Kansas State University virologists publish new findings on SARS-CoV-2 treatment option
2021-07-02
(Press-News.org) MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- A recent study by Kansas State University virologists demonstrates successful postinfection treatment for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
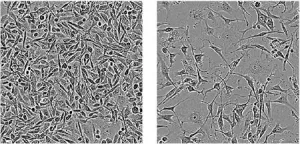
College of Veterinary Medicine researchers Yunjeong Kim and Kyeong-Ok "KC" Chang published the study in the prestigious journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, or PNAS. They found that animal models infected with SARS-CoV-2 and treated with a deuterated protease inhibitor had significantly increased survival and decreased lung viral load.
The results suggest that postinfection treatment with inhibitors of proteases that are essential for viral replication may be an effective treatment against SARS-CoV-2. These protease inhibitors are a class of antiviral drugs that prevent viral replication by selectively binding to viral proteases and blocking the activation of proteins that are necessary for the production of infectious viral particles.
"We developed the protease inhibitor GC376 for treating a fatal coronavirus infection in cats, which is now under commercial development as an investigational new animal drug," said Kim, associate professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology. "After COVID-19 emerged, many research groups reported that this inhibitor is also effective against the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, and many are currently pursuing the development of protease inhibitors as a treatment."
Kim and Chang modified GC376 using a tool called deuteration to test its efficacy against SARS-CoV-2.
"Treating SARS-CoV-2-infected mice with deuterated GC376 significantly improved survival, viral replication in lungs and weight losses, which shows the efficacy of the antiviral compound," said Chang, professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology. "The results suggest deuterated GC376 has a potential for further development, and this deuteration method can be utilized to other antiviral compounds to generate potent inhibitors."
The virologists are continuing to develop improved inhibitors using various methods. Deuterated GC376 is currently being evaluated for further potential development.
INFORMATION:
Previous work done by Kim and Chang is continuing development through licensing agreements with industry partners.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-02
How on Earth?
It has puzzled scientists for years whether and how bacteria, that live from dissolved organic matter in marine waters, can carry out N2 fixation. It was assumed that the high levels of oxygen combined with the low amount of dissolved organic matter in the marine water column would prevent the anaerobic and energy consuming N2 fixation.
Already in the 1980s it was suggested that aggregates, so-called "marine snow particles", could possibly be suitable sites for N2 fixation, but this was never proven.
Until now..
In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen demonstrate, by use of mathematical models, ...
2021-07-02
During the large second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in fall 2020, pulmonologist and critical care provider Juan C. Rojas, MD, reflected on how disproportionately members of minority populations were being affected by the disease. After hearing similar thoughts from colleagues in New Orleans and New York City, Rojas began to wonder how, if at all, state governments planned to ensure these disparities would be addressed when COVID-19 vaccines were rolled out to the public.
In a new study published July 2 in JAMA Network Open, Rojas and his team were surprised ...
2021-07-02
(Boston)--Would you be more willing to get vaccinated against the COVID-19 virus if you could participate in a lottery for cash and prizes? The answer was surprisingly no, according to Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) researchers who found that Ohio's "Vax-a-Million" lottery-based incentive system, intended to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates, was not associated with an increase in COVD-19 vaccinations.
Prior reports in the media had suggested that the Ohio lottery increased COVID-19 vaccinations, leading other states to use COVID-19 vaccine incentive lotteries in an attempt to increase slowing vaccination rates. "However, prior evaluations of ...
2021-07-02
Some three quarters of the biomass in hop plants used in beer-making ends up in landfills. But a group of Japanese researchers has developed a technique that 'upcycles' that waste hop into cellulose nanofibers (CNFs). A paper describing the technique was published in the journal ACS Agricultural Science & Technology on June 11.
In the past few years, craft beer-making has exploded in popularity around the world, including many beer styles that make use of many more and different types of hops than conventional commercial beers. A traditional preservative in beer, hops also add ...
2021-07-02
Berkeley -- Many insects and spiders get their uncanny ability to scurry up walls and walk upside down on ceilings with the help of specialized sticky footpads that allow them to adhere to surfaces in places where no human would dare to go.
Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have used the principle behind some of these footpads, called electrostatic adhesion, to create an insect-scale robot that can swerve and pivot with the agility of a cheetah, giving it the ability to traverse complex terrain and quickly avoid unexpected obstacles.
The robot is constructed from a thin, layered material that bends and contracts when an electric voltage is applied. In a 2019 paper, the research team demonstrated that this simple ...
2021-07-02
Wander around a desert most anywhere in the world, and eventually you'll notice dark-stained rocks, especially where the sun shines most brightly and water trickles down or dew gathers. In some spots, if you're lucky, you might stumble upon ancient art - petroglyphs - carved into the stain. For years, however, researchers have understood more about the petroglyphs than the mysterious dark stain, called rock varnish, in which they were drawn.
In particular, science has yet to come to a conclusion about where rock varnish, which is unusually rich in manganese, comes from.
Now, scientists at the California Institute of Technology, the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator ...
2021-07-02
Neuroscientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have demonstrated in new research that dopamine plays a key role in how songbirds learn complex new sounds.
Published in the Journal of Neuroscience, the finding that dopamine drives plasticity in the auditory pallium of zebra finches lays new groundwork for advancing the understanding of the functions of this neurotransmitter in an area of the brain that encodes complex stimuli.
"People associate dopamine with reward and pleasure," says lead author Matheus Macedo-Lima, who performed the research in the lab of senior author Luke Remage-Healey as a Ph.D. student in UMass Amherst's Neuroscience and Behavior graduate program. "It's a very well-known concept that dopamine is involved in learning. ...
2021-07-02
In cancer research, it's a common goal to find something about cancer cells -- some sort of molecule -- that drives their ability to survive, and determine if that molecule could be inhibited with a drug, halting tumor growth. Even better: The molecule isn't present in healthy cells, so they remain untouched by the new therapy.
Plenty of progress has been made in this approach, known as molecular targeted cancer therapy. Some current cancer therapeutics inhibit enzymes that become overactive, allowing cells to proliferate, spread and survive beyond ...
2021-07-02
What The Study Did: Researchers in this study aimed to determine how each state and the District of Columbia planned to ensure equitable COVID-19 vaccine distribution.
Authors: Juan C. Rojas, M.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.15653)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2021-07-02
What The Study Did: Changes in the use of women's preventive health services during the COVID-19 pandemic, including screening for sexually transmitted infections, breast and cervical cancer, and obtaining contraceptives from pharmacies are described by researchers in this study.
Authors: Nora V. Becker, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1408)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Kansas State University virologists publish new findings on SARS-CoV-2 treatment option