Manufacturing the core engine of cell division
By modelling the kinetochore from scratch, Max Planck Institute's researchers get a step closer to creating artificial chromosomes
2021-07-01
(Press-News.org) A wonder of nature
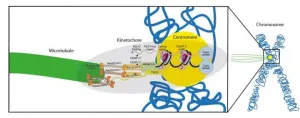
As a human cell begins division, its 23 chromosomes duplicate into identical copies that remain joined at a region called the centromere. Here lies the kinetochore, a complicated assembly of proteins that binds to thread-like structures, the microtubules. As mitosis progresses, the kinetochore gives green light to the microtubules to tear the DNA copies apart, towards the new forming cells. "The kinetochore is a beautiful, flawless machine: You almost never lose a chromosome in a normal cell!", says Musacchio. "We already know the proteins that constitute it, yet important questions about how the kinetochore works are still open: How does it rebuild itself during chromosome replication? How does it bind to the microtubules? And how does it control them?"
A life´s endeavour
Musacchio´s quest for answers started more than 20 years ago and has been guided by a simple motto: "Before we understand how things go wrong, we better understand why and how things work". He therefore embarked in the mission of rebuilding the kinetochore in vitro. In 2016 he could synthesize a partial kinetochore made of 21 proteins. In the new publication, Musacchio, graduate student Kai Walstein, and their colleagues at MPI Dortmund have been able to fully reconstruct the system: All subunits, from the ones that bind the centromere to the ones that bind the microtubules, are now present in the right numbers and stoichiometry. Scientists proved that the new system functions properly, by successfully substituting parts of the original kinetochore in the cell with artificial ones. "This is a real milestone in the reconstruction of an object that exists, unaltered, in all eukaryotic cells since more than one billion years!", says Musacchio. This breakthrough paves the way towards the making of synthetic chromosomes carrying functions that can be replicated in organisms. "The potential for biotech applications could be huge", he says.
In the protein factory
MPI scientists had to overcome a major hurdle to rebuild the kinetochore, namely to fully reconstruct the highly flexible Centromeric Protein C (CENP-C). This is an essential protein that bridges the centromeric region to the outer proteins of the kinetochore. Researchers rebuilt CENP-C by "gluing" together the two ends of it.
A highly organised laboratory, similar to a factory, is fundamental for the reconstitution of complex protein assemblies. For each protein of the kinetochore, MPI scientists built a production pipeline to isolate the genes, express them in insects´ cells, and collect them. "When we put them together in vitro, these proteins click-in to form the kinetochore, just like LEGO pieces following the instructions", he says. Other than the famous toys though, each kinetochore protein has a different interface and interaction with closer proteins. The group will now step up to the next level of complexity: Investigating how the kinetochore functions and interacts in the presence of microtubules and supplied energy (in the form of ATP). The project has been recently granted an ERC Synergy Grant and will be carried out by an international team comprising Musacchio's group and researchers from Cambridge, UK, and Barcelona, Spain.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-01
Researchers at the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku, Finland, study insect biodiversity particularly in Amazonia and Africa. In their studies, they have discovered hundreds of species previously unknown to science. Many of them are exciting in their size, appearance, or living habits.
"The species we have discovered show what magnificent surprises the Earth's rainforests can contain. The newly discovered Dolichomitus meii wasp is particularly interesting for its large size and unique colouring. With a quick glance, its body looks black but glitters electric blue in light. Moreover, its wings are golden yellow. Therefore, you could say it's like a flying jewel," says Postdoctoral Researcher Diego Pádua from the Instituto Nacional ...
2021-07-01
Contrary to what science once suggested, older people with a declining sense of smell do not have comprehensively dampened olfactory ability for odors in general - it simply depends upon the type of odor. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen reached this conclusion after examining a large group of older Danes' and their intensity perception of common food odours.
That grandpa and grandma aren't as good at smelling as they once were, is something that many can relate to. And, it has also been scientifically demonstrated. One's sense of smell gradually begins to decline from about the age of 55. Until now, it was believed that one's sense of smell broadly ...
2021-07-01
Plastic waste is considered one of the biggest environmental problems of our time. IASS researchers surveyed consumers in Germany about their use of plastic packaging. Their research reveals that fundamental changes in infrastructures and lifestyles, as well as cultural and economic transformation processes, are needed to make zero-waste shopping the norm.
