(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS - Finding treatments for advanced multiple sclerosis (MS) has been difficult. But new research may help neurologists identify which drugs are best for people with the advanced form of MS called secondary progressive MS. The new study, published in the June 30, 2021, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, found that the more potent disease-modifying drugs are more effective in reducing flare-ups in secondary progressive MS than the less potent drugs that tend to be safer to take. However, the researchers found no difference in how fast the disease progressed between these two types of drugs.
Most people with MS are initially diagnosed with relapsing-remitting MS, marked by symptom flare-ups called relapses followed by quiet periods called remission. More than half of these people eventually transition to secondary progressive MS, which is a slow, steady, worsening of the disease that may or may not include relapses.
"Multiple sclerosis is a complicated disease to treat and must be closely monitored as it is managed with various medications, some of which can have serious side effects," said study author Tomas Kalincik, MD, PhD, of the University of Melbourne in Australia. "High-efficacy medications are prescribed in early multiple sclerosis to more aggressively treat the disease and have been found to more effectively prevent flare-ups and modify progression, but less is known about how effective these therapies may be later when relapsing-remitting MS transitions to secondary progressive MS."
The study involved 1,000 people with secondary progressive MS. Participants were followed for 10 years to see whether they had relapses and if they became more disabled over time.
Researchers divided participants into two groups, those treated with one of the more potent drugs, or high-efficacy drugs (natalizumab, alemtuzumab, mitoxantrone, ocrelizumab, rituximab, cladribine and fingolimod) and those treated with one of the less potent drugs, or low-efficacy drugs (interferon β, glatiramer acetate and teriflunomide). People in each group were matched for factors like disability level and how long they had secondary progressive MS.
After accounting for the lag time before a person starts to experience the benefit of a medication, researchers found that in people with active disease, or those experiencing relapses within the past two years, people who were treated with high-efficacy medications experienced 30% fewer relapses than people treated with low-efficacy medications. People in the high-efficacy group experienced an average of 0.17 relapses per year compared 0.27 relapses per year in the low-efficacy group.
"Our study finding that high-efficacy therapies are superior to low-efficacy therapies only in reducing relapses in people with active secondary progressive MS provides valuable guidance for neurologists when choosing the most effective therapies for people with this form of MS," said Kalincik. "When the goal is to alleviate ongoing relapse activity, more potent therapy is justified. But when the goal is to limit disability progression in secondary progressive MS, both types of drugs show comparable effectiveness."
A limitation of the study was that participants were grouped by those taking high-efficacy or low-efficacy therapies. However, therapies were not studied individually. Kalincik said it is possible that individual therapies may have different effects on symptoms and disability and recommend that they be examined separately in future research.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council in Australia, the Multiple Sclerosis International Federation in the United Kingdom, and the ARSEP Foundation and EDMUS Foundation in France.
Learn more about MS at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology's free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world's largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 36,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
M.A. Rosko, mrosko@aan.com, (612) 928-6169
MINNEAPOLIS - A new study suggests that even when differences in socioeconomic status are taken into consideration, Black people with multiple sclerosis (MS) may be more negatively impacted by the disease than white people with MS. The research is published in the June 30, 2021, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study found that Black people with MS had lower scores on certain measures of neurological health, like dexterity and walking tests and showed more evidence of disease progression on brain scans.
"While lower socioeconomic status appears to be linked to doing worse on tests ...
June 30, 2021 - For most patients, the reasons for having a facelift are simple: to "turn back the clock" for a younger and more attractive appearance. Even during the pandemic year 2020, more than 234,000 patients underwent facelift surgery, according to American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) statistics.
When considering facelift surgery, patients may ask, "How much younger will I look?" For plastic surgeons, that has been a difficult question to answer. Typically, the cosmetic outcomes of facelifting have been judged on a case-by-case basis, or with the use of subjective ratings.
Now research suggests a new, objective approach to assessing the reduction in apparent age after facelift surgery: artificial intelligence (AI) networks trained to estimate age based on facial ...
