smaller p value threshold is widely recommended for declaring ...
Multi-material multi-photon 3D laser micro- and nanoprinting
2021-06-28
Multi-photon approaches provide printing rates of up to about ten million voxels per second. And, multi-photon-based 3D approaches structure matter with a resolution approaching sub-micrometer and nanometer feature sizes. Such spatial resolution is crucial for many applications in photonics and electronics and is inaccessible to most other 3D additive manufacturing approaches. However, the vast majority of 3D printed objects and devices made along these lines has been composed of only a single polymeric material. Multi-material architectures are much less investigated ...
Has the stilling of the surface wind speed ended in China?
2021-06-28
The most significant feature of global land surface wind speed (SWS) recently is the long-term weakening trend since the 1960s, that is, the phenomenon known as global terrestrial stilling. Many studies have found that stilling is widespread worldwide. It has seriously affected the ecological environment and social economy, especially restricted the sustainable development of the wind energy industry. It is found that the stilling reversed around 2010 and global SWS is strengthening; then, has the stilling of surface wind speed ended in China? A recent study systematically answered this question. The related paper titled "Has the stilling of the surface wind ...
Attomolar sensing: Fabrication of surface-enhanced raman scattering substrate
2021-06-28
In the 1970s, Fleischmann, the scientist in British, discovered that on noble metallic nanostructure, the Raman scattering of pyridine was enhanced hundreds-hold. Then, the scientists attributed the enhancement to the localized electric field highly amplified near the surface of specific noble metallic nanostructures. Thus, this phenomenon was termed surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Currently, although the enhancement mechanism of SERS is still in the debate, the SERS exhibits incomparable abilities of monitoring and sensing with high sensitivity in diverse fields ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Transforming the layered ferromagnet F5GT for future spintronicsRecord-high electron doping in a layered ferromagnet