'The focea': A region of improved vision in mice.
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) Mice are an important animal model of human vision due to the powerful genetic tools available in this species. However, mouse vision was thought to be different to that of humans because humans have a region of the retina specialized for fine details called the 'fovea' whereas mice do not. Researchers from the Netherlands Institute of Neuroscience (NIN) have shown that the visual cortex of mice does contain a region of enhanced visual sensitivity dubbed the 'focea', making the mouse a better model of human vision than previously expected. The findings were published in Nature Communications on the 29th June.
A specialization for high resolution vision
The fovea is a region in the human retina in which the light-sensitive cells are more closely packed together yielding higher resolution vision. It is used for reading and recognizing faces. Humans move their eyes three times per second to point the fovea at interesting parts of the world. Mice do not have this specialization and it was thought that they have no reason to move their eyes to 'scan the world' in more detail.
While studying how the retina of the mouse was mapped in cortical regions of the brain, the researchers found that the map of visual space in the cortex has a better visual resolution at a location that represents a region directly in front of and slightly above the mouse in space. They named this cortical location the 'focea' as it is reminiscent of the fovea of humans.
A better organized map of space.
To determine the source of the better resolution the researchers measured the responses from individual brain cells using electrodes. The cells at the focea did not appear to the differ from other cells. "Initially we were puzzled" explains Matthew Self, lead researcher on the project, "we were seeing a very clear focea in the map, but nothing when we measured the data from single-neurons. We realized that the focea could originate from regions of the cortex where the maps are better organized across cells".
To study this, the researchers measured maps of space across thousands of cells using a two-photon microscope. The results confirmed their hypothesis; maps of space in the focea were well-organized with neighboring cells responding to neighboring parts of space. In contrast, the maps outside the focea were more scattered. The results suggested that mice might have better vision in the focea than elsewhere.
The focea in natural behaviors
The fact that mice have a focea could mean that they also move their eyes to point their focea at interesting parts of world, analogous to the human fovea. The findings have important consequences for the use of mice as a model of human vision. Dr Self stated: "The fact that mice have a focea opens up the possibility of understanding the neural circuits underlying high-detail vision and studying the neural basis of attention and eye-movements in this species".
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
Lithia, Florida -- June 29, 2021 -- Surgical resident training has traditionally occurred in a master-apprentice-type relationship, with graduated responsibilities until trainees are expected to perform procedures on their own. Given recent changes in the health care system, including reduced operating room time, increased difficulty of procedures and working hour restrictions, there is less time for residents to learn using traditional methods.
Researchers from the University of Manitoba and the Pan Am Clinic recently published a paper in the journal Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, ...
2021-06-29
Aerosol generated by playing woodwind and brass instruments is less than that produced when vocalising (speaking and singing) and is no different than a person breathing, new research has found. The findings, published online in the journal Aerosol Science and Technology, could be crucial to developing a roadmap for lifting COVID-19 restrictions in the performing arts, which have been significantly restricted since the start of the pandemic.
The research project, known as PERFORM (ParticulatE Respiratory Matter to InForm Guidance for the Safe Distancing of PerfOrmeRs in a COVID-19 PandeMic), was supported by Public Health England, the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS), and UKRI and was carried out by a collaborative team from ...
2021-06-29
The death of neurons specialised in the synthesis of dopamine, one of the brain's main neurotransmissors, deteriorates the motor and cognitive capacities of those with Parkinson's disease. The loss of these neurons is related to alpha-synuclein aggregation. Recent studies show that oligomers, the initial aggregates of this protein, are the most pathogenic forms of α-synuclein and are responsible for the spreading of the disease in the brain.
Therefore, one of the more promising approaches in fighting this disorder consists in neutralising these oligomers and, thus, slow down the pathological progression. ...
2021-06-29
During the last twenty years, the trading in stock markets has undergone significant changes. Researchers from the University of Turku and the University of Palermo have investigated the role of high-frequency traders in the markets.
Technological evolution and innovations both in the technology used by stock exchanges and the resources of the traders using their services have made faster trading possible. As a result, high-frequency trading in sub millisecond scale has increased.
However, not everyone has the opportunity to use high-frequency trading, and generally, the scales can be anything from microseconds to tens of thousands of seconds. The role of high-frequency traders has given rise to broad debate over ...
2021-06-29
HERSHEY, Pa. -- A new study by researchers at Penn State College of Medicine indicates that people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) -- approximately 38 million worldwide -- are more likely to have suicidal thoughts and die from suicide than members of the general population. The researchers said that despite significant medical advancements related to HIV treatment and patients' quality of life, risk of suicide in these patients is high and health care providers should prioritize mental health screenings in this population.
According to the World Health Organization, roughly 800,000 people worldwide die from suicide annually. Among ...
2021-06-29
Tuesday, 29 June 2021 - New research has shown that early testing for blood clots in patients who had received the AstraZeneca/Oxford vaccine led to them being treated successfully, highlighting the need for heightened awareness of the risk among doctors.
The work, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and the National Coagulation Centre at St James's Hospital, is published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Unusual blood clots with low blood platelets have been recognised as a very rare complication of the AstraZeneca vaccine. However, with increased awareness, ...
2021-06-29
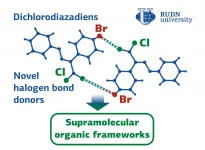
RUDN University chemists derived molecules that can assemble into complex structures using chlorine and bromine halogen atoms. They bind to each other as "velcro" - chlorine "sticks" to bromine, and vice versa. As a result supramolecules are assembled from individual molecules. The obtained substances will help to create supramolecules with catalytic, luminescent, conducting properties. The study is published in Mendeleev Communications.
Supramolecules are the structures made of several molecules. Individual molecules are combined, for example, by self-assembly or without external control. The resulting structure has properties that the molecules did not have individually. That is the way to create new materials, catalysts, molecular machines for ...
2021-06-29
For the first time, scientists detected gravitational waves caused by mergers between black holes and neutron stars. Researchers from LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA detected the two gravitational wave events--from distances of more than 900 million light-years away--within a span of 10 days in January 2020 during the second half of LIGO and Virgo's third observing run. Astrophysical Journal Letters published the results and their implications today: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac082e.
Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology's Center ...
2021-06-29
The LSL60101 compound, a specific ligand of the I2-IR receptors in the brain, could shed light on the development of future strategies against Alzheimer's disease. This is stated in the recent studies by the Research Group on Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacology of Neurodegenerative Diseases of the University of Barcelona, published in the journals European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry and British Journal Pharmacology. In studies carried out with mice, LSL60101 has improved the cognitive deficit and the biomarkers related to the disease in these animal models.
These studies result from the collaboration of the research teams led by professors Carmen Escolano, from the Faculty of Pharmacy and Food Sciences and the Institute of Biomedicine of the UB ...
2021-06-29
Preschool children are sensitive to the gap between how much they know and how much there is to learn, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
The research, published in the journal END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'The focea': A region of improved vision in mice.