(Press-News.org) Researchers have identified a new treatment candidate that appears to not only halt neurodegenerative symptoms in mouse models of dementia and Alzheimer's disease, but also reverse the effects of the disorders.
The team, based at Tohoku University, published their results on June 8 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. The treatment candidate has been declared safe by Japan's governing board, and the researchers plan to begin clinical trials in humans in the next year.
"There are currently no disease-modifying therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, Huntington disease and frontotemporal dementia in the world," said paper author Kohji Fukunaga, professor emeritus in Tohoku University's Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences. "We discovered the novel, disease-modifying therapeutic candidate SAK3, which, in our studies, rescued neurons in most protein-misfolding, neurodegenerative diseases."
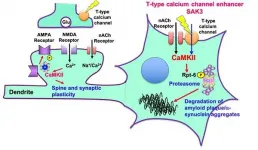
In a previous study, the team found that the SAK3 molecule - the base structure of which is found in the enhancement of T-type Ca2+ channel activity - appeared to help improve memory and learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
According to previous studies, SAK3 enhances the function of a cell membrane channel thereby promoting neuronal activity in the brain. Typically, SAK3 promotes neurotransmitter releases of acetylcholine and dopamine that are significantly reduced in Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia. The Ca2+ channel enhancement is thought to trigger a change from resting to active in neuronal activity. When the Ca2+ channel is dysregulated in the brain, the acetylcholine and dopamine releases are reduced. The result is a dysregulated system that a person experiences as cognitive confusion and uncoordinated motor function.
SAK3 directly binds to the subunit of this channel, resulting in the enhancement of neurotransmission thereby improving cognitive deficits. The researchers found that the same process also appeared to work in a mouse model of Lewy body dementia, which is characterized by a build-up of proteins known as Lewy bodies.
"Even after the onset of cognitive impairment, SAK3 administration significantly prevented the progression of neurodegenerative behaviors in both motor dysfunction and cognition," Fukunaga said.
In comparison, Aduhelm, the Alzheimer's drug recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reduces the number of amyloid plaques in the brain, but it is not yet known if the amyloid reduction actually prevents further cognitive or motor decline in patients. According to Fukunaga, SAK3 helps destroy amyloid plaque - at least in mice.
SAK3 also helps manage the destruction of misfolded alpha-synuclein. Normal alpha-synuclein helps regulate neurotransmitter transmission in the brain. The protein can misfold and aggregate, contributing to what researchers suspect may be an underlying cause of neurodegenerative symptoms. This aggregation can also lead to the loss of dopamine neurons, which help with learning and memory.
"We found that chronic administration of SAK3 significantly inhibited the accumulation of alpha-synuclein in the mice," Fukunaga said, noting that the mice received a daily oral dose of SAK3.
According to Fukunaga, SAK3 enhances the activity of the system that identifies and destroys misfolded proteins. In neurodegenerative diseases, this system is often dysfunctional, leaving misfolded proteins to muck up the cell's machinery.
"SAK3 is the first compound targeting this regulatory activity in neurodegenerative disorders," Fukunaga said. "SAK3 administration promotes the destruction of misfolded proteins, meaning the therapeutic has the potential to solve the problems of diverse protein misfolding diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Lewy body dementia and Huntington disease, in addition to Alzheimer's disease."
INFORMATION:
As our society and transportation systems become increasingly electrified, scientists worldwide are seeking more efficient and higher capacity storage systems. Researchers at KAUST have made an important contribution by modifying lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries to suppress a problem known as polysulfide shuttling.
"The bottleneck in the utilization of renewable energy, especially in transportation, is the need for high-density batteries," says Eman Alhajji, Ph.D. student and first author of the research paper.
Li-S batteries have several potential advantages over ...
Bobtail and bottletail squids are tiny marine invertebrates that are found throughout the world's oceans and are useful model animals for research
There are 68 recognized species of bobtail squid and five recognized species of bottletail squid, but the timing of their divergence from one another is still relatively unknown
Researchers at OIST, Hiroshima University and the National University of Ireland Galway, collected 32 species of bobtail and bottletail squids
They looked at the genetic variations across the entire genomes of these species to estimate their evolutionary relationships
The results showed that the divergence of these species aligned with major ...
