Beam steering angle expander with two liquid crystal polymeric diffractive optical elements
2021-07-01
(Press-News.org) Flat optics based on patterned liquid crystals (LCs) has recently received extensive research interest. Comparing with dielectric metasurfaces which are usually fabricated by sophisticated lithography process, LC polymer-based planar optics, owing to the self-assembly properties, can be fabricated through all-solution process. During the past decades, a variety of planar optical devices have been demonstrated based on geometric phase (also termed as Pancharatnum-Berry phase) manipulation. The total effective thickness of the device, including the underlying liquid crystal alignment layer and the liquid crystal polymer, is usually in the order of 1 μm. Amazingly, commercial-quality transmissive lenses, gratings, optical vortex processors, etc., have been developed in the past few years. Engineering of their operating spectral/angular bands has been illustrated in both passive and active devices. For example, a multi-twist structure can be designed to customize the spectral/angular bandwidth as a passive means, while active devices that can respond to external stimuli such as mechanical stress, electric field, and light, have also been realized. Nevertheless, the existing explorations have been focused on optical functionalities that can be fulfilled by a single-layer device. One way to go beyond the current limit is to design cascaded flat optics, where more degree of freedom is involved and thereby more distinct functionalities can be rationally achieved. In the meantime, the cascaded optical elements should still preserve the advantages such as high efficiency, compact and lightweight, easy processing, flexibility, and low cost.
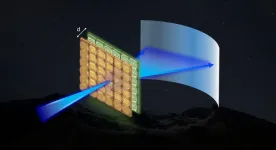
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Prof. Shin-Tson Wu from the College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, USA, proposed a cascaded LC flat optical element, termed miniature planar telescope, to achieve steering angle magnification independent of the incident beam position. Such an angle magnification function cannot be achieved with a single layer optical device such as a grating or a refractive surface. This miniature planar telescope consists of two flat optical elements, as schematically shown in Fig. 1. Both layers are assigned phase profiles following the sum of even order polynomials and they are separated in space by d. Through ray-tracing simulations, the system can be optimized according to specific aperture size and incident angle range, and nearly diffraction-limited performance can be obtained.
In experiments, different LC diffractive devices in millimeter sizes with various f/# were fabricated through all-solution processing and assembled into two telescope modules with designed magnification factors of 1.67 (module I) and 2.75 (module II), respectively. The measured magnification agreed well with the designed values. Moreover, a reasonably high efficiency (>89.8% for module I and >84.6% for module II) was achieved within the designed incident angle range. Through error analysis, the efficiency could be improved by optimizing the fabrication process. The team demonstrated that the telescope module can be a promising candidate for non-mechanical beam steering to expand the currently limited steering range (also known as field of regard). For example, for LiDAR (light detection and ranging) applications at λ=905 nm, a maximum output angle range of ±27° can be expected. Comparing to a high-efficiency optical phase array (most matured electronic beam steerer) with an incident field range of ~±5°, a magnification of 5.4 can be acquired. For a longer operating wavelength, say λ=1550 nm, the steering range can be expanded to about ±37°, corresponding to a magnification of 7.4. In this regard, the team also characterized the output beam profile to ensure the high quality of the telescope modules and the compatibility with high-end beam steerers.
With the presented work, Wu and co-workers demonstrated lightweight, cost effective, miniature planar telescopes for optical angle magnification based on LC polymer flat optics. High efficiency, designable magnification factors, and excellent beam quality make the proposed telescopes highly promising for practical applications requiring advanced laser beam steering technology. More importantly, this is a new milestone for planar LC optics to go beyond its current development.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-01
Hitherto, the development of valvular heart disease in patients with chronic heart failure has been underestimated and rarely treated. This is the finding of a study conducted at the Division of Cardiology within the Department of Medicine II at Vienna General Hospital and MedUni Vienna and published in the prestigious British Medical Journal (BMJ). Mitral regurgitation was often previously interpreted as part of the progression of heart failure rather than a treatable disease in its own right.
Mitral regurgitation is a disease, in which the valve between the left atrium and left ventricle starts to leak, so that blood refluxes with ...
