Nanoscale thermoplasmonic heating shows promise for studies of nanomaterials
A research of glassy polymers was recently published in ACS Photonics
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) Atomic nuclei contain enormous energy that can be extracted through their fission mechanism, for example, as a result of the radioactive decay of uranium or plutonium nuclei. Likewise, a quantum of light of several electron-volts (2.4 eV in a laser pointer with a green beam) has colossal energy. If all photons were absorbed by matter, then its temperature could reach several thousand degrees. However, in practice this does not happen. The reason is the weak light-matter interaction due to the fact that the wavelength of light (500 nm) is a thousand times larger than the size of an emitting / absorbing atom (0.5 nm). It is this physical mechanism that prevents the destruction of matter when illuminated. The efficiency of light absorption increases with the decreasing wavelength and the increasing imaginary part of the dielectric constant of the substance. When metal structures are illuminated with light of a certain wavelength, free electrons can oscillate coherently. Such oscillations of the charge density in metals are called plasmon resonances, which depend not only on the wavelength of the incident light, but the chemical nature of the metal, its size and shape as well. Due to plasmon resonance, the electric field near a metal nanoparticle can be enhanced by tens and hundreds of times. This means that such nanostructures function as optical nanoantennas that enhance the light-matter interaction. Nanoantennas are widely used in nanosensor technologies, which have found applications in materials science, nanoelectronics, and biomedicine. In the plasmon resonance regime, the density of electromagnetic energy inside the metal nanostructure increases strongly and this inevitably leads to giant optical heating from tens to several hundred degrees. For example, upon illuminating a gold spherical nanoparticle with a diameter of 50 nm with 532 nm laser light and the intensity of 20 MW/cm2, such nanostructure will melt. The field of photonics focusing on plasmon-assisted optical heating is called thermoplasmonics.
This paper proposes the concept of a plasmonic metasurface consisting of an array of square refractory nanoantennas on a silicon substrate. Titanium nitride (TiN) with the melting point of 2950 °C was used as a material for the nanoantennas. The optical heating was controlled by varying the pump power. However, the maximum temperature is limited by the size and shape of the nanoantenna. Upon changing in the size and shape, the plasmon resonance is spectrally shifted and, therefore, it is necessary to additionally tune the wavelength of the incident radiation. The publication develops an alternative way to control temperature through designing a silicon wafer by using focused ion beam etching. As a result, nanoantennas are turned to be located not on the silicon surface, but on engraved Si nanopillars, the height of which limits the maximum photoheating temperature. This method is capable of creating a controlled non-uniform temperature profile on the surface. The proposed thermoplasmonic heater was used to detect the local glass transition temperature of an amorphous polymer by scanning a focused laser beam over its surface. To test this method, the authors used an 100 nm thick film of polymethyl methacrylate.
The thermoplasmonic heater, for the first time, has provided the possibility of local sensing the glass transitions of amorphous polymers with nanometer spatial resolution. This method opens unique opportunities for studying the physicochemical properties of spatially inhomogeneous polymer films, multicomponent polymer blends, liquid crystals, and 3D spatially confined polymer nanostructures (polymer dots). It is important to emphasize that this method can be used to detect first-order phase transitions. The study of the local physicochemical properties of nanostructured polymers is an important task for the development of the element base (microfluidic channels, gates, etc.) of labs on a chip.
In the near future, the plan is to use the thermoplasmonic heater to study biological responses on single neuronal cells. An important development of the technology is subwavelength thermal microscopy, which makes it possible to visualize nanoobjects. This technology will be used to create a cognitive metasurface based on plasmon multiplexing, capable of autonomously performing simple calculations. In addition, such a local heater can be used to write/read information beyond the diffraction limit of light. Great hopes are pinned on the development of an all-optical ultrafast calorimetry method that allows not only studying kinetic processes in polymers and liquid crystals, but also creating new highly nonequilibrium phase states of nanomaterials.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
Researchers have identified a new treatment candidate that appears to not only halt neurodegenerative symptoms in mouse models of dementia and Alzheimer's disease, but also reverse the effects of the disorders.
The team, based at Tohoku University, published their results on June 8 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. The treatment candidate has been declared safe by Japan's governing board, and the researchers plan to begin clinical trials in humans in the next year.
"There are currently no disease-modifying therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, Huntington ...
2021-06-29
As our society and transportation systems become increasingly electrified, scientists worldwide are seeking more efficient and higher capacity storage systems. Researchers at KAUST have made an important contribution by modifying lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries to suppress a problem known as polysulfide shuttling.
