(Press-News.org) Mineral resources from Chile are of great importance to Germany. According to statistics from the World Bank, thousands of tons of valuable minerals are imported from the South American country every year, including raw materials for lithium-ion batteries. But their extraction causes ecological and social problems: "The use of the limited freshwater resources in northern Chile for mining regularly fuels conflicts with the local population," says Professor Thomas Kohl from KIT's Institute of Applied Geosciences (AGW). "Northern Chile is one of the driest regions on earth, but has extensive geothermal resources. With a novel type of plant, it is not only possible to generate electricity in a climate-friendly way, but also to extract drinking water and even mineral resources at the same time." The AGW team of BrineMine, a German-Chilean research project, is developing the necessary strategies and technologies.
AGW has a long history of cooperation in the field of geothermal research in Chile. Its main partner is the Centro de Excelencia en Geotermia de Los Andes (CEGA). "BrineMine demonstrates how well the cooperation between Chilean and German institutions works," says Professor Diego Morata, director of CEGA. "Sustainable development, achieved by the combination of geothermal and green mining, can benefit Europe and the Andean region alike."
First Demonstration Plant on the Upper Rhine Graben
Part of the transdisciplinary research initiative is dedicated to the geochemical and geothermal potential of thermal wells in Chile in order to identify suitable sites. A data survey is being conducted to determine the raw materials potential with a focus on the thermal fields of the Atacama Desert. In addition, the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) takes part in the BrineMine project by developing the plant technology for later industrial use. It is based on a novel process chain: First, heat from the geothermal brine is used for energy recovery. The cooled liquid, which has a relatively low concentration, is then pre-concentrated by reverse osmosis; at the same time, drinking water is obtained. The brine concentrate is then further concentrated by membrane distillation until it is saturated. "The thermal energy required for the entire process can be covered directly from the excess heat of the power plant process," explains project manager Dr. Joachim Koschikowski from ISE. "We have already set up a demonstration plant in a geothermal power plant in the Upper Rhine Graben and successfully integrated key components into ongoing power plant operations."
Optimization of Processes for Raw Material Mining
Most of the process steps are based on proven methods, but they have never been combined in this way. Detailed research is required, because, for example, both concentration and cooling increase the risk of silicate deposits. "Conventional strategies for silicate removal would greatly impair the extraction of the resources. Without water treatment, the technical plant components would be damaged," explains Valentin Goldberg from KIT's AGW. The researchers found a viable solution by changing the pH value of the brine and adding divalent cations (e.g. calcium or magnesium). "Our silicate removal method is fast and effective. Most importantly, it has no negative impact on raw material extraction," Goldberg says. The researchers describe this new approach in the Geothermics journal.
Before the first plants can be installed in Chile, further details about the process need to be clarified. In addition, specific models for economic operation are also being developed.
INFORMATION:
About BrineMine
BrineMine was initiated in 2019 by Professor Thomas Kohl and Dr. Sebastian Held. The German-Chilean research consortium is coordinated by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE). Other project partners besides KIT are the companies Geothermie Neubrandenburg (GTN) and SolarSpring membrane solutions in Germany as well as Fraunhofer Chile and Centro de Excelencia en Geotermia de Los Andes (CEGA) in Chile. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is funding the project with approx. EUR 1.5 million. The great interest of the Chilean industry in BrineMine became evident at a webinar hosted by the German-Chilean Chamber of Industry and Commerce, which was attended by hundreds of participants. The Chilean Ministry of Energy also provides support for the project.
Recording of webinar: https://ecominingconcepts.cl/de/summary-brinemine-sustainable-mineral-and-fresh-water-extraction-from-geothermal-brines-in-chile
More information about BrineMine:
https://geothermics.agw.kit.edu/brinemine.php
https://www.bmbf-client.de/projekte/brinemine
Original publications
Spitzmüller, L., Goldberg, V., Held, S., Grimmer, J. C., Winter, D., Genovese, M., Koschikowski, J,. and Kohl, T. (2021): Selective silica removal in geothermal fluids: Implications for applications for geothermal power plant operation and mineral extraction, Geothermics.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102141
Goldberg, V., Winter, D., Nitschke, F., Rath, M., Held, S., Spitzmüller, L., Budach, I., Pavez, M., Morata, D., Koschikowski J. and Kohl, T. (2021). The potential of raw material extraction from thermal brines-Successful milestones of the BrineMine project, Oil gas, DOI 10.19225/210306
https://geothermics.agw.kit.edu/downloads/OGA_001_21_026-033_Goldberg_et_al_HP-Liz.pdf
Details about the KIT Energy Center: https://www.energy.kit.edu/index.php
Contact for this press release:
Dr Martin Heidelberger, Editor/Press Officer, Phone: +49 721 608-41169, E-mail: martin.heidelberger@kit.edu
Being "The Research University in the Helmholtz Association", KIT creates and imparts knowledge for the society and the environment. It is the objective to make significant contributions to the global challenges in the fields of energy, mobility, and information. For this, about 9,600 employees cooperate in a broad range of disciplines in natural sciences, engineering sciences, economics, and the humanities and social sciences. KIT prepares its 23,300 students for responsible tasks in society, industry, and science by offering research-based study programs. Innovation efforts at KIT build a bridge between important scientific findings and their application for the benefit of society, economic prosperity, and the preservation of our natural basis of life. KIT is one of the German universities of excellence.