2021-07-01
Computer models have been standard tools in basic biomedical research for many years. However, around 70 years after the first publication of an ion current model of a nerve cell by Hodgkin & Huxley in 1952, researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), in collaboration with the Medical University of Graz and the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, have finally succeeded in developing the world's first cancer cell model, thus launching "an essential tool for modern cancer research and drug development," reports a delighted Christian Baumgartner. The head of the Institute of Health Care Engineering with European Testing ...
2021-07-01
Chronic fatigue syndrome / myalgic encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME) is a disabling disease, in which people have great difficulties in carrying out their daily activities. Despite its high prevalence, there are still no effective tools for its diagnosis, monitoring and treatment. To better understand and promote follow-up, as well as stratify fatigue in these patients, Vall d'Hebron, the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya · BarcelonaTech (UPC) have developed a mobile application that could be useful in the assessment of the severity of fatigue in this syndrome, especially in women. The results of the study in which this technology has been tested have ...
2021-07-01
Crystals have fascinated people through the ages. Who hasn't admired the complex patterns of a snowflake at some point, or the perfectly symmetrical surfaces of a rock crystal The magic doesn't stop even if one knows that all this results from a simple interplay of attraction and repulsion between atoms and electrons. A team of researchers led by Atac Imamoglu, professor at the Institute for Quantum Electronics at ETH Zurich, have now produced a very special crystal. Unlike normal crystals, it consists exclusively of electrons. In doing so, they have confirmed a theoretical prediction that was made almost ninety years ago and which has since been regarded as a kind of holy grail ...
2021-07-01
When researchers at Lund University in Sweden performed advanced analyses of sputum from the airways of severely ill Covid-19 patients, they found high levels of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). It is already a known fact that NETs can contribute to sputum thickness, severe sepsis-like inflammation and thrombosis. After being treated with an already existing drug, the NETs were dissolved and patients improved. The study has now been published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Using advanced fluorescence microscopy, the researchers examined sputum in the airways of three severely ...
2021-07-01
There might be fewer bonobos left in the wild than we thought. For the last 40 years, scientists have estimated the abundance of endangered bonobos by counting the numbers of sleeping nests left by the apes in forests of the Congo Basin. Now, researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior report that the rate of sleeping nest "decay" has lengthened by 17 days over the last 15 years as a result of declining rainfall in the Congo Basin. The study warns that longer nest decay times have serious implications for ape conservation: failure to account for these ...
2021-07-01
DALLAS - June 30, 2021 - A relative decline in wealth during midlife increases the likelihood of a cardiac event or heart disease after age 65 while an increase in wealth between ages 50 and 64 is associated with lower cardiovascular risk, according to a new END ...
2021-07-01
The cells that make up our bodies are constantly exposed to a wide variety of mechanical stresses. For example, the heart and lungs have to withstand lifelong expansion and contraction, our skin has to be as resistant to tearing as possible whilst retaining its elasticity, and immune cells are very squashy so that they can move through the body. Special protein structures, known as "intermediate filaments", play an important role in these characteristics. Researchers at Göttingen University have now succeeded for the first time in precisely measuring which physical effects determine the properties of the individual filaments, and which specific features only occur through the interaction ...
2021-07-01
Melbourne researchers have found that liquid chalk, commonly used in gyms to improve grip, acts as an antiseptic against highly infectious human viruses, completely killing both SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) and influenza A viruses.
University of Melbourne Professor Jason Mackenzie, a laboratory head at the Peter Doherty Institute of Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) wanted to investigate whether liquid chalk stopped SARS-CoV-2 transmission after conversations with his daughter - an elite rock climber heading to the Tokyo Olympics.
"Both of my daughters were lamenting the closure of gyms at the beginning of the pandemic, particularly my daughter Oceania who was trying to train ...
2021-07-01
There are certain rules that even the most extreme objects in the universe must obey. A central law for black holes predicts that the area of their event horizons -- the boundary beyond which nothing can ever escape -- should never shrink. This law is Hawking's area theorem, named after physicist Stephen Hawking, who derived the theorem in 1971.
Fifty years later, physicists at MIT and elsewhere have now confirmed Hawking's area theorem for the first time, using observations of gravitational waves. Their results appear in Physical Review Letters.
In the study, the researchers take a closer look at GW150914, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Beam steering angle expander with two liquid crystal polymeric diffractive optical elements