"The bottleneck in the utilization of renewable energy, especially in transportation, is the need for high-density batteries," says Eman Alhajji, Ph.D. student and first author of the research paper.
Li-S batteries have several potential advantages over ...
2021-06-29
Bobtail and bottletail squids are tiny marine invertebrates that are found throughout the world's oceans and are useful model animals for research
There are 68 recognized species of bobtail squid and five recognized species of bottletail squid, but the timing of their divergence from one another is still relatively unknown
Researchers at OIST, Hiroshima University and the National University of Ireland Galway, collected 32 species of bobtail and bottletail squids
They looked at the genetic variations across the entire genomes of these species to estimate their evolutionary relationships
The results showed that the divergence of these species aligned with major ...
2021-06-29
Tel Aviv University's groundbreaking technology may revolutionize the treatment of cancer and a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. In the framework of this study, the researchers were able to create a new method of transporting RNA-based drugs to a subpopulation of immune cells involved in the inflammation process, and target the disease-inflamed cell without causing damage to other cells.
The study was led by Prof. Dan Peer, a global pioneer in the development of RNA-based therapeutic delivery. He is Tel Aviv University's Vice President for Research and Development, head of the Center for Translational Medicine and a member of both the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research, George S. Wise Faculty ...
2021-06-29
What if electricity could be squeezed out of something? It turns out some materials have this property. Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solids when mechanical stress is applied on them. Piezoelectric materials, like bismuth ferrite thin films, when grown on a single lanthanum aluminate substrate give rise to highly strained epitaxial thin films that exhibit excellent electromechanical and ferroelectric properties. In bismuth ferrite thin films "doped" or polluted with lanthanum (BLFOs), piezoelectricity is attributed to the presence of "mixed-phase structures" with stripe patterns.
The formation of stripe patterns and controlling the mixed-phase structures of BLFO have been the ...
2021-06-29
A FLEET theoretical study out this week has found a 'smoking gun' in the long search for the topological magnetic monopole referred to as the END ...
2021-06-29
HARWELL, UK (29 June 2021) Researchers working on the Faraday Institution project on the recycling of lithium-ion batteries (ReLiB) at the Universities of Leicester and Birmingham have solved a critical challenge in the recovery of materials used in electric vehicle batteries at the end of their life, enabling their re-use in the manufacture of new batteries. The new method, which uses ultrasonic waves to separate out valuable material from the electrodes, is 100 times quicker, greener and leads to a higher purity of recovered materials relative to current separation methods.
The research has been published in Green Chemistry and the team have applied for a patent for the technique.
To ...
2021-06-29
Patients with mild Covid-19 infections experience a significantly increased longer lasting reduced sense of taste and smell. This is also the case for long-term shortness of breath, although relatively few people are affected. And women and the elderly are particularly affected. This is shown by new research findings from Aarhus University Aarhus University Hospital and Regional Hospital West Jutland
The last 14 months have taught us that there are different symptoms and outcomes of Covid-19. However, the vast majority of people who fall ill with Covid-19 experience mild symptoms and get over ...
2021-06-29
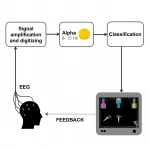
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects about 7% of children, with a two out of three chance of persisting into adulthood. This neurodevelopmental disorder is characterised by concentration difficulties, increased distractibility, impulsivity and hyperactivity. Today, ADHD is treated with pharmaceutical drugs that may have unwanted side effects. This is why scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, explored a new technique called 'neurofeedback', which enables ADHD patients to train their attention, based on instant feedback from the level of their brain activity. The team of neuroscientists found that not only did the training have a positive effect on patients' concentration abilities, but also that the ...
2021-06-29
An international team of researchers has identified a novel mechanism in barley plants, which could help crop growers achieve high yields as temperatures rise.
With grain production highly sensitive to changing environmental conditions, rising temperatures are known to reduce the number of seeds that can be produced on each plant. One solution is to increase the number of flowers or branches on each 'spike', which is the reproductive structure from which grain is harvested.
In a study published in Nature Plants, research led by Professor Dabing Zhang from the University of Adelaide's Waite Research Institute and Shanghai Jiao Tong University's Joint Lab for Plant Science and Breeding, explored the possibility of increasing seed production through ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nanoscale thermoplasmonic heating shows promise for studies of nanomaterials
A research of glassy polymers was recently published in ACS Photonics