(Press-News.org) A surprising study by UNSW on the behaviour of unrelated lizards in very different parts of the world has demonstrated how evolution can lead to different species learning the same skills.
The study in Ecology Letters documents how the Anolis lizard species in the Caribbean, and the Draco lizard species in Southeast Asia, have solved the challenge of communicating with one another to defend territories and attract mates.
It found males from both species perform elaborate head bob and push up displays, and rapidly extend and retract their often large and conspicuously coloured dewlap, or throat fan, specifically in habitats with lots of wind-blown vegetation or low light.
The lizards occupy the same range of rainforest and grassland habitats, and therefore face the same problems when it comes to communicating to a potential mate or enemy in visually 'noisy' environments.
Remarkably, they have evolved the same strategy to cope with the same selection problems, lead author Dr Terry Ord from the Evolution & Ecology Research Centre at the UNSW School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences says.
According to his research, this scenario of two unrelated lizards displaying similar behaviour shows that natural selection directs evolution towards the same common set of adaptive outcomes over and over again.
"The surprise is that lizards in both groups have evolved remarkably similar displays for communication, but they also tailor the production of those displays according to the prevailing conditions experienced at the time of display," Dr Ord says.
"That is, increasing the speed or the length of time they spend displaying the movements as the viewing conditions deteriorate.
"Really there should be essentially innumerable ways these lizards could have adapted their displays to remain effective, and there is strong evolutionary predictions that would lead us to expect this as well."
Dr Ord says what this study shows is that natural selection driving similarities between different species.
Formally, this is known as convergent evolution -- the independent origin of similar adaptations, he says.
"It seemed that these types of convergent, common adaptations are outcomes that would only really occur among species that are closely-related in some capacity," he says.
"The reason for this is a bit complicated and it rests on the fact that adaptations build on characteristics that a species already possesses."
"So, the longer species have evolved independently of each other, the less likely they would evolve the same adaptive solutions if they were exposed to the same change in the environment."
But what this study highlights, he says, is what many evolutionary ecologists have argued - that natural selection is an extremely powerful process that can override the "baggage" of past history to produce the same adaptations.
"So if arm-waving is the most effective solution to some change in the environment, then natural selection would ultimately lead to its evolution rather than a more subtle (less effective) modification to an existing vocal call," he says.
"Evolutionary biologists are excited about convergent evolution because it gives us multiple examples of the same adaptation evolving time and time again in very different animals.?
"So it tells us what the challenges are faced by these animals and how they have solved it in terms of evolutionary adaptation."
The study documents this independent evolution of common communication strategies amongst groups that have evolved separately from each other for hundreds of millions of years.
Dr Ord says the striking similarities in communication strategies for maintaining an effective communication system in noisy conditions has evolved in various forms in many insects, fish, frogs, birds and mammals.
"For example, increasing the volume of calls when there's lots of acoustic background noise, or extending the length of those calls or even vibrational signals by spiders and such," Dr Ord says .
"The fact that many other groups of animals have also evolved thesesame adaptive strategies is even more extraordinary."
Read the study in Ecology Letters.
INFORMATION:
The muskrat, a stocky brown rodent the size of a Chihuahua - with a tail like a mouse, teeth like a beaver and an exceptional ability to bounce back from rapid die-offs - has lived for thousands of years in one of Earth's largest freshwater deltas, in northeastern Alberta, Canada.
Today, this delta lies within one of the largest swaths of protected land in North America: a national park five times the size of Yellowstone that's home to the planet's biggest herd of free-roaming bison and the last natural nesting ground for the endangered whooping crane. It's also central to the culture ...
Guadalupe fur seals (Arctocephalus townsendi) have established a large resting colony in the Gulf of California--bringing the total number of sites where this endangered species now occurs to just four. This new haul-out was discovered on El Farallón de San Ignacio Island, along the mainland coast of Mexico, according to researchers from Mexico and the University of British Columbia.
Guadalupe fur seals were hunted for their furs and declared extinct in the late 1800's. However, 14 individuals were discovered on Guadalupe Island in 1950--and the population has grown since then. While still designated as vulnerable to extinction, according to IUCN, the population is believed to total 41,000 individuals and is growing ...
In an Australian world-first, researchers have successfully repurposed two existing medications to reduce the severity of sleep apnoea in people by at least 30 per cent.
Affecting millions around the world, sleep apnoea is a condition where the upper airway from the back of the nose to the throat closes repetitively during sleep, restricting oxygen intake and causing people to wake as often as 100 times or more per hour.
