A protein complex from plant stem cells regulates their division and response to stress
2021-07-06
(Press-News.org) A multidisciplinary research team, led by the CSIC biologist at CRAG, Ana I. Caño Delgado, and the physicist from the University of Barcelona, Marta Ibañes, has discovered that two plant stem cell proteins, known for their role in the correct development of the root, physically interact and regulate each other to avoid cellular division. The study, result of fifteen years of continued research carried out by the two researchers, reveals that these two proteins, known as BRAVO and WOX5, act in a specific manner in a small group of stem cells, and that their interaction is key to the plant's survival under genomic and environmental stress factors like extreme cold, heat, or floods. The results, obtained with the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, have recently been published in the high impact journal Molecular Systems Biology.
In the same way that the proteins BRAVO and WOX5 need each other to function properly, this discovery could not have been possible without uniting the knowledge and the academic disciplines provided by both research teams: the biochemistry, genetics and cellular biology, on one hand, and the mathematical modelling, on the other.
"Previous work from my team and others had demonstrated that the loss of either one of the proteins, BRAVO or WOX5, produced the root stem cells division. However, their molecular connection was not yet understood," explains Ana I. Caño Delgado.
"In general, genetic regulations involve a complexity that is often not intuitive and that can only be understood through mathematical models and computer simulations. The mathematical models we have created have made it possible to make sense of the amount of data gathered by the CRAG team", adds Marta Ibañes, researcher at the UB Institute of Complex Systems.
These new mathematical models will allow now the in silico experimentation, creating hypothetical situations that may happen at the root's stem cells, such as the effect of applying hormones or the possible responses during stress situations.
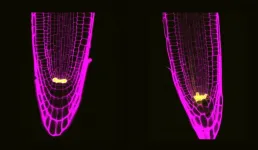
The quiescent centre: a reservoir of stem cells
Plants have a set of stem cells in the tip of the primary root that gives them the ability to grow indefinitely. The majority of these cells divide at a fast pace, creating other stem cells and the different cells that form the root's tissues, like the epidermis or the vascular tissue. However, at one end of this niche there are a few stem cells that divide at a slower pace; this is why, the area they occupy is called "quiescent centre".
Every time a cell duplicates its genetic material to divide itself is at risk of incorporating replication errors, mutations that can have negative consequences for the organism. This is why the stem cells of the quiescent centre represent an insurance, a reservoir of genetically safe cells. If necessary, these cells can "wake up" and divide to fill the stem cell niche.
It is exactly in these few cells of the quiescent centre where BRAVO and WOX5 proteins exercise their important function: suppressing cell division.
"We created arabidopsis plants with simultaneous mutations in BRAVO and WOX5 genes and we observed that they had less capacity to regenerate the roots, which were shorter and less abundant", explains Isabel Betegón-Putze, first author of the article, who carried out these experiments during her PhD.
Upon severe or prolonged stress, two specific responses take place at the stem cell niche: the death of the fast-dividing stem cells and the activation of the quiescent centre cells. The quiescent centre cells activate, for example, after a cut at the root apex, or after root freezing or lead poisoning. In doing so, they replace the dead stem cells allowing the root to keep growing and developing correctly, which in turn guarantees the nutrition and support for the plant.
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate these processes is key to obtaining more resilient crops, especially in the current situation, with climates getting more extreme.
An extraordinary source of youth
Plants, unlike animals, can form new organs (leaves, flowers, etc.) at adult age and, furthermore, they keep growing during their whole life (which can last more than 2000 years!). Stem cells in animals and plants seem to use similar strategies to resolve similar biological problems; however, the molecular processes that regulate them seem to be different. Understanding these differences can be very helpful to design useful strategies in medicine and cosmetics that slow down cellular aging and promote the regeneration of damaged tissue. This study and others led by Ana I. Caño-Delgado are one step forward in this direction.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-06
A team of researchers at the Department of Chemistry and Pharmacy at Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) has successfully solved the problem of finding a straightforward, cost-effective process for producing hexaarylbenzene molecules with six different aromatic rings. These molecules are important functional materials. The results were published in the reputable journal Angewandte Chemie.
Until now, it has been possible to use certain chemical procedures to produce simple, symmetrical hexaarylbenzene (HAB) molecules, in which the hydrogen atoms of the benzene are replaced by the same atomic groups. However, only very little HAB was produced in this way.
The team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Svetlana Tsogeva and Prof. Dr. Norbert Jux, both professors of organic ...
