(Press-News.org) During the last twenty years, the trading in stock markets has undergone significant changes. Researchers from the University of Turku and the University of Palermo have investigated the role of high-frequency traders in the markets.
Technological evolution and innovations both in the technology used by stock exchanges and the resources of the traders using their services have made faster trading possible. As a result, high-frequency trading in sub millisecond scale has increased.
However, not everyone has the opportunity to use high-frequency trading, and generally, the scales can be anything from microseconds to tens of thousands of seconds. The role of high-frequency traders has given rise to broad debate over the past years.
- On the one hand, people have argued that the presence of high-frequency traders makes the operation of the markets more efficient and lowers the trading expenses. On the other hand, there have been arguments that this type of trading increases the volatility of the markets, meaning strong fluctuation of prices, and makes them more prone to crashes, says University Research Fellow, Docent Jyrki Piilo from the University of Turku.
The researchers used data from the years 2004-2006, 2010-2011, and 2018. In the first decade of this millennium, the high-frequency trading was still limited while in the second decade it has become much more widely spread due to significant technological development.
- Using statistical analysis of data and the modern methods of network theory, the study allows us to see how the actions of the market members and their reactions to other members' actions has changed over the years, says Dr. Federico Musciotto from the University of Palermo.
A member of the market can trade for their own account or complete commissions for other traders on their request. The study also shows what kind of role the high-frequency traders have in this transformation.
- Based on the data, we have constructed the trading networks of market members, which allows us to detect in which pairs of market members there is a preference to trade with each other and for which pairs there is avoidance to trade with each other. In other words, the results show which type of market members have a preference to react for the order to buy or sell of other type of market member, and which type of market members avoid trading with each other, says Professor Rosario N. Mantegna from the University of Palermo.
The central outcome of the study is that the markets have become significantly more networked as trading has become faster through technological development. The networked character has increased significantly over the years - even though the anonymity in the markets has also increased.
Over the years, there has been a clear increase in the preference for the high-frequency traders to trade with other types of traders. Instead, high-frequency traders avoid mutual trading between themselves, as do other types of traders also. In general, the increasing presence of high-frequency traders has led to the increased networked structure of the market where the strong preferential trading patterns between specific pairs of market members can last up to several months.
Made possible by their technological edge and fast trading compared to others, the high-frequency traders have the ability to perform strategic trading decisions not accessible to other market members or investors, and thereby significantly influence the liquidity of the markets.
The networked structure of the market and the competition among market members are not necessarily the optimal solutions for the best operation of the markets
- The results emphasise the importance of the debate and further investigations of how we can ensure the fair and efficient operation of the markets, summarises Mantegna.
INFORMATION:
> The article has been published in the journal Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America:
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2015573118
HERSHEY, Pa. -- A new study by researchers at Penn State College of Medicine indicates that people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) -- approximately 38 million worldwide -- are more likely to have suicidal thoughts and die from suicide than members of the general population. The researchers said that despite significant medical advancements related to HIV treatment and patients' quality of life, risk of suicide in these patients is high and health care providers should prioritize mental health screenings in this population.
According to the World Health Organization, roughly 800,000 people worldwide die from suicide annually. Among ...
Tuesday, 29 June 2021 - New research has shown that early testing for blood clots in patients who had received the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine led to them being treated successfully, highlighting the need for heightened awareness of the risk among doctors.
The work, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and the National Coagulation Centre at St James's Hospital, is published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Unusual blood clots with low blood platelets have been recognised as a very rare complication of the AstraZeneca vaccine. However, with increased awareness, ...
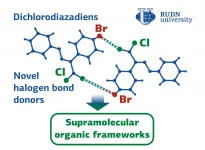
RUDN University chemists derived molecules that can assemble into complex structures using chlorine and bromine halogen atoms. They bind to each other as "velcro" - chlorine "sticks" to bromine, and vice versa. As a result supramolecules are assembled from individual molecules. The obtained substances will help to create supramolecules with catalytic, luminescent, conducting properties. The study is published in Mendeleev Communications.
Supramolecules are the structures made of several molecules. Individual molecules are combined, for example, by self-assembly or without external control. The resulting structure has properties that the molecules did not have individually. That is the way to create new materials, catalysts, molecular machines for ...
For the first time, scientists detected gravitational waves caused by mergers between black holes and neutron stars. Researchers from LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA detected the two gravitational wave events--from distances of more than 900 million light-years away--within a span of 10 days in January 2020 during the second half of LIGO and Virgo's third observing run. Astrophysical Journal Letters published the results and their implications today: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac082e.
Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology's Center ...
The LSL60101 compound, a specific ligand of the I2-IR receptors in the brain, could shed light on the development of future strategies against Alzheimer's disease. This is stated in the recent studies by the Research Group on Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacology of Neurodegenerative Diseases of the University of Barcelona, published in the journals European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and British Journal Pharmacology. In studies carried out with mice, LSL60101 has improved the cognitive deficit and the biomarkers related to the disease in these animal models.
These studies result from the collaboration of the research teams led by professors Carmen Escolano, from the Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences and the Institute of Biomedicine of the UB ...
Preschool children are sensitive to the gap between how much they know and how much there is to learn, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
The research, published in the journal END ...
Under a concrete drainage culvert at the edge of a town in Botswana, a troop of banded mongoose is getting ready to leave its den. Moving from shade into light, the cat-sized animals scan the area for signs of danger and for opportunities to find something to eat in an increasingly crowded neighborhood.
Unbeknownst to them, the genetics of this troop's members -- and others like them -- are providing researchers in the College of Natural Resources and Environment with new understandings of how and why animal behavior changes in proximity to human development and how that change can impact infectious disease spread.
The researchers used genetic tools to identify changes in movement behavior among mongooses ...
An immunotherapy based on supercharging the immune system's natural killer cells has been effective in treating patients with recurrent leukemia and other difficult to treat blood cancers. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown in preclinical studies conducted in mice and human cells that this type of cell-based immunotherapy also could be effective against solid tumors, starting with melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can be deadly if not caught early.
The study is published June 29 in Clinical Cancer Research, ...
[BRIDGEWATER, NJ; June 29, 2021] The American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) has released the updated 2021 AAFP Feline Senior Care Guidelines to be published in the July issue of the Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. This update provides emerging advances in feline medicine with respect to the aging cat. The Task Force of experts provides a thorough current review in feline medicine that emphasizes the individual senior patient.
As defined in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines, cats over 10 years of age are considered to be 'senior.' Understanding the changing needs of each individual senior cat is critical for both veterinary professionals and cat owners. "Veterinary professionals are encouraged to use the 2021 ...
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists led by the Department of Applied Physics at Osaka University, the Department of Physics and Electronics at Osaka Prefecture University, and the Department of Materials Chemistry at Nagoya University used photoinduced force microscopy to map out the forces acting on quantum dots in three dimensions. By eliminating sources of noise, the team was able to achieve subnanometer precision for the first time ever, which may lead to new advances in photocatalysts and optical tweezers.
Force fields are not the invisible barriers of science fiction but are a set of vectors indicating the magnitude and direction of forces acting in a region ...