At what temperature the weather becomes a problem
Climate change leads to increasing heat strain for humans, animals and crops
2021-07-02
(Press-News.org) "We have studied which temperatures are preferable and which are harmful in humans, cattle, pigs, poultry, and agricultural crops and found that they are surprisingly similar," says Senthold Asseng, Professor of Digital Agriculture at TUM. According to the study, preferable temperatures range from 17 to 24 degrees Celsius.
When does it become too hot for humans?
At high humidity, mild heat strain for humans begins at about 23 degrees Celsius and at low humidity at 27 degrees Celsius. "If people are exposed to temperatures above 32 degrees Celsius at extremely high humidity or above 45 degrees Celsius at extremely low humidity for a lengthy period of time, it can be fatal," says Prof. Asseng. "During extreme heat events with temperatures far above 40 degrees Celsius, such as those currently being observed on the U.S North West Coast and in Canada, people require technical support, for example in the form of air-conditioned spaces."
To mitigate increasing heat strain, Prof. Asseng cites a variety of strategies, including increasing natural shade from trees or structural shading. Cities and buildings can be made more temperature-passive, for example, by using roof and wall insulation or by using lighter, reflective roof and wall colors to reduce heat strain.
How do high temperatures affect livestock?
In cattle and pigs, heat strain occurs at 24 degrees Celsius with high humidity and at 29 degrees Celsius with low humidity. The milk yield from cows can decrease by 10 to 20 percent when exposed to heat stress, and the fattening performance in pigs is also reduced. The comfortable temperature range for poultry is 15 to 20 degrees. Chickens experience mild heat strain at 30 degrees Celsius. At 37 degrees Celsius and above, they experience severe heat stress and their egg laying rate declines.
Heat stress overall leads to reduced growth in cattle and dairy cows, pigs, chickens and other livestock, which means both lower yields and reproductive performance. "There are examples of evolutionary adaptations to warm weather in terrestrial mammals. Transylvanian naked chickens are more heat tolerant than other varieties of chickens because of a complex genetic mutation that suppresses feather growth. They are naturally air-conditioned because they lack feathers on their necks," says Prof. Asseng.
How do crops react to high temperature?
"In crops, the optimal temperature zone and temperature thresholds seem to be more diverse due to differences between species and varieties," explains Prof. Asseng.
Cold-temperate crops such as wheat, for example, do better at cooler temperatures, while warm-temperature crops such as corn are sensitive to frost but can tolerate warmer temperatures. Strategies to reduce heat stress in crop production include changes in planting dates to avoid heat stress later in the season, irrigation (if feasible), switching to more heat-resistant crops, and breeding to increase heat tolerance.
How is climate change affecting life on Earth?
"By the end of the century, 45 to 70 percent of the global land area could be affected by climate conditions in which humans cannot survive without technological support, such as air conditioning. Currently, it's 12 percent," says Prof. Asseng. This means that in the future, 44 to 75 percent of the human population will be chronically stressed by heat. A similar increase in heat stress is expected for livestock, poultry, agricultural crops and other living organisms.
"Genetic adaptation to a changing climate often takes many generations. The time available is too short for many higher forms of life. If current climate trends persist, many living things could be severely affected or even disappear completely from Earth due to temperature change," concludes Prof. Asseng.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-02
Plastics are a growing problem for natural ecosystems around the globe, and in particular for our marine and freshwater environments. Rivers are the leading source of plastic pollution, as it has been estimated that they deliver several million metric tons of plastic annually to our oceans from poor land-based waste management. The problem is that the estimates made for plastics flowing from the rivers are tens to hundreds of times higher than the quantity of plastics floating on the ocean's surface. So where is all of this river-derived plastic actually going - is there a missing plastic 'sink' somewhere in the ocean? Are the estimates correct?
In a paper published ...
2021-07-02
Originally discovered as a bacterial mode of defense against invading viruses, the remarkable ability of CRISPR-Cas9 to modify specific locations of DNA has made it a researcher favorite among gene editing tools. The ongoing effort to explore further possibilities of the CRISPR-Cas9 system is ushering in newer developments to this tool. In one of the latest refinements of the technique, as illustrated in a study published in BioDesign Research, scientists from Stanford University, USA have developed a CRISPR-Cas9 system that induces highly effective silencing of target genes.
The versatility of CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing is largely ...