Tel Aviv University's groundbreaking technology may revolutionize the treatment of cancer and a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. In the framework of this study, the researchers were able to create a new method of transporting RNA-based drugs to a subpopulation of immune cells involved in the inflammation process, and target the disease-inflamed cell without causing damage to other cells.
The study was led by Prof. Dan Peer, a global pioneer in the development of RNA-based therapeutic delivery. He is Tel Aviv University's Vice President for Research and Development, head of the Center for Translational Medicine and a member of both the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research, George S. Wise Faculty ...
What if electricity could be squeezed out of something? It turns out some materials have this property. Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solids when mechanical stress is applied on them. Piezoelectric materials, like bismuth ferrite thin films, when grown on a single lanthanum aluminate substrate give rise to highly strained epitaxial thin films that exhibit excellent electromechanical and ferroelectric properties. In bismuth ferrite thin films "doped" or polluted with lanthanum (BLFOs), piezoelectricity is attributed to the presence of "mixed-phase structures" with stripe patterns.
The formation of stripe patterns and controlling the mixed-phase structures of BLFO have been the ...
A FLEET theoretical study out this week has found a 'smoking gun' in the long search for the topological magnetic monopole referred to as the END ...
HARWELL, UK (29 June 2021) Researchers working on the Faraday Institution project on the recycling of lithium-ion batteries (ReLiB) at the Universities of Leicester and Birmingham have solved a critical challenge in the recovery of materials used in electric vehicle batteries at the end of their life, enabling their re-use in the manufacture of new batteries. The new method, which uses ultrasonic waves to separate out valuable material from the electrodes, is 100 times quicker, greener and leads to a higher purity of recovered materials relative to current separation methods.
The research has been published in Green Chemistry and the team have applied for a patent for the technique.
To ...
Patients with mild Covid-19 infections experience a significantly increased longer lasting reduced sense of taste and smell. This is also the case for long-term shortness of breath, although relatively few people are affected. And women and the elderly are particularly affected. This is shown by new research findings from Aarhus University Aarhus University Hospital and Regional Hospital West Jutland
The last 14 months have taught us that there are different symptoms and outcomes of Covid-19. However, the vast majority of people who fall ill with Covid-19 experience mild symptoms and get over ...
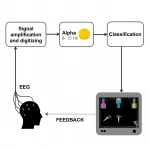
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects about 7% of children, with a two out of three chance of persisting into adulthood. This neurodevelopmental disorder is characterised by concentration difficulties, increased distractibility, impulsivity and hyperactivity. Today, ADHD is treated with pharmaceutical drugs that may have unwanted side effects. This is why scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, explored a new technique called 'neurofeedback', which enables ADHD patients to train their attention, based on instant feedback from the level of their brain activity. The team of neuroscientists found that not only did the training have a positive effect on patients' concentration abilities, but also that the ...
An international team of researchers has identified a novel mechanism in barley plants, which could help crop growers achieve high yields as temperatures rise.
With grain production highly sensitive to changing environmental conditions, rising temperatures are known to reduce the number of seeds that can be produced on each plant. One solution is to increase the number of flowers or branches on each 'spike', which is the reproductive structure from which grain is harvested.
In a study published in Nature Plants, research led by Professor Dabing Zhang from the University of Adelaide's Waite Research Institute and Shanghai Jiao Tong University's Joint Lab for Plant Science and Breeding, explored the possibility of increasing seed production through ...
Tsukuba, Japan - As far back as the 1930s, inventors have commercialized fuel cells as a versatile source of power. Now, researchers from Japan have highlighted the impressive chemistry of an essential component of an upcoming fuel cell technology.
In a study recently published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed successive proton transport--energy transfer--in an advanced carbon-based crystal for future fuel cells, and the chemistry that underpins this phenomenon.
Such crystals are exciting as solid electrolytes--energy transfer media--in upcoming fuel cell technologies. Solid electrolytes have advantages, such as high power efficiency and long-term ...