Electron motion in atoms and molecules is of fundamental importance to many physical, biological, and chemical processes. Exploring electron dynamics within atoms and molecules is essential for understanding and manipulating these phenomena. Pump-probe spectroscopy is the conventional technique. The 1999 Nobel Prize in Chemistry provides a well-known example wherein femtosecond pumped laser pulses served to probe the atomic motion involved in chemical reactions. However, because the timescale of electron motion within atoms and molecules is on the order of attoseconds (10-18 seconds) rather than femtoseconds (10-15 seconds), attosecond pulses are required to probe electron motion. With the development of ...
A recent University of Arizona College of Pharmacy study suggests that Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) may be a valuable means of assesing clinical skills while providing learning experiences for pharmacy students in community pharmacy settings. While the OSCEs were designed to assess health care professionals in a clinical setting, there was limited data on its use in testing skills required in community pharmacies, until now.
For pharmacists working in retail, guiding patients on the use of over-the-counter (OTC) drugs is a common part of the job. According to a recent survey from the American ...
Directing a meeting, dialing up an old acquaintance, dictating the perfect tuna salad sandwich across a drive-through window. For business and for pleasure, human beings are in constant communication.Our proclivity for socialization is lifelong, equally prominent in the lives of adolescents and adults. A recent study determined key differences in the ways that various age groups communicate, as well as one conversational component that stands the test of time: friendship. Specifically, bonds between individuals who identify as female.
Led by former Beckman Institute postdoctoral researchers Michelle Rodrigues and Si On Yoon, an interdisciplinary team evaluated how interlocutors' age and familiarity with one another impacts a conversation, reviewing the interaction's ...
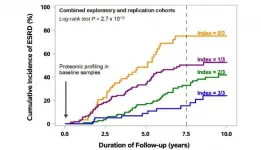
Elevated levels of three specific circulating proteins are associated with protection against kidney failure in diabetes, according to research from the Joslin Diabetes Center that will be published 30th June in Science Translational Medicine.
"As well as acting as biomarkers for advancing kidney disease risk in diabetes, the proteins may also serve as the basis for future therapies against progression to the most serious types of kidney disease," said Andrzej S. Krolewski MD, PhD, senior author on the publication, senior investigator at Joslin Diabetes Center and professor of medicine ...
A 7- to 15-year longitudinal study of 358 diabetics has linked 3 proteins in blood with a slower progression of diabetic kidney disease and progressive kidney failure. The results from Zaipul Md Dom and colleagues suggest that the proteins could help researchers identify diabetics most at risk of kidney damage, potentially enabling earlier interventions and treatment. Despite advancements in blood sugar control and kidney therapies, patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes still face a high risk of diabetic kidney disease. This condition can eventually progress to end-stage kidney disease, but some patients show slower kidney decline than others. In recent ...
Despite unprecedented advancements in technology and countless depictions of complex human-AI interactions in sci-fi movies, we have yet to fully achieve AI bots that can engage in conversation as naturally as humans can. Kushal Chawla, researcher at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies (ICT) and a doctoral student in computer science, along with collaborators at both the USC Information Sciences Institute (ISI) and ICT are taking us one step closer to this reality by teaching AI how to negotiate with humans.
The research, presented at the 2021 Annual Conference of ...
Although cardiovascular disease is the main cause of illness among women in the U.S., certain conditions such as coronary microvascular disease (CMD) cannot be easily diagnosed. In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have identified specific biomarkers for CMD, which might reduce future hospitalizations.
CMD damages the inner walls of blood vessels causing spasms and decreased blood flow to the heart muscle. "Clinicians look for plaque formation in the blood vessels, which does not occur in CMD," said Zeynep Madak-Erdogan (CGD/EIRH/GSP), an associate professor of nutrition. "Usually, ...
The virus that gives rise to COVID-19 is the third coronavirus to threaten humanity in the past two decades. It also happens to move more efficiently from person to person than either SARS or MERS did. The first African case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in Egypt in mid-February of 2020. Four weeks later, the first lockdowns began across Africa. Steven Schiff, Brush Chair Professor of Engineering at Penn State, who already had established research partnerships in Uganda, saw an opportunity for his team to apply what they were learning from their ongoing efforts to track and control infectious disease and ...