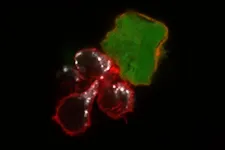
(Press-News.org) An immunotherapy based on supercharging the immune system's natural killer cells has been effective in treating patients with recurrent leukemia and other difficult to treat blood cancers. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown in preclinical studies conducted in mice and human cells that this type of cell-based immunotherapy also could be effective against solid tumors, starting with melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can be deadly if not caught early.
The study is published June 29 in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
In recent years, an immunotherapy called immune checkpoint inhibitors has revolutionized treatment for advanced melanoma. In one well-known example, this immunotherapy was successfully used to treat former President Jimmy Carter, whose melanoma had spread to his liver and brain.
But the therapy only works in about half of such patients. And even among those who respond well to the initial therapy, about half go on to develop resistance to it. Consequently, researchers have been seeking different ways to harness the immune system to attack melanoma cells. One possibility is to use natural killer (NK) cells, a part of the immune system's first line of defense against dangerous cells, whether cancer cells or invading bacteria.
Todd A. Fehniger, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine, and his team have had success in clinical trials treating recurrent leukemia with a patient's own natural killer cells or those from a donor. The NK cells are harvested from the patient's or a donor's blood and exposed to a set of chemical signals called cytokines that activate the cells and prime them to remember this activation. When these "cytokine-induced memory-like" NK cells are given to the patient, they are more potent in attacking the cancer because they already have been revved up, as Fehniger puts it.
"These 'revved-up' memory-like NK cells attack blood cancers quite well," said Fehniger, the study's co-senior author and an oncologist who treats patients at Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine. "But relatively little work has been done on whether these cells can be used against solid tumors. This is an unmet need in solid tumor oncology. Our study provides proof of principle that memory-like NK cells respond better than normal NK cells against melanoma, and it serves as a stepping stone to a first-in-human clinical trial of these cells in advanced melanoma."
Added co-senior author Ryan C. Fields, MD, the Kim and Tim Eberlein Distinguished Professor of Surgical Oncology: "We hope this is also a step toward harnessing NK cells against multiple solid tumors. Melanoma was a good place to start because we know it responds to immune therapy. But because many patients don't respond or develop resistance, we felt that targeting a different aspect of the immune system was a promising strategy to pursue."
The standard checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy that works well in some melanoma patients targets T cells, another type of immune cell that also frequently is harnessed against different forms of cancer. According to the researchers, patients who don't respond well or stop responding to the T cell-based standard therapy and have no other options would be good candidates for NK cell therapy.
The researchers studied human NK cells from both healthy people and from patients with melanoma and found that the cytokine-induced memory-like NK cells could effectively treat mice harboring human melanoma tumors. Tumors shrank to the point of being almost undetectable in many of the mice, and the memory-like NK cells prevented the tumors from returning in most cases for the duration of the 21-day experiment. While normal NK cells also reduced and controlled melanoma tumors, they did not do so to the same degree.
"We are currently designing a clinical trial to evaluate these NK cells in patients with advanced melanoma who have exhausted all other treatment options," Fehniger said. "We would like to investigate NK cells from a donor and, separately, a patient's own NK cells to see if the cytokine-induced memory-like NK cells offer an effective treatment option for patients with this aggressive skin cancer."
The NK cell-based immunotherapy is potentially safer than other cell-based immunotherapies because the NK cells do not trigger a cytokine storm, as is seen sometimes in CAR-T cell therapy, which often is used for blood cancers, nor do the NK cells cause graft-versus-host disease, which sometimes follows a stem cell transplant.
"Even 10 years ago, we had no effective therapies for advanced melanoma -- much like the lack of therapies for glioblastoma or advanced pancreatic cancer today," said Fields, a surgeon who treats patients at Siteman. "Checkpoint immunotherapy has revolutionized melanoma treatment, but we're still not satisfied with the 50% response rate. We want to do better, and this NK cell therapy is a promising approach. And in the future, we may be able to combine an NK cell-based therapy with checkpoint inhibition for an even better response."
Fehniger and his colleagues have worked with Washington University's Office of Technology Management to license the cytokine-induced memory-like NK cell technology to a company called Wugen. Fehniger is a co-founder of Wugen and serves on its scientific advisory board.
INFORMATION:
Fehniger and co-author Melissa M. Berrien-Elliott, PhD, an instructor in medicine, are consultants and have equity interest in Wugen and may receive royalty income based on technology they developed and that was licensed by Washington University to Wugen.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grant numbers T32 HL007088; R01CA248277, R01CA205239, CCSG P30 CA091842, NIHU54CA224083, K12CA167540, and a SPORE in Leukemia P50CA171063. Additional funding was provided by a Sidney Kimmel Translational Science Scholar Award; a Society of Surgical Oncology Clinical Investigator Award; the David Riebel Cancer Research Fund; the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society; the V Foundation for Cancer Research; and the AAI Intersect Fellowship Program for Computational Scientists and Immunologists. Research reported in this publication was supported by the Washington University School of Medicine Surgical Oncology Basic Science and Translational Research Training Program, grant number T32CA009621 from the National Cancer Institute. Further support was provided by the Siteman Flow Cytometry Core; the Immune Monitoring Lab; the Siteman Tissue Procurement Core; and the core grant/services of the Washington University Digestive Diseases Research Core Center, grant number P30 DK052574.
