New work showcases the chemistry of an upcoming fuel cell electrolyte
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba demonstrate successive proton transport mechanism in a material that may be a future source of reliable primary and backup power
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - As far back as the 1930s, inventors have commercialized fuel cells as a versatile source of power. Now, researchers from Japan have highlighted the impressive chemistry of an essential component of an upcoming fuel cell technology.
In a study recently published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed successive proton transport--energy transfer--in an advanced carbon-based crystal for future fuel cells, and the chemistry that underpins this phenomenon.
Such crystals are exciting as solid electrolytes--energy transfer media--in upcoming fuel cell technologies. Solid electrolytes have advantages, such as high power efficiency and long-term stability, which some electrolytes lack. Solid electrolytes based on imidazole are common focuses of study. Researchers hypothesize that crystals of imidazolium hydrogen succinate can exhibit successive proton transport, also known as proton jumping. At present, this has not been rigorously confirmed, something the researchers at the University of Tsukuba aimed to address.
"A wide range of lab work and computer simulations are consistent with unidirectional proton transport in crystals of imidazolium hydrogen succinate," says lead and senior author of the study, Professor Yuta Hori. "Because this hypothesis requires further testing, we computed the molecular energy versus molecular geometry of our crystals, and compared our results with experimental data."
To do this, the researchers studied known crystal structures to investigate a chemical structure known as hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen dynamics on these bonds facilitate proton transport within the crystals and can be characterized experimentally by infrared spectroscopy.
"The spectroscopy results were clear," explains Hori. "We found that at 100°C, compared with 30°C, there was a shift to higher energy in a peak that pertains to proton transport."
Furthermore, the researchers' calculated peaks--those corresponding to chemical units that strongly contribute to hydrogen bonding--were consistent with the experimental data.
"We used these results to construct a model that traced how a proton is transferred from one imidazole unit to another," says Hori. "Our calculated potential energy surface provided geometric and energetic data that are consistent with proton jumping."
Fuel cells are used today to power a wide range of civil infrastructure and technologies, and typically produce few emissions. Improving the utility of fuel cells in more diverse applications, achieved in part by understanding how they work, will help minimize wasted power in the coming years.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Proton conduction mechanism for anhydrous imidazolium hydrogen succinate based on local structures and molecular dynamics," was published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters at DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01280
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
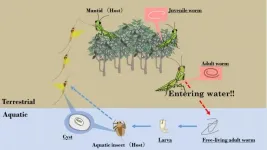
Researchers have revealed that praying mantis (mantids) infected with parasitic hairworms are attracted to horizontally polarized light that is strongly reflected off the surface of water, which causes them to enter the water. In a world-first, these research results demonstrate that parasites can manipulate the host's specific light perception system to their advantage, causing the host to behave in an abnormal manner.
This discovery was made by an international research group consisting of Graduate student OBAYASHI Nasono, Associate Professor SAKURA Midori and Associate Professor SATO Takuya of Kobe University's Graduate School of Science, Associate Professor IWATANI Yasushi (Faculty of Science and Technology, Hirosaki University), ...
2021-06-29
A team of scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a test kit for malaria that delivers results in 30 minutes. The kit could facilitate the diagnosis of malaria in the field, as the equipment needed is anticipated to be lightweight, easy-to-use, and able to detect the disease in its early stages.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), an estimated 229 million people suffered from malaria in 2019. The disease, transmitted by mosquitoes, caused the deaths of 409,000 people across 87 mainly developing countries.
Efforts to treat and control malaria in ...
2021-06-29
A microfilter device that can easily separate and capture trace amounts of cancer cells in blood has been developed by a Kumamoto University research group. The palm-sized device is expected to contribute to the development of new cancer diagnostic technologies based on cancer cells in the blood, such as early detection by blood test, postoperative management, and recurrence monitoring.
The blood of people with cancer contains trace amounts of cancer cells (CTCs) that have detached from the primary cancer site. However, the amount of these cells is only a few per milliliter, whereas red or white blood cells number in the billions, making ...
2021-06-29
INDIANAPOLIS - With the growing prevalence of chronic pain, depression, anxiety, and other symptom-based conditions, physicians and the healthcare systems for which they work are increasingly considering how to augment the care they can provide within the limited time allotted for patient appointments.
According to Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist Kurt Kroenke, M.D., writing in the Journal of General Internal Medicine (JGIM), collaborative care can and should play a major role targeting the treatment of symptoms and functional decline, both too frequently marginalized in medically oriented care delivery.
Collaborative care is a team-based ...
2021-06-29
Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) is a promising treatment for melanoma and other cancer types, and has recently been shown to provide a modest survival benefit for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. To improve the treatment efficacy, researchers are looking for vulnerabilities in surgically removed glioblastoma tissues, but this has been difficult due to the vast differences within the tumor and between patients.
To address this challenge, researchers at Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and their collaborators developed a new way to study tumors. The method builds ...
2021-06-29
Sophia Antipolis - 29 June 2021: Heart attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic were more likely to result in heart failure compared with heart attacks one year earlier, according to research presented today at Heart Failure 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"Heart attack patients waited an average of 14 hours to get help during the pandemic, with some delaying for nearly two days. That compares to a delay of six hours in the previous year," said study author Dr. Ali Aldujeli of the Hospital of Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Kaunas, Lithuania. "This gap may have been one contributor to the higher incidence of subsequent heart failure."
Urgent treatment for heart attacks is essential to restore the flow of oxygen-rich ...
2021-06-29
Scientists have for the first time detected black holes eating neutron stars, "like Pac Man", in a discovery documenting the collision of the two most extreme and enigmatic objects in the Universe.
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the US and the Virgo gravitational-wave observatory in Italy have captured the gravitational waves from the death spiral and merger of a neutron star with a black hole, not once but twice. The findings are published today.
The researchers say their observations will help unlock some of the most complex mysteries of the Universe, including the building blocks of matter and the workings of space and time.
More than 1,000 scientists were involved with the ...
2021-06-29
As smoky air becomes more common during Washington's wildfire season, many wildlife enthusiasts wonder: What happens to the birds?
Few studies have looked at wildfire smoke impacts on animals, let alone birds. And as Washington and the larger West Coast continue to experience more massive wildfires and smoke-filled air, understanding how birds are affected by smoke -- and how air pollution may influence our ability to detect birds -- are important factors for bird conservation.
Researchers from the University of Washington now provide a first look at the probability of observing common birds as air pollution worsens during wildfire seasons. They found that smoke affected the ability to detect more than a third of the bird species studied ...
2021-06-29
For the first time, researchers have confirmed the detection of a collision between a black hole and a neutron star. In fact, the scientists detected not one but two such events occurring just 10 days apart in January 2020. The extreme events made splashes in space that sent gravitational waves rippling across at least 900 million light-years to reach Earth. In each case, the neutron star was likely swallowed whole by its black hole partner.
Gravitational waves are disturbances in the curvature of space-time created by massive objects in motion. During the five years since the waves were first measured, a finding that led to the END ...
2021-06-29
A long time ago, in two galaxies about 900 million light-years away, two black holes each gobbled up their neutron star companions, triggering gravitational waves that finally hit Earth in January 2020.
Discovered by an international team of astrophysicists including Northwestern University researchers, two events -- detected just 10 days apart -- mark the first-ever detection of a black hole merging with a neutron star. The findings will enable researchers to draw the first conclusions about the origins of these rare binary systems and how often they merge.
"Gravitational ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New work showcases the chemistry of an upcoming fuel cell electrolyte
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba demonstrate successive proton transport mechanism in a material that may be a future source of reliable primary and backup power