(Press-News.org) Preschool children are sensitive to the gap between how much they know and how much there is to learn, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
The research, published in the journal END
Just enough information will motivate young children to learn, drive curiosity
Preschoolers need to know just enough, but not all, about something to motivate them to learn more
2021-06-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mongoose in the city: How landscape can impact disease transmission in Botswana
2021-06-29
Under a concrete drainage culvert at the edge of a town in Botswana, a troop of banded mongoose is getting ready to leave its den. Moving from shade into light, the cat-sized animals scan the area for signs of danger and for opportunities to find something to eat in an increasingly crowded neighborhood.
Unbeknownst to them, the genetics of this troop's members -- and others like them -- are providing researchers in the College of Natural Resources and Environment with new understandings of how and why animal behavior changes in proximity to human development and how that change can impact infectious disease spread.
The researchers used genetic tools to identify changes in movement behavior among mongooses ...
Cell-based immunotherapy shows promise against melanoma
2021-06-29
An immunotherapy based on supercharging the immune system's natural killer cells has been effective in treating patients with recurrent leukemia and other difficult to treat blood cancers. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown in preclinical studies conducted in mice and human cells that this type of cell-based immunotherapy also could be effective against solid tumors, starting with melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can be deadly if not caught early.
The study is published June 29 in Clinical Cancer Research, ...
AAFP releases updated feline senior care guidelines to the veterinary community
2021-06-29
[BRIDGEWATER, NJ; June 29, 2021] The American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) has released the updated 2021 AAFP Feline Senior Care Guidelines to be published in the July issue of the Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. This update provides emerging advances in feline medicine with respect to the aging cat. The Task Force of experts provides a thorough current review in feline medicine that emphasizes the individual senior patient.
As defined in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines, cats over 10 years of age are considered to be 'senior.' Understanding the changing needs of each individual senior cat is critical for both veterinary professionals and cat owners. "Veterinary professionals are encouraged to use the 2021 ...
A world first! Visualizing atomic-scale structures with the optical force
2021-06-29
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists led by the Department of Applied Physics at Osaka University, the Department of Physics and Electronics at Osaka Prefecture University, and the Department of Materials Chemistry at Nagoya University used photoinduced force microscopy to map out the forces acting on quantum dots in three dimensions. By eliminating sources of noise, the team was able to achieve subnanometer precision for the first time ever, which may lead to new advances in photocatalysts and optical tweezers.
Force fields are not the invisible barriers of science fiction but are a set of vectors indicating the magnitude and direction of forces acting in a region ...
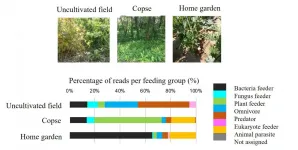
DNA barcodes decode the world of soil nematodes
2021-06-29
Overview
The research team of Professor Toshihiko Eki of the Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science (and Research Center for Agrotechnology and Biotechnology), Toyohashi University of Technology used a next-generation sequencer to develop a highly efficient method to analyze soil nematodes by using the 18S ribosomal RNA gene regions as DNA barcodes. They successfully used this method to reveal characteristics of nematode communities that inhabit fields, copses, and home gardens. In the future, the target will be expanded to cover all soil-dwelling organisms in agricultural soils, etc., to allow investigations into a soil's environment and bio-diversity. This is expected to contribute to advanced agriculture.
Details
Similar to when the ...
What makes vets feel good at work?
2021-06-29
Receiving a simple thank you, spending time with peers and further developing their expertise, are all factors that make veterinarians feel good at work, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Adelaide.
In the study published by Vet Record, researchers investigated the positive side of veterinary work and specifically what brings vets pleasure in their job.
Lead author Madeleine Clise, a psychologist and Adjunct Lecturer at the University of Adelaide's School of Psychology says: "At a time in Australia when there are national shortages of vets, particularly in regional areas, and increased publicity about the ...
To adsorb or to do not adsorb? That is the question
2021-06-29
Prolonged exposure to antibiotics leads to the gain of bacteria's ability to defeat the drugs designed to fight them. Thus, if such antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause the infection, the only chance to use a specialized virus called phage infecting specific bacteria species. It is a powerful weapon against deadly diseases. At the same time, the effective treatment depends on factors that would not be suspected for years to impact the successful therapy. Recently, researchers from the Institute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences led by dr. Jan Paczesny and Professor ...
Using artificial intelligence to overcome mental health stigma
2021-06-29
Tsukuba, Japan - Depression is a worldwide problem, with serious consequences for individual health and the economy, and rapid and effective screening tools are thus urgently needed to counteract its increasing prevalence. Now, researchers from Japan have found that artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to detect signs of depression.
In a study published this month in BMJ Open, researchers from University of Tsukuba have revealed that an AI system using machine learning could predict psychological distress among workers, which is a risk factor for depression. ...
Nanoscale thermoplasmonic heating shows promise for studies of nanomaterials
2021-06-29
Atomic nuclei contain enormous energy that can be extracted through their fission mechanism, for example, as a result of the radioactive decay of uranium or plutonium nuclei. Likewise, a quantum of light of several electron-volts (2.4 eV in a laser pointer with a green beam) has colossal energy. If all photons were absorbed by matter, then its temperature could reach several thousand degrees. However, in practice this does not happen. The reason is the weak light-matter interaction due to the fact that the wavelength of light (500 nm) is a thousand times larger than the size of an emitting / absorbing atom (0.5 nm). It is this physical mechanism that prevents the destruction of matter when illuminated. The efficiency of light absorption increases ...
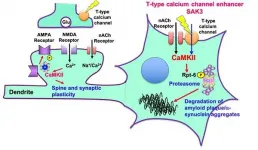
Success in reversing dementia in mice sets the stage for human clinical trials
2021-06-29
Researchers have identified a new treatment candidate that appears to not only halt neurodegenerative symptoms in mouse models of dementia and Alzheimer's disease, but also reverse the effects of the disorders.
The team, based at Tohoku University, published their results on June 8 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. The treatment candidate has been declared safe by Japan's governing board, and the researchers plan to begin clinical trials in humans in the next year.
"There are currently no disease-modifying therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, Huntington ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Just enough information will motivate young children to learn, drive curiosityPreschoolers need to know just enough, but not all, about something to motivate them to learn more