Marin ND, et al. Memory-like differentiation enhances NK cell responses to melanoma. Clinical Cancer Research. June 29, 2021.
Washington University School of Medicine's 1,500 faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is a leader in medical research, teaching and patient care, consistently ranking among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.
[BRIDGEWATER, NJ; June 29, 2021] The American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) has released the updated 2021 AAFP Feline Senior Care Guidelines to be published in the July issue of the Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. This update provides emerging advances in feline medicine with respect to the aging cat. The Task Force of experts provides a thorough current review in feline medicine that emphasizes the individual senior patient.
As defined in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines, cats over 10 years of age are considered to be 'senior.' Understanding the changing needs of each individual senior cat is critical for both veterinary professionals and cat owners. "Veterinary professionals are encouraged to use the 2021 ...
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists led by the Department of Applied Physics at Osaka University, the Department of Physics and Electronics at Osaka Prefecture University, and the Department of Materials Chemistry at Nagoya University used photoinduced force microscopy to map out the forces acting on quantum dots in three dimensions. By eliminating sources of noise, the team was able to achieve subnanometer precision for the first time ever, which may lead to new advances in photocatalysts and optical tweezers.
Force fields are not the invisible barriers of science fiction but are a set of vectors indicating the magnitude and direction of forces acting in a region ...
Overview
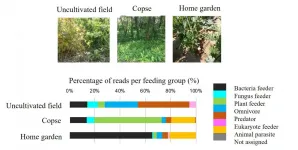
The research team of Professor Toshihiko Eki of the Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science (and Research Center for Agrotechnology and Biotechnology), Toyohashi University of Technology used a next-generation sequencer to develop a highly efficient method to analyze soil nematodes by using the 18S ribosomal RNA gene regions as DNA barcodes. They successfully used this method to reveal characteristics of nematode communities that inhabit fields, copses, and home gardens. In the future, the target will be expanded to cover all soil-dwelling organisms in agricultural soils, etc., to allow investigations into a soil's environment and bio-diversity. This is expected to contribute to advanced agriculture.
Details
Similar to when the ...
Receiving a simple thank you, spending time with peers and further developing their expertise, are all factors that make veterinarians feel good at work, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Adelaide.
In the study published by Vet Record, researchers investigated the positive side of veterinary work and specifically what brings vets pleasure in their job.
Lead author Madeleine Clise, a psychologist and Adjunct Lecturer at the University of Adelaide's School of Psychology says: "At a time in Australia when there are national shortages of vets, particularly in regional areas, and increased publicity about the ...
Prolonged exposure to antibiotics leads to the gain of bacteria's ability to defeat the drugs designed to fight them. Thus, if such antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause the infection, the only chance to use a specialized virus called phage infecting specific bacteria species. It is a powerful weapon against deadly diseases. At the same time, the effective treatment depends on factors that would not be suspected for years to impact the successful therapy. Recently, researchers from the Institute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences led by dr. Jan Paczesny and Professor ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Depression is a worldwide problem, with serious consequences for individual health and the economy, and rapid and effective screening tools are thus urgently needed to counteract its increasing prevalence. Now, researchers from Japan have found that artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to detect signs of depression.
In a study published this month in BMJ Open, researchers from University of Tsukuba have revealed that an AI system using machine learning could predict psychological distress among workers, which is a risk factor for depression. ...
Atomic nuclei contain enormous energy that can be extracted through their fission mechanism, for example, as a result of the radioactive decay of uranium or plutonium nuclei. Likewise, a quantum of light of several electron-volts (2.4 eV in a laser pointer with a green beam) has colossal energy. If all photons were absorbed by matter, then its temperature could reach several thousand degrees. However, in practice this does not happen. The reason is the weak light-matter interaction due to the fact that the wavelength of light (500 nm) is a thousand times larger than the size of an emitting / absorbing atom (0.5 nm). It is this physical mechanism that prevents the destruction of matter when illuminated. The efficiency of light absorption increases ...
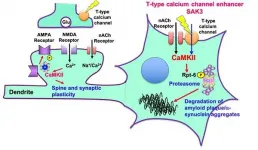
Researchers have identified a new treatment candidate that appears to not only halt neurodegenerative symptoms in mouse models of dementia and Alzheimer's disease, but also reverse the effects of the disorders.
The team, based at Tohoku University, published their results on June 8 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. The treatment candidate has been declared safe by Japan's governing board, and the researchers plan to begin clinical trials in humans in the next year.
"There are currently no disease-modifying therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, Huntington ...
As our society and transportation systems become increasingly electrified, scientists worldwide are seeking more efficient and higher capacity storage systems. Researchers at KAUST have made an important contribution by modifying lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries to suppress a problem known as polysulfide shuttling.
"The bottleneck in the utilization of renewable energy, especially in transportation, is the need for high-density batteries," says Eman Alhajji, Ph.D. student and first author of the research paper.
Li-S batteries have several potential advantages over ...
Bobtail and bottletail squids are tiny marine invertebrates that are found throughout the world's oceans and are useful model animals for research
There are 68 recognized species of bobtail squid and five recognized species of bottletail squid, but the timing of their divergence from one another is still relatively unknown
Researchers at OIST, Hiroshima University and the National University of Ireland Galway, collected 32 species of bobtail and bottletail squids
They looked at the genetic variations across the entire genomes of these species to estimate their evolutionary relationships
The results showed that the divergence of these species aligned with major ...