2021-07-06
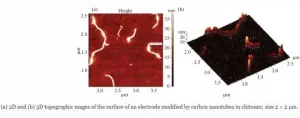
The paper describes amperometric biosensors developed for the determination of diclofenac based on planar platinum electrodes modified with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in chitosan, fullerene C60 in Boltorn H20, gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) in chitosan, and immobilized tyrosinase enzyme. It was found that diclofenac is a reversible tyrosinase inhibitor (a decrease in the analytical signal is observed), which makes it possible to determine it using appropriate biosensors modified with nanomaterials in the concentration range from 10 pM to 1 μM with CH 5 pM. Modification with composites of CNT / Au NPs and fullerene C60 / Au NPs made it possible to improve the analytical characteristics of the developed biosensors, in particular, ...
2021-07-06
A new study by researchers at the University of Eastern Finland shows for the first time that blood-based measurement of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) enables distinguishing patients with frontotemporal dementia from those with primary psychiatric disorders or healthy individuals.
Frontotemporal dementia is the second most common cause of dementia in the working age population. Its diagnostics are complicated by the similar symptoms presented by patients with psychiatric disorders or other neurodegenerative diseases as well as the lack of reliable diagnostic tools for differentiating these patients from each other.
A new study by researchers at the University of Eastern Finland ...
2021-07-06
The international collaborative team of Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) in Japan and Indian Institute of Technology Ropar (IIT Ropar) in India has explored, for the first time, viscous fingering (VF, one of classical interfacial hydrodynamics) of annular ring where VF in fluid of finite volume grow radially through combination of experiment and numerical simulation. They demonstrate that the VF of an annular ring is a persistent phenomenon in contrast to the transient nature of VF of a slice where VF in fluid of finite volume grow rectilinearly.
The researchers published their results ...
2021-07-06
New research evaluating the drugs commonly used by rheumatoid arthritis patients suggests two combinations could reduce the risk of heart attack and strokes.
The new publication in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine has found that anti-rheumatic drug regimens that include either tumour necrosis factor inhibitors or hydroxychloroquine might significantly protect the endothelium in rheumatoid arthritis.
Occurring in about one in 100 people, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease which leads to inflammation and pain in the connective tissue of a patient's joints.
"Rheumatoid arthritis patients have an increased ...
2021-07-06
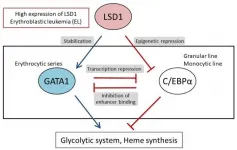
A research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has shown that lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1), an enzyme involved in gene expression, produces individualized metabolism depending on the type of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer cells are known to have a unique ability to metabolize substances differently from normal cells, and this ability is considered to be a promising therapeutic target. The new research findings may contribute to the safe and effective use of LSD1 inhibitors as potential anticancer agents, and to the development of highly specific treatments for various ...
2021-07-06
Researchers have devised a way to multiply by more than ten-fold the accessible details of gene activity in individual cells. It's a big leap in the effort to understand cancer development, brain function, immunity and other biological processes driven by the complex interactions of multitudes of different cell types.
Organs and tissues are made up of cells that may look the same, but individual cells can actually differ dramatically. Single-cell analysis allows the study of this cell-to-cell variation within an organ, tissue or cancerous tumor. But the research has been hampered by limits on the depth of information that can be gleaned at the single-cell level when working with large numbers of cells.
"The downside has been the low-quality of ...
2021-07-06
Most of us are familiar with the fact that women live longer than men. But fellas, if we told you there was one thing that could be done to increase your lifespan, would you do it?
In a study published today in eLife , University of Otago researchers along with collaborators from the United States, have shown that castration of male sheep delays aging of DNA compared to intact males, and that it also drives feminine characteristics of DNA and the chemical tags it holds, known as DNA methylation.
"Both farmers and scientists have known for some time that castrated male sheep live on average much longer than their intact counterparts; however, this is ...
2021-07-06
Three mutations in the Epsilon coronavirus spike protein dampen the neutralizing potency of antibodies induced by current vaccines or past COVID infections.
The mutations give this coronavirus variant of concern a means to totally evade specific monoclonal antibodies used in clinics and reduce the effectiveness of antibodies from the plasma of vaccinated people.
To better understand the exact immune escape strategies at work here, the scientists visualized this variant's infection machinery to see what is different from the original configuration of the pandemic coronavirus, and what the implications of these changes are.
The international project was led by David Veesler's lab in the Department of Biochemistry at the University of Washington ...
2021-07-06
In a retrospective, multi-centre cohort study conducted by researchers from Nanjing University, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Jinling Hospital and the Second Hospital of Nanjing, a microRNA-like small RNA encoded by SARS-CoV-2 was identified in the serum of COVID-19 patients, which can be developed as a non-invasive biomarker for stratification of severe patients from mild/moderate ones and for identification of high-risk individuals before clinical manifestation of severe symptoms. This biomarker ensures proper allocation of patients to different ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A protein complex from plant stem cells regulates their division and response to stress