96 percent of the German population consider it important to reduce packaging waste. Nevertheless, the private end consumption of packaging in Germany has increased continuously since 2009. At 3.2 million tons in 2018, the amount of plastic packaging waste generated by end consumers in Germany ...
2021-07-01
One year after infection by SARS-CoV-2, most people maintain anti-Spike antibodies regardless of the severity of their symptoms, according to a study with healthcare workers co-led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), the Catalan Health Institute (ICS) and the Jordi Gol Institute (IDIAP JG), with the collaboration of the Daniel Bravo Andreu Private Foundation. The results suggest that vaccine-generated immunity will also be long-lasting.
One of the key questions to better predict the pandemic's evolution is the duration of natural immunity. A growing number of studies suggest that most people generate a humoral ...
2021-07-01
The eruption of the Laacher See volcano in the Eifel, a low mountain range in western Germany, is one of Central Europe's largest eruptions over the past 100,000 years. The eruption ejected around 20 cubic kilometers of tephra and the eruption column is believed to have reached at least 20 kilometers in height, comparable to the Pinatubo eruption in the Philippines in 1991. Technical advances in combination with tree remains buried in the course of the eruption now enabled an international research team to accurately date the event. Accordingly, the eruption of the Laacher See volcano occurred 13,077 years ago and thus 126 years earlier than previously assumed. This sheds new light on the climate history of the entire North ...
2021-07-01
Scientists at the University of Helsinki have found an essential factor from the extracellular matrix that regulates functionality of the breast tissue for instance during pregnancy.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) has previously been recognised as an important element for the growth of various epithelial cells, but rather as a scaffold. A new study shows that ECM can also regulate the function of epithelial cells.
Our tissues constitute of differentiated cell types, which perform specific tasks that are tightly controlled. Normal growth and functioning of tissues is possible only when the various differentiated cell types interact appropriately. Differentiation and function of breast epithelium is guided by a group of cells responsive for estrogen and progesterone hormones. In the recent ...
2021-07-01
Flat optics based on patterned liquid crystals (LCs) has recently received extensive research interest. Comparing with dielectric metasurfaces which are usually fabricated by sophisticated lithography process, LC polymer-based planar optics, owing to the self-assembly properties, can be fabricated through all-solution process. During the past decades, a variety of planar optical devices have been demonstrated based on geometric phase (also termed as Pancharatnum-Berry phase) manipulation. The total effective thickness of the device, including the underlying liquid crystal ...
2021-07-01
Hitherto, the development of valvular heart disease in patients with chronic heart failure has been underestimated and rarely treated. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Division of Cardiology within the Department of Medicine II at Vienna General Hospital and MedUni Vienna and published in the prestigious British Medical Journal (BMJ). Mitral regurgitation was often previously interpreted as part of the progression of heart failure rather than a treatable disease in its own right.
Mitral regurgitation is a disease, in which the valve between the left atrium and left ventricle starts to leak, so that blood refluxes with ...
2021-07-01
Computer models have been standard tools in basic biomedical research for many years. However, around 70 years after the first publication of an ion current model of a nerve cell by Hodgkin & Huxley in 1952, researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), in collaboration with the Medical University of Graz and the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, have finally succeeded in developing the world's first cancer cell model, thus launching "an essential tool for modern cancer research and drug development," reports a delighted Christian Baumgartner. The head of the Institute of Health Care Engineering with European Testing ...
2021-07-01
Chronic fatigue syndrome / myalgic encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME) is a disabling disease, in which people have great difficulties in carrying out their daily activities. Despite its high prevalence, there are still no effective tools for its diagnosis, monitoring and treatment. To better understand and promote follow-up, as well as stratify fatigue in these patients, Vall d'Hebron, the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya · BarcelonaTech (UPC) have developed a mobile application that could be useful in the assessment of the severity of fatigue in this syndrome, especially in women. The results of the study in which this technology has been tested have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Manufacturing the core engine of cell division
By modelling the kinetochore from scratch, Max Planck Institute's researchers get a step closer to creating artificial chromosomes