Assessment tool helps future pharmacists prepare for work in the community
2021-06-30
(Press-News.org) A recent University of Arizona College of Pharmacy study suggests that Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) may be a valuable means of assesing clinical skills while providing learning experiences for pharmacy students in community pharmacy settings. While the OSCEs were designed to assess health care professionals in a clinical setting, there was limited data on its use in testing skills required in community pharmacies, until now.
For pharmacists working in retail, guiding patients on the use of over-the-counter (OTC) drugs is a common part of the job. According to a recent survey from the American Pharmacists Association (APhA), pharmacists make an average of 29 OTC recommendations each week, and approximately 81% of consumers purchase an OTC product their pharmacists recommended. As the profession evolves to providing more patient care services, there is a continued need for pharmacy curricula to maintain pace.
Self-Care Pharmacotherapeutics, a course required by the UArizona Doctor of Pharmacy program, teaches students the appropriate use of medications for self-care inquiries including selection of medications, appropriate dosing, and analysis of safety in a community pharmacy setting. But there was limited information on how best to assess the skills taught during this training. Seeking to fill this gap, a study by College of Pharmacy Assistant Professors Bernadette Cornelison, PharmD, MS, BCPS, and Beth Zerr, PharmD, BCACP, evaluated the use of a community pharmacy-based OSCE in assessing pharmacy students in their first year. The analysis found that students and facilitators believed the OSCE tested the skills needed to provide care in a community setting.
"We teach the self-care therapeutics course in the first semester of the first year in pharmacy school," explained Dr. Cornelison. "We felt it was important to innovate and evaluate new ways of teaching that would educate the students and, hopefully, help them retain information."
The study, published in the Journal of the American College of Clinical Pharmacy, also found that the design of the simulation reflected the accurate amount of time a student intern would have to complete the Pharmacist' Patient Care Process (PPCP). This finding further demonstrates that the PPCP can be applied to patients even when time may seem limited. The standardization of this process is an important step in advancing pharmacists as recognized patient care providers across the country.
Drs. Cornelison and Zerr say the results show a strong case for fully implementing OSCEs in program curricula and are hopeful other colleges of pharmacy will, too.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-30
Directing a meeting, dialing up an old acquaintance, dictating the perfect tuna salad sandwich across a drive-through window. For business and for pleasure, human beings are in constant communication.Our proclivity for socialization is lifelong, equally prominent in the lives of adolescents and adults. A recent study determined key differences in the ways that various age groups communicate, as well as one conversational component that stands the test of time: friendship. Specifically, bonds between individuals who identify as female.
Led by former Beckman Institute postdoctoral researchers Michelle Rodrigues and Si On Yoon, an interdisciplinary team evaluated how interlocutors' age and familiarity with one another impacts a conversation, reviewing the interaction's ...
2021-06-30
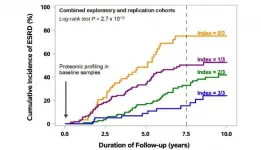
Elevated levels of three specific circulating proteins are associated with protection against kidney failure in diabetes, according to research from the Joslin Diabetes Center that will be published 30th June in Science Translational Medicine.
"As well as acting as biomarkers for advancing kidney disease risk in diabetes, the proteins may also serve as the basis for future therapies against progression to the most serious types of kidney disease," said Andrzej S. Krolewski MD, PhD, senior author on the publication, senior investigator at Joslin Diabetes Center and professor of medicine ...
2021-06-30
A 7- to 15-year longitudinal study of 358 diabetics has linked 3 proteins in blood with a slower progression of diabetic kidney disease and progressive kidney failure. The results from Zaipul Md Dom and colleagues suggest that the proteins could help researchers identify diabetics most at risk of kidney damage, potentially enabling earlier interventions and treatment. Despite advancements in blood sugar control and kidney therapies, patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes still face a high risk of diabetic kidney disease. This condition can eventually progress to end-stage kidney disease, but some patients show slower kidney decline than others. In recent ...