When positioned strategically, garment seams sewn with conductive yarn can be used to accurately track body motion, according to computer scientists at the University of Bath in the UK. Best of all, these charged seams are able to respond to subtle movements that aren't picked up by popular fitness trackers, such as watches and wristbands.
In a new study, the Bath researchers found that clothing made with conductive seams can be analysed to identify the wearer's movements.
PhD student Olivia Ruston, who presented the work at the ACM Designing Interactive Systems conference this month, said: "There are lots of potential applications for conductive yarn in any activity where you want to identify and improve ...
Mice are an important animal model of human vision due to the powerful genetic tools available in this species. However, mouse vision was thought to be different to that of humans because humans have a region of the retina specialized for fine details called the 'fovea' whereas mice do not. Researchers from the Netherlands Institute of Neuroscience (NIN) have shown that the visual cortex of mice does contain a region of enhanced visual sensitivity dubbed the 'focea', making the mouse a better model of human vision than previously expected. The findings were published ...
Lithia, Florida -- June 29, 2021 -- Surgical resident training has traditionally occurred in a master-apprentice-type relationship, with graduated responsibilities until trainees are expected to perform procedures on their own. Given recent changes in the health care system, including reduced operating room time, increased difficulty of procedures and working hour restrictions, there is less time for residents to learn using traditional methods.
Researchers from the University of Manitoba and the Pan Am Clinic recently published a paper in the journal Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, ...
Aerosol generated by playing woodwind and brass instruments is less than that produced when vocalising (speaking and singing) and is no different than a person breathing, new research has found. The findings, published online in the journal Aerosol Science and Technology, could be crucial to developing a roadmap for lifting COVID-19 restrictions in the performing arts, which have been significantly restricted since the start of the pandemic.
The research project, known as PERFORM (ParticulatE Respiratory Matter to InForm Guidance for the Safe Distancing of PerfOrmeRs in a COVID-19 PandeMic), was supported by Public Health England, the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS), and UKRI and was carried out by a collaborative team from ...
The death of neurons specialised in the synthesis of dopamine, one of the brain's main neurotransmissors, deteriorates the motor and cognitive capacities of those with Parkinson's disease. The loss of these neurons is related to alpha-synuclein aggregation. Recent studies show that oligomers, the initial aggregates of this protein, are the most pathogenic forms of α-synuclein and are responsible for the spreading of the disease in the brain.
Therefore, one of the more promising approaches in fighting this disorder consists in neutralising these oligomers and, thus, slow down the pathological progression. ...
During the last twenty years, the trading in stock markets has undergone significant changes. Researchers from the University of Turku and the University of Palermo have investigated the role of high-frequency traders in the markets.
Technological evolution and innovations both in the technology used by stock exchanges and the resources of the traders using their services have made faster trading possible. As a result, high-frequency trading in sub millisecond scale has increased.
However, not everyone has the opportunity to use high-frequency trading, and generally, the scales can be anything from microseconds to tens of thousands of seconds. The role of high-frequency traders has given rise to broad debate over ...
HERSHEY, Pa. -- A new study by researchers at Penn State College of Medicine indicates that people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) -- approximately 38 million worldwide -- are more likely to have suicidal thoughts and die from suicide than members of the general population. The researchers said that despite significant medical advancements related to HIV treatment and patients' quality of life, risk of suicide in these patients is high and health care providers should prioritize mental health screenings in this population.
According to the World Health Organization, roughly 800,000 people worldwide die from suicide annually. Among ...
Tuesday, 29 June 2021 - New research has shown that early testing for blood clots in patients who had received the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine led to them being treated successfully, highlighting the need for heightened awareness of the risk among doctors.
The work, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and the National Coagulation Centre at St James's Hospital, is published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Unusual blood clots with low blood platelets have been recognised as a very rare complication of the AstraZeneca vaccine. However, with increased awareness, ...
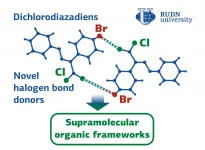
RUDN University chemists derived molecules that can assemble into complex structures using chlorine and bromine halogen atoms. They bind to each other as "velcro" - chlorine "sticks" to bromine, and vice versa. As a result supramolecules are assembled from individual molecules. The obtained substances will help to create supramolecules with catalytic, luminescent, conducting properties. The study is published in Mendeleev Communications.
Supramolecules are the structures made of several molecules. Individual molecules are combined, for example, by self-assembly or without external control. The resulting structure has properties that the molecules did not have individually. That is the way to create new materials, catalysts, molecular machines for ...
For the first time, scientists detected gravitational waves caused by mergers between black holes and neutron stars. Researchers from LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA detected the two gravitational wave events--from distances of more than 900 million light-years away--within a span of 10 days in January 2020 during the second half of LIGO and Virgo's third observing run. Astrophysical Journal Letters published the results and their implications today: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac082e.
Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology's Center ...