Cell biology -- Masters of synapse modulation
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich researchers have shown how RNA-binding proteins modulate synaptic responses that mediate the transmission of nerve cell impulses.
Cells in the central nervous system possess a high degree of flexibility, which enables them to adapt to fluctuating demands and respond to changing patterns of neuronal activity. This is achieved by modulating the connections between nerve cells, which are mediated by structures called synapses that determine how neighboring neurons respond to stimulation. These adjustments in turn require the intracellular transport of mRNAs. Consequently, the required proteins can be synthesized close to the synapses themselves. Specific mRNA-binding proteins play a vital role in this process. A research team led by LMU biochemist Michael Kiebler has now characterized two such proteins in detail. The study demonstrates that they modulate different aspects of synaptic transmission. Thereby, they are complementing each other in order to maintain balanced neuronal activity.
The RNA-binding proteins in question, named Staufen and Pumilio respectively, are known to have essential functions in the central nervous system. Both are involved in the regulation of synaptic transmission, and they share a common set of target RNAs. They can even be found in the same RNA granules - heterogeneous particles made up of mRNAs and proteins that guide them to their final destinations. "The functional interactions between the two RNA-binding proteins, and the nature of the signaling pathways that they regulate in nerve cells had remained unknown up to now", says Rico Schieweck, lead author of the new report.
Using cultured nerve cells, Kiebler's research group has now shown that Staufen and Pumilio control the activity of synapses in quite distinct ways. Staufen primarily controls mRNA levels and thereby the amount of proteins they encode. Pumilio, on the other hand, regulates directly the process of mRNA translation, and controls how much protein is synthesized per mRNA molecule. In fact, it plays a dual role in synaptic transmission itself. "We demonstrated that Pumilio is a hitherto unrecognized coordinator of inhibitory synapses, and therefore regulates the excitability of neuronal synapses," Schieweck explains. If the gene for Pumilio is deleted, synapses become hyperactive, and the overall level of neuronal activity increases. Based on their results, Kiebler and his colleagues propose that Pumilio and Staufen can be regarded as yin and yang factors, which together control the expression of synaptic proteins. Thanks to their differential and highly selective effects on a variety of processes, they sensitively tune the activity of individual synapses.
Disruption of the neuronal equilibrium is a hallmark of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders, such as epilepsy and autism. The researchers believe that their findings will contribute to a better understanding of these conditions, because they provide insight into the mechanisms that enable different RNA-binding proteins to alter the functional characteristics of synapses.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
Earthworms experience constant chemical interactions with bacteria, fungi, plants and small invertebrates across soil ecosystems. Even within their tissues, earthworms harbor symbiotic microbes and small animal parasites that trigger internal metabolic responses such as innate immunity. To reveal the fundamental processes that enable animal-microbe symbioses to form and persist, we have to study their metabolic interactions in situ. By combining novel imaging techniques, a team of researchers around Benedikt Geier from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology ...
2021-06-29
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and the UK investigated the safety and efficacy of new chemistry in antisense oligonucleotides used to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a debilitating genetic disease. Their results may lead to the development of drugs with less toxicity and fewer injections needed thanks to prolonged action. The paper was published in the journal Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.
Antisense oligonucleotides are single stranded chemically modified fragments of DNA that target pre-messenger RNA, short bits of genetic information a ribosome reads to make a protein. Depending on how a particular antisense oligonucleotide works, the target mRNA can either be destroyed or undergo subtle changes in how it's spliced, i.e. how exons, the ...
2021-06-29
Russian scientists have experimentally proved the existence of a new type of quasiparticle - previously unknown excitations of coupled pairs of photons in qubit chains. This discovery could be a step towards disorder-robust quantum metamaterials. The study was published in Physical Review B.
Superconducting qubits are a leading qubit modality today that is currently being pursued by industry and academia for quantum computing applications. However, the performance of quantum computers is largely affected by decoherence that contributes to a qubits extremely short lifespan and causes computational errors. Another ...
2021-06-29
Pioneering research has revealed the erosion of ancient sediments found deep beneath Antarctic ice could be a vital and previously unknown source of nutrients and energy for abundant microbial life.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment journal, sheds new light on the many compounds supporting various microbes which form part of a huge subglacial ecosystem.
Lead author Dr Beatriz Gill Olivas, a Post-Doctoral Research Associate at the University of Bristol, said: "Although the study focused on samples obtained from a single ...
2021-06-29
During summer 2020, the Yangtze River basin experienced persistent, record-breaking meiyu rainfall. Likewise, the region suffered from severe flooding and water damage as accumulated rainfall broke records dating back to 1954. Regions outside the meiyu rain belt received significant summer rainfall as well, including Beijing, located in northeastern China.
Typically, an above average meiyu rainfall season follows a strong El Niño during the previous winter. However, summer 2020 followed a neutral El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) event. Therefore, scientists are working ...
2021-06-29
A stimulating environment keeps the "hippocampus" - which is the brain's memory control center - young, so to speak. Causes of this are molecular mechanisms that affect gene regulation. These current findings from studies in mice provide clues as to why an active, varied life can help preserve mental fitness in old age. Researchers from the DZNE and the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) at the Technische Universität Dresden report on this in the journal Nature Communications.
Human DNA - and this also applies to mice - contains thousands of genes. However, it is not only the genetic blueprint that is decisive for the function of a cell and whether it is healthy or not, but above all which genes can be switched on or off. ...
2021-06-29
FECYT - Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology - presented today at the headquarters of the National Museum of Science and Technology, MUNCYT, IN Alcobendas, the results of the third Social Perception Survey of scientific aspects of the COVID-19 in a debate moderated by Pampa García Molina, Editor-in-Chief of the SINC Agency, in which Raquel Yotti, Director of the Carlos III Health Institute of Madrid, Josep Lobera, Professor of Sociology at the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) and scientific director of the Social Perception Survey on the scientific aspects of COVID-19 and ...
2021-06-29
Polymers are long, chain-like molecules which are everywhere in biology. DNA and RNA are polymers formed by many consecutive copies of nucleotides coupled together. When being transported within or between cells, these biological polymers must pass through nanometre-sized holes called "nanopores".
This process also underlies a rapidly developing method for analysing and sequencing DNA called nanopore sensing.
The study, published in the journal END ...
2021-06-29
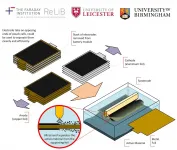
Researchers at the University of Leicester have developed a new method to recycle electric vehicle batteries using a ground-breaking new approach that many will have experienced in the dentist's chair.
The Faraday Institution project on the recycling of lithium-ion batteries (ReLiB) led by Professor Andy Abbott at the University of Leicester used a new method, involving ultrasonic waves, to solve a critical challenge: how to separate out valuable materials from electrodes so that the materials can be fully recovered from batteries at the end of their life.
Current recycling ...
2021-06-29
A new corona test developed at the University Hospital Bonn can analyze a large number of swabs simultaneously using sequencing technology and has a similarly high sensitivity as the common qPCR test. The innovative method offers great potential, especially for systematic testing in daycare centers, schools or companies. Today, the results of the study on the new Corona test have been published in the renowned journal "Nature Biotechnology".
Bonn, 6/29/2021 - In addition to vaccination, systematic testing of the population remains of central importance in order to effectively monitor and contain the spread of infections during the Coronavirus pandemic. Only in this way can the spread of the virus be effectively monitored and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cell biology -- Masters of synapse modulation