2021-06-30
Despite unprecedented advancements in technology and countless depictions of complex human-AI interactions in sci-fi movies, we have yet to fully achieve AI bots that can engage in conversation as naturally as humans can. Kushal Chawla, researcher at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies (ICT) and a doctoral student in computer science, along with collaborators at both the USC Information Sciences Institute (ISI) and ICT are taking us one step closer to this reality by teaching AI how to negotiate with humans.
The research, presented at the 2021 Annual Conference of ...
2021-06-30
Although cardiovascular disease is the main cause of illness among women in the U.S., certain conditions such as coronary microvascular disease (CMD) cannot be easily diagnosed. In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have identified specific biomarkers for CMD, which might reduce future hospitalizations.
CMD damages the inner walls of blood vessels causing spasms and decreased blood flow to the heart muscle. "Clinicians look for plaque formation in the blood vessels, which does not occur in CMD," said Zeynep Madak-Erdogan (CGD/EIRH/GSP), an associate professor of nutrition. "Usually, ...
2021-06-30
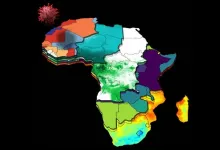
The virus that gives rise to COVID-19 is the third coronavirus to threaten humanity in the past two decades. It also happens to move more efficiently from person to person than either SARS or MERS did. The first African case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in Egypt in mid-February of 2020. Four weeks later, the first lockdowns began across Africa. Steven Schiff, Brush Chair Professor of Engineering at Penn State, who already had established research partnerships in Uganda, saw an opportunity for his team to apply what they were learning from their ongoing efforts to track and control infectious disease and ...
2021-06-30
Ten estuaries on the West Coast of North America have been identified as priority locations for expanding the use of conservation aquaculture in a study led by the Native Olympia Oyster Collaborative and funded by the Science for Nature and People Partnership (SNAPP). SNAPP is a research collaboration supported by the National Center for Ecological Analysis & Synthesis (NCEAS) at UC Santa Barbara.
The study, published in Plos One, recommends locations and methods for the strategic expansion of conservation aquaculture to bring back Olympia oyster populations -- both to local estuaries where they have most declined, and into more local restaurants for oyster lovers to dine on. The authors propose using aquaculture in these estuaries -- ...
2021-06-30
Even the mundane act of swallowing requires a well-coordinated dance of more than 30 muscles of the mouth. The loss of function of even one of these, due to disease or injury, can be extremely debilitating. For these people, nerve stimulation offers a ray of hope to regain some of their lost oral function.
In a new study, researchers at Texas A&M University have delineated the minimum size of electrical currents needed to provide sensation in different parts of the mouth. The researchers said their study is a first but vital step toward building electrical stimulation implants that can restore essential intraoral functions that are lost due to nerve or brain damage.
The results of the study are published in the journal ...
2021-06-30
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used in medicine to detect, diagnose and treat diseases such as cancer, while relying on experts' interpretation of images. Quantitative MRI, which obtains numerical measurements during the scans, can now potentially offer greater accuracy, repeatability and speed -- but rigorous quality control is needed for it to reach its full potential, according to a new study.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) led the study by 11 institutions comparing measurements by 27 MRI scanners from three vendors at nine clinical sites around the country. To obtain reference values and disentangle sources of bias and variation, the study used a tissue stand-in, or "phantom," originally ...
2021-06-30
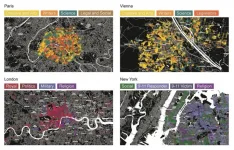
A city's street names can provide a glimpse into its cultural value system and a way to quantify cultural indicators, according to a study published June 30, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Melanie Bancilhon from Washington University in Saint Louis, U.S., and colleagues.
Ever since named streets have existed, they have been used as a form of social engineering, mirroring a town or city's social, cultural, political, and religious values. Building off this concept in what they term "streetonomics," Bancilhon and colleagues used street names as an alternative route to quantify cultural indicators in four influential Western cities: Paris, Vienna, London, and New York.
The authors used multiple open data sources ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Assessment tool helps future pharmacists prepare for work in the community