Those with untreated sleep apnoea are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease, dementia and depression, and are two to four times more likely to crash a car than the general population.
Despite almost thirty years of research, there are no approved drug therapies to treat the condition.
Professor Danny Eckert, Principal ...
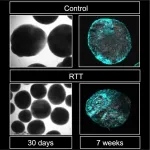
Fukuoka, Japan--Medical researchers led by Kyushu University have revealed a possible underlying genetic pathway behind the neurological dysfunction of Rett syndrome. The team found that deficiencies in key genes involved in the pathology triggers neural stem cells to generate less neurons by producing more astrocytes--the brain's maintenance cells.
The researchers hope that the molecular pathology they identified, as reported in the journal Cell Reports, can lead to potential therapeutic targets for Rett syndrome in the future.
Rett syndrome is a progressive neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impairments in cognition and coordination--with varying severity--and occurs in roughly one in every 10,000 to 15,000 female births. However, it ...
Japanese astronomers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) technique to remove noise in astronomical data due to random variations in galaxy shapes. After extensive training and testing on large mock data created by supercomputer simulations, they then applied this new tool to actual data from Japan's Subaru Telescope and found that the mass distribution derived from using this method is consistent with the currently accepted models of the Universe. This is a powerful new tool for analyzing big data from current and planned astronomy surveys.
Wide area survey data can be used to study the large-scale structure of the Universe through measurements of gravitational lensing patterns. In gravitational lensing, the ...
Microorganisms produce natural products, for example, as disease-causing virulence factors or as defense substances against predators and competitors. A team led by Dr. Robin Teufel and first author Ying Duan from the Institute of Biology II at the Faculty of Biology of the University of Freiburg, together with researchers from the University of Bonn, have now discovered a novel enzyme that is crucial for the production of so-called bacterial tropone natural products. The researchers presented their results in the current issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Previously unknown enzyme type
Bacteria found in terrestrial and marine environments produce tropone natural products, among other things, when they interact symbiotically with plants, algae or lower animals, for ...
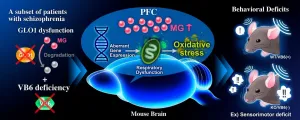
Methylglyoxal (MG) is a highly reactive α-ketoaldehyde formed endogenously as a byproduct of the glycolytic pathway. MG accumulates under conditions of hyperglycemia, impaired glucose metabolism, or oxidative stress. An excess of MG formation causes mitochondrial impairment and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production that further increases oxidative stress. It also leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) due to MG reacting with proteins, DNA, and other biomolecules, which can induce aberrant inflammation via binding to receptors for AGEs (RAGE). To remove the toxic MG, ...
This insight is the result of the close collaboration of several research groups at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology. A team around Cedric Hahn and Gunter Wegener recently discovered ethane-degrading microbes at hydrothermal vents of the Guaymas Basin at a water depth of 2,000 meters in the Gulf of California. They named it Ethanoperedens thermophilum, which means "heat-loving ethane-eater". Cedric Hahn a PhD student from the research group Molecular Ecology cultured the ethane-degrading microbes in the laboratory. Hahn, Wegener and colleagues of the research group Microbial Metabolism, Tristan Wagner and Olivier Lemaire took a closer look at these microorganisms. This collaborative work unraveled the secrets behind ...
"We have studied which temperatures are preferable and which are harmful in humans, cattle, pigs, poultry, and agricultural crops and found that they are surprisingly similar," says Senthold Asseng, Professor of Digital Agriculture at TUM. According to the study, preferable temperatures range from 17 to 24 degrees Celsius.
When does it become too hot for humans?
At high humidity, mild heat strain for humans begins at about 23 degrees Celsius and at low humidity at 27 degrees Celsius. "If people are exposed to temperatures above 32 degrees Celsius at extremely high humidity or above 45 degrees Celsius at extremely low humidity for a lengthy period of time, it can be fatal," says Prof. Asseng. "During extreme heat events with temperatures far above 40 degrees Celsius, such as those ...
Plastics are a growing problem for natural ecosystems around the globe, and in particular for our marine and freshwater environments. Rivers are the leading source of plastic pollution, as it has been estimated that they deliver several million metric tons of plastic annually to our oceans from poor land-based waste management. The problem is that the estimates made for plastics flowing from the rivers are tens to hundreds of times higher than the quantity of plastics floating on the ocean's surface. So where is all of this river-derived plastic actually going - is there a missing plastic 'sink' somewhere in the ocean? Are the estimates correct?
In a paper published ...