2021-07-02
New research published in The Journal of Physiology shows that researchers have successfully repurposed two existing medications to reduce the severity of sleep apnoea in people by at least 30 per cent.
Affecting around 1.5 million adults in the UK, sleep apnoea is a condition where the upper airway from the back of the nose to the throat closes repetitively during sleep, restricting oxygen intake and causing people to wake as often as 100 times or more per hour (1).
Those with untreated sleep apnoea are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease, dementia and depression, ...
2021-07-02
NDIANAPOLIS--Indiana University School of Medicine researchers are developing a new, noninvasive brain stimulation technique to treat neurological disorders, including pain, traumatic brain injury (TBI), epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and more.
"Given the increasing use of brain stimulation in human brain study and treatment of neurological diseases, this research can make a big impact on physicians and their patients," said Xiaoming Jin, PhD, associate professor of anatomy, cell biology and physiology.
When someone experiences a brain injury, nerve injury, or neurodegeneration, such as in epilepsy and TBI, there is damage to the brain which can lead to loss ...
2021-07-02
Small children learn language at a pace far faster than teenagers or adults. One explanation for this learning advantage comes not from differences between children and adults, but from the differences in the way that people talk to children and adults.
For the first time, a team of researchers developed a method to experimentally evaluate how parents use what they know about their children's language when they talk to them. They found that parents have extremely precise models of their children's language knowledge, and use these models to tune the language they use when speaking to them. The results are available in an advance online publication ...
2021-07-02
Lugano, Switzerland, 2 July 2021 - Obese patients with colorectal cancer receive lower cumulative doses of adjuvant chemotherapy, relative to their body surface area (BSA), than non-obese patients, show results from a large meta-analysis reported at the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2021 (1). Further findings showed that cumulative relative chemotherapy dose was associated with survival so may explain the poorer survival that has been seen in obese patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for colorectal cancer. (2)
"Adjuvant chemotherapy ...
2021-07-02
Lugano, Switzerland, 2 July 2021 - Doctors and patients are being advised to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use following new data suggesting that these medicines may increase the risk of cancer of the large intestine (colon), especially in people under 50 years. (1) The results, presented at the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer (30 June-3 July) raise fresh concerns about the impact of the estimated 65% increase in global antibiotic consumption reported between 2000 and 2015, despite not showing a direct cause and effect. (2)
"To our knowledge, ...
2021-07-02
Plastic is notoriously hard to break down, but researchers in Austria have found that bacteria from a cow's rumen - one of the four compartments of its stomach - can digest certain types of the ubiquitous material, representing a sustainable way to reduce plastic litter.
The scientists suspected such bacteria might be useful since cow diets already contain natural plant polyesters. "A huge microbial community lives in the rumen reticulum and is responsible for the digestion of food in the animals," said Dr Doris Ribitsch, of the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences in Vienna, "so we suspected that some biological activities could also be used for polyester hydrolysis," a type of chemical reaction ...
2021-07-02
Oncotarget published "Loss of CPAP causes sustained EGFR signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral cancer" which reported that not only do the abnormal functions of microtubule and microtubule-organizing centers such as centrosomes lead to cancers, but also the malignant tissues are characterized by aberrant centriolar features and amplified centrosomes.
In this study, the authors show that the loss of expression of a microtubule/tubulin binding protein, centrosomal protein 4.1-associated protein, which is critical for centriole biogenesis and normal functioning of the centrosome, caused an increase in the EGFR levels and its signaling and, enhanced the EMT features and invasiveness of OSCC cells.
Further, depletion of CPAP ...
2021-07-02
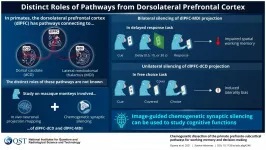
The human brain is a wonderfully enigmatic organ, helping to juggle multiple tasks efficiently to help us get through a long day! This feature, called executive function, seats primates like us at the pinnacle of evolution. The prospect of losing the spectacular flow of neural information in our brains because of an accident or disease is, thus, unnerving. In the event of such an unfortunate occurrence, to restore the brain to its previous working condition with full functionality--to reboot it, so to speak--would need a better understanding of the specific neural pathways involved in our daily activities that rely on working memory and decision-making--two important executive functions.
To achieve this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] At what temperature the weather becomes a problem
Climate change leads to increasing heat strain for humans, animals and crops