(Press-News.org) LOUISVILLE, Ky. - Historically, most large-scale immunogenomic studies - those exploring the association between genes and disease - were conducted with a bias toward individuals of European ancestry. Corey T. Watson, Ph.D., assistant professor in the University of Louisville Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, is leading a call to actively diversify the genetic resources he and fellow immunogenomics researchers use in their work to advance genomic medicine more equitably.
Watson, along with UofL post-doctoral fellow Oscar Rodriguez, Ph.D., and visiting fellow Yana Safonova, Ph.D., are part of an international group of researchers who say the narrow studies limit their ability to identify variation in human adaptive immune responses across populations.
"We need to better understand how genetics influences immune system function by studying population cohorts that better represent the diversity observed across the globe if we are to fully understand disease susceptibility, as well as design more tailored treatments and preventative measures," Watson said.
In an article published in Nature Methods, Diversity in immunogenomics: the value and the challenge, the group advocates for resources used in immunogenomics research to actively include and specifically identify additional populations and minority groups. They say such diversity will make their research more relevant and help in understanding population and ancestry-specific gene-associated disease, leading to improvements in patient care.
"As scientists, we have a say in which populations are investigated. Therefore, it is critical for us to be actively inclusive of individuals representative of the world we live in. This is especially critical for genes that are as diverse and clinically relevant as those that encode antibodies and T cell receptors," Rodriguez said.
Watson's research focuses on immune function and molecular genetics. His team is studying a specific area of the genetic code that controls antibody function to better understand how differences in an individual's genes determine their susceptibility to certain diseases or immune responses to vaccines.
In collaboration with Melissa Smith, Ph.D., assistant professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, the team is conducting the largest sequencing efforts of the antibody gene regions in humans and in animal models, Watson said.
"Specifically in humans, we are working to build catalogs of genetic variation in samples from multiple ethnic backgrounds and are engaged in projects that seek to understand how this genetic variation influences the immune response in infection, vaccination and other disease contexts," he said.
Watson is involved in efforts to improve the resources and data standards for antibody and T cell receptor genes for immunogenomics researchers around the world.
The article in Nature Methods was co-authored by researchers from the United States, Canada, Norway, France, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Israel, South Africa, Nigeria, Chile, Peru, China, Japan, Taiwan and French Polynesia with expertise in biomedical and translational research, population and public health genetics, health disparities and computational biology as well as immunogenomics.
INFORMATION:
PHILADELPHIA -- (June 29, 2021) -- New biomarkers that predict HIV remission after antiretroviral therapy (ART) interruption are critical for the development of new therapeutic strategies that can achieve infection control without ART, a condition defined as functional cure. These biomarkers can also provide critical clues into the biological mechanisms that control HIV replication after stopping therapy, and can help design novel strategies to cure HIV. Scientists at The Wistar Institute have identified metabolic and glycomic signatures in the blood of a rare population of HIV-infected individuals who can naturally sustain viral suppression after ART cessation, known as post-treatment controllers. These findings were published in Nature ...
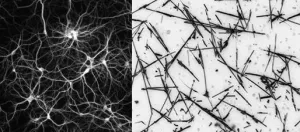
Scientists at the University of Sydney and Japan's National Institute for Material Science (NIMS) have discovered that an artificial network of nanowires can be tuned to respond in a brain-like way when electrically stimulated.
The international team, led by Joel Hochstetter with Professor Zdenka Kuncic and Professor Tomonobu Nakayama, found that by keeping the network of nanowires in a brain-like state "at the edge of chaos", it performed tasks at an optimal level.
This, they say, suggests the underlying nature of neural intelligence is physical, and their discovery opens an exciting avenue for the development of artificial intelligence.
The study is published today in Nature Communications.
"We used wires 10 micrometres long and no thicker than 500 nanometres ...
