Microbes feast on crushed rock in subglacial lakes beneath Antarctica
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) Pioneering research has revealed the erosion of ancient sediments found deep beneath Antarctic ice could be a vital and previously unknown source of nutrients and energy for abundant microbial life.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment journal, sheds new light on the many compounds supporting various microbes which form part of a huge subglacial ecosystem.
Lead author Dr Beatriz Gill Olivas, a Post-Doctoral Research Associate at the University of Bristol, said: "Although the study focused on samples obtained from a single subglacial lake, the results could have much wider implications. Subglacial Lake Whillans is part of a large interconnected hydrological system, so erosion taking place upstream could represent a potential source of biologically important compounds to this and other lakes within the system that might harbour thriving communities of microbial life."
The international research team replicated erosion processes in ice sheets by crushing sediments extracted from Lake Whillans, a subglacial lake in Antarctica, spanning around 60 km2, some 800m below the ice surface, then wetting these sediments and keeping them at 0 °C without oxygen, to approximate subglacial conditions.
Findings showed a single crushing event down to a depth of 10 cm, followed by a 41-day incubation period, of these same sediments has the potential to provide up to a quarter (24 per cent) of the estimated methane required by methanotrophs, tiny microbes which depend on methane as their source of carbon and energy, present in these environments. Substantial concentrations of hydrogen and carbon dioxide were also produced during crushing and incubation. These gases could potentially be used by methane-generating microbes, called methanogens, to produce enough methane which would help explain its widely varying levels within Lake Whillans.
Another previously unidentified finding was the detection of measurable concentrations of ammonium in water after incubation with crushed sediments. This is of particular significance to Lake Whillans, where there is an abundance of microbial taxa that have the potential to derive energy from ammonium oxidation, a process known as nitrification. The study demonstrated a single high-energy crushing event, followed by the same incubation period, has the potential to produce more than the annual ammonium demand (120 per cent) within the lake.
"Our previous understanding suggests the structure and function of subglacial ecosystems depends on the presence of redox species and redox gradients within liquid water. This study shows the process of erosion could potentially split water on freshly abraded mineral surfaces and produce hydrogen (a reducing end member species) and hydrogen peroxide (a highly oxidizing compound), creating a redox gradient and providing a previously unrecognised source of energy to microbial ecosystems," Dr Gill Olivas explained.
"Only two previous studies have looked at the potential influence of erosion on subglacial energy and nutrient sources, which involved crushing largely unweathered rock samples. This is the first study to use highly weathered, ancient marine sediments, yet concentrations of gases measured largely agreed with previous results."
Dr Gill Olivas added: "Whilst these experiments do not reflect the true extent of erosion under glaciers, they do hint at the potential for the crushing of sediments to supply important sources of nutriment to subglacial ecosystems. Further study is now needed to identify the complete range of reactions resulting directly from erosion processes and how they may vary with differences in the underlying sediment."
INFORMATION:
Paper
'Subglacial erosion has the potential to sustain microbial processes in Subglacial Lake Whillans, Antarctica' in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment by Beatriz Gill Olivas et al.
Notes to editors
Dr Beatriz Gill Olivas is available for interview. To schedule this, please email b.gillolivas@bristol.ac.uk and Victoria Tagg, Media & PR Manager (Research) at the University of Bristol: victoria.tagg@bristol.ac.uk
Pictures
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u4/oc20541/cZaG1n4K8avOooiM_rropw1Y6/
Caption: Photo of core catcher used to extract subglacial sediments.
Credit: John Priscu
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u4/oc20541/oHwU0KX1XdN7MrpuotdU2A1X2/
Caption: Photo of the field location including the tents and labs set up at Subglacial Lake Whillans, Antarctica
Credit: John Priscu
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u4/oc20541/_GphuYnUKJlkYIO8BZmhkA1Xx/
Caption: Taken from a different project, SALSA, which involved drilling another subglacial lake, Lake Mercer, the photo shows the UV collar, borehole and hot water drill.
Credit: Billy Collins
https://fluff.bris.ac.uk/fluff/u3/oc20541/jgSn9XYxeM12YZr3flm6ww1XK/
Caption: Taken from the SALSA project at Subglacial Lake Mercer, the photo shows the UV collar in the borehole.
Credit: Kathy Kasic
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
During summer 2020, the Yangtze River basin experienced persistent, record-breaking meiyu rainfall. Likewise, the region suffered from severe flooding and water damage as accumulated rainfall broke records dating back to 1954. Regions outside the meiyu rain belt received significant summer rainfall as well, including Beijing, located in northeastern China.
Typically, an above average meiyu rainfall season follows a strong El Niño during the previous winter. However, summer 2020 followed a neutral El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) event. Therefore, scientists are working ...
2021-06-29
A stimulating environment keeps the "hippocampus" - which is the brain's memory control center - young, so to speak. Causes of this are molecular mechanisms that affect gene regulation. These current findings from studies in mice provide clues as to why an active, varied life can help preserve mental fitness in old age. Researchers from the DZNE and the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) at the Technische Universität Dresden report on this in the journal Nature Communications.
Human DNA - and this also applies to mice - contains thousands of genes. However, it is not only the genetic blueprint that is decisive for the function of a cell and whether it is healthy or not, but above all which genes can be switched on or off. ...
2021-06-29
FECYT - Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology - presented today at the headquarters of the National Museum of Science and Technology, MUNCYT, IN Alcobendas, the results of the third Social Perception Survey of scientific aspects of the COVID-19 in a debate moderated by Pampa García Molina, Editor-in-Chief of the SINC Agency, in which Raquel Yotti, Director of the Carlos III Health Institute of Madrid, Josep Lobera, Professor of Sociology at the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) and scientific director of the Social Perception Survey on the scientific aspects of COVID-19 and ...
2021-06-29
Polymers are long, chain-like molecules which are everywhere in biology. DNA and RNA are polymers formed by many consecutive copies of nucleotides coupled together. When being transported within or between cells, these biological polymers must pass through nanometre-sized holes called "nanopores".
This process also underlies a rapidly developing method for analysing and sequencing DNA called nanopore sensing.
The study, published in the journal END ...
2021-06-29
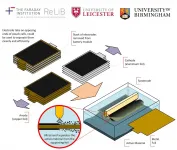
Researchers at the University of Leicester have developed a new method to recycle electric vehicle batteries using a ground-breaking new approach that many will have experienced in the dentist's chair.
The Faraday Institution project on the recycling of lithium-ion batteries (ReLiB) led by Professor Andy Abbott at the University of Leicester used a new method, involving ultrasonic waves, to solve a critical challenge: how to separate out valuable materials from electrodes so that the materials can be fully recovered from batteries at the end of their life.
Current recycling ...
2021-06-29
A new corona test developed at the University Hospital Bonn can analyze a large number of swabs simultaneously using sequencing technology and has a similarly high sensitivity as the common qPCR test. The innovative method offers great potential, especially for systematic testing in daycare centers, schools or companies. Today, the results of the study on the new Corona test have been published in the renowned journal "Nature Biotechnology".
Bonn, 6/29/2021 - In addition to vaccination, systematic testing of the population remains of central importance in order to effectively monitor and contain the spread of infections during the Coronavirus pandemic. Only in this way can the spread of the virus be effectively monitored and ...
2021-06-29
Crystallization is one of the most fundamental processes found in nature - and it's what gives minerals, gems, metals, and even proteins their structure.
In the past couple of decades, scientists have tried to uncover how natural crystals self-assemble and grow - and their pioneering work has led to some exciting new technologies - from the quantum dots behind colorful QLED TV displays, to peptoids, a protein-mimic that has inspired dozens of biotech breakthroughs.
Now, a research team led by scientists at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley has developed a nanoparticle composite that grows ...
2021-06-29
The electronic properties of graphene can be specifically modified by stretching the material evenly, say researchers at the University of Basel. These results open the door to the development of new types of electronic components.
Graphene consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. The material is very flexible and has excellent electronic properties, making it attractive for numerous applications - electronic components in particular.
Researchers led by Professor Christian Schönenberger at the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have now studied how the material's ...
2021-06-29
Mineral resources from Chile are of great importance to Germany. According to statistics from the World Bank, thousands of tons of valuable minerals are imported from the South American country every year, including raw materials for lithium-ion batteries. But their extraction causes ecological and social problems: "The use of the limited freshwater resources in northern Chile for mining regularly fuels conflicts with the local population," says Professor Thomas Kohl from KIT's Institute of Applied Geosciences (AGW). "Northern Chile is one of the driest regions on earth, but has extensive geothermal resources. With a novel type of plant, it is not only possible to generate electricity in a climate-friendly way, but also to extract ...
2021-06-29
When positioned strategically, garment seams sewn with conductive yarn can be used to accurately track body motion, according to computer scientists at the University of Bath in the UK. Best of all, these charged seams are able to respond to subtle movements that aren't picked up by popular fitness trackers, such as watches and wristbands.
In a new study, the Bath researchers found that clothing made with conductive seams can be analysed to identify the wearer's movements.
PhD student Olivia Ruston, who presented the work at the ACM Designing Interactive Systems conference this month, said: "There are lots of potential applications for conductive yarn in any activity where you want to identify and improve ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microbes feast on crushed rock in subglacial lakes beneath Antarctica