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have identified a protein that could be used to aid in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Findings from the new study suggest that a protein called pentraxin 3 (PTX3) may be a specific diagnostic biomarker - or biological measure - for pancreatic cancer, with the ability to differentiate pancreatic cancer from other non-cancerous conditions of the pancreas.
The research was published today in npj Precision Oncology, and primarily funded by the Pancreatic Cancer Research Fund, Barts Charity and Cancer Research UK.
PTX3 levels elevated in patients with pancreatic ...
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Maria Cerrillo Martinez presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Fertility patients who have a poor response to ovarian stimulation represent a stubborn challenge in IVF. Few eggs are collected, success rates are low, and several treatments are usually needed to achieve pregnancy (if at all). Clinical guidelines indicate that increasing the drug dose for stimulation or applying any of several adjunct therapies are of little benefit. Now, however, a study assessing two cycles of ovarian stimulation and two egg collections in the same menstrual cycle may yet provide ...
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Gulam Bahadur presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2020: Studies indicate that the optimal and safe number of oocytes needed for achieving an ongoing pregnancy is between six and 15. However, the use of egg freezing, frozen embryo replacement (FER) cycles and aggressive stimulation regimes has increased this number in order to boost success rates in older women and in poor responders who produce fewer eggs. What is not known is the impact of numbers of eggs retrieved and of over-stimulation practices on the health of patients, and on their emotional and financial well-being.
Now, a retrospective observational ...
After centuries of human impact on the world's ecosystems, a new study from Flinders University details an example of how a common native bee species has flourished since the very first land clearances by humans on Fiji.
In a new paper in Molecular Ecology (DOI: 10.1111/mec.16034), research led by Flinders University explores a link between the expansion of Homalictus fijiensis, a common bee in the lowlands of Fiji, which has increased its spread on the main island Viti Levu alongside advancing land clearance and the introduction of new plants and weeds to the environment.
"Earlier research connected the relatively recent population expansion to warming climates, ...
What is unique about the study is the combination of interviews with current and former people in prison, custodial professionals, and healthcare providers to identify and understand barriers in delivering high-quality healthcare and support to those in custody. In addition, researchers gathered data on the number, types and stages of cancers diagnosed in patients within prisons.
Moving forward, the researchers believe that findings from this study will help inform prison cancer care policy and develop priorities for improving it within the prison system. The research was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the research partner of the NHS, public health and social ...
Arlington, Va., June 29, 2021 - In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, infection preventionists at two Southern California hospitals took extreme measures to stop the spread of a deadly fungus that has emerged in the U.S. and around the world. The two will detail their proactive responses in oral presentations today at the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology's (APIC's), 48th Annual Conference.
In separate responses, Scripps Memorial in La Jolla and UCLA Health in Los Angeles isolated suspected or confirmed patients, worked closely with public health departments and information technology and lab teams at their facilities, and implemented aggressive measures ...
The devastating 2012 - 2016 drought in California triggered widespread tree cover loss and die-offs of a variety of species in the region. A new study in the open access journal Frontiers in Climate is the first to show that California's iconic blue oak (Quercus douglasii) woodlands have also decreased by more than 1,200 km2. By another metric, which reflects the altered or deteriorating condition of the tree cover, the blue oak range has lost over 600 km2 in addition. These findings highlight the need to raise awareness about the vulnerability of these ecosystems and to adapt conservation strategies to increasing climate extremes.
"Our ...
Black men most likely to benefit from advanced prostate cancer therapies are 11 percent less likely to get them than non-Black men. This happens despite apparent equal opportunities in obtaining health care services, a new study in American veterans shows.
Publishing in the journal Cancer online June 29, the study showed that Black male veterans were slightly (5 percent) more likely to receive radiation or surgery for prostate cancer than non-Black men and that veterans of all races likely to benefit from such definitive therapy were also 40 percent more likely to get it compared to those who did not need it.
Led by researchers from NYU Langone Health and Perlmutter Cancer Center, the